Journal of Tourism & Hospitality
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0269
ISSN: 2167-0269
Case Report - (2023)Volume 12, Issue 2
Achieving common prosperity is the essential requirement of the leadership of the communist party of China and China's socialist system, and it is also the general expectation of the broad masses of the people. Tourism is an important means to develop the economy, inherit culture, promote transformation, and promote common prosperity. The protection and development of intangible cultural heritage is a dialectical and unified relationship, the foundation of which is excavation and protection, the core is inheritance and utilization, and the essence is to exert its value. To develop in protection, protect in development. Heritage scholars have also started to concern themselves with processes of engagement and the construction of meaning. Intangible cultural heritage is an important part of tourism, tourism is an important way to protect and utilize intangible cultural heritage, and intangible cultural heritage resources are inevitably related to tourism development.
Tourism; Cultural heritage; Gorges reservoir area; Resources; China
Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) is a very interesting topic. ICH is the living remains of ancient culture and the precious wealth left by our ancestors. Culture represents the oldest accumulation of human social activity and displays the most innovative developments of human society [1]. Chinese ICH symbolizes the outstanding accumulation of Chinese history and culture, giving Chinese civilization a special identity symbol, and Chinese ethnic groups nurture it through long-term social practice. ICH carries the critical qualities of national culture and has important historical, social, artistic, and aesthetic values [2].
The three Gorges project's interception of water storage and relocation not only affects the protection of tangible cultural heritage but also has an impact on intangible cultural heritage with a strong local atmosphere [3]. The three Gorges reservoir area is rich in intangible cultural heritage resources, and traditional skill, traditional music, quyi, traditional dance, traditional art, and folklore are highly displayable, participatory, and experiential [4], which has laid a spatial and material foundation for the tourism activation of intangible cultural heritage in the three Gorges reservoir area. The development of intangible cultural heritage resources should be oriented to the high-quality development of tourism, the integrated development of urban and rural areas, and the all-around development of people [5].
Tourism activation of intangible cultural heritage
Scholars at home and abroad have conducted relevant research on the tourism activation of intangible cultural heritage from different perspectives. Space activation and reactivation are hotbutton industry topics [6]. The case study of a historical site, the supernatural theme was successfully used as a part of its space reactivation and brand remodeling [7]. Cross-disciplinary cultural theory to try to construct a management conceptual model for the activation of traditional skills and cultural heritage tourism, which enriched the theoretical development of the integration of traditional skills culture, and tourism, and also expanded the scope of cultural research theory [8]. The local brand construction mode of rural culture and the tourism activation path based on local brand construction through theoretical model construction and case study [9]. Tourism activation of heritage is a means of tourism development based on tourists' experience, which enlivens static cultural heritage resources and enriches tourists' experience under the experience economy [10]. As the common "living memory" of mankind, intangible cultural heritage is a kind of local unique, imitable, and irreplaceable strategic assets and tourism resources [11], the concentration of intangible cultural heritage resources is the basis of tourism revitalization, too scattered intangible cultural heritage resources will affect tourism development and tourist experience, which is also the origin of spatial analysis of intangible cultural heritage resources.
"Activation" itself has the connotation of innovation and adaptation, and the activation of intangible cultural heritage tourism mainly refers to the content innovation and form adaptation of intangible cultural heritage relying on tourism. The activation of intangible cultural heritage tourism in the Three Gorges reservoir area should take innovation as the core, fully tap the cultural connotation and tourism elements of intangible cultural heritage, realize the creative transformation of intangible cultural heritage resources, the innovative development of intangible cultural heritage tourism, and achieve the vertical deepening and symbiosis of intangible cultural heritage and tourism from interaction to activation to synergy. It not only pays attention to the authenticity of intangible cultural heritage but also pays more attention to its integrity and diversity, providing principal guidance for tourism revitalization. The driving layer stems from "the guiding force of cultural administrative departments, the driving force of cultural tourism enterprises, and the participation of intangible inheritors and the general public", forming an organic whole of cultural undertakings and tourism industries. In a visualized, experiential and large-scale way, intangible cultural heritage will be presented and experienced, to achieve the goal of turning intangible cultural heritage into cultural products and eventually becoming tourism commodities.
Intangible cultural heritage tourism activation case
The three Gorges is a world-renowned attraction and represents the image of China. There are many cases of intangible cultural heritage tourism activation in the three Gorges reservoir area, which is prominently represented by the fire dragon performance in Chongqing. The dragon is the totem of the Chinese nation and the ancestor of the faith; the dragon dance is a symbol of the Chinese spirit, which embodies the spirit of the Chinese nation's unity and pioneering spirit, contains the cultural connotation of harmony between heaven and man, benefits mankind, and is the most common entertainment method for Chinese in auspicious and blessing seasons.
Until now, the dragon dance is still one of the popular dance forms in folk festivals. The most basic means of expression of the dragon dance are its prop shape, composition changes, and movement routines. According to the different materials of the dragon-shaped props, it is divided into cloth dragon, sarong dragon, paper dragon, grass dragon, money dragon, bamboo dragon, brown dragon, bench dragon, hundred leaf dragon, lotus dragon, fire dragon, chicken hair dragon, meat dragon, so on; the production of the Northern dragon dance is generally tall and heavy, and the style is simple and rigid; the Southern dragon dance is delicate and meticulous, lively and agile. The dragon dance can be divided into yellow, white, blue, red, black, etc. in terms of color, with the yellow dragon being the noblest. The composition and movements of the dragon dance generally have the characteristics of "round", "tumbling", "twisting", "interspersed", "jumping" and so on. The traditional performance procedure of the dragon dance is generally as follows: "Invite the dragon", "out of the dragon", "dance the dragon" and "send the dragon". There is a saying among the people that "seven or eight years old play grass dragon, fifteen or six play a small dragon, young and middle-aged dance big dragon". The number of dragon dancers is small, one person dances double dragon, and most people dance a large dragon.
Chongqing Tongliang dragon dance is a dance art form with dragons as the main props spread in Tongliang county, Chongqing. It arose in the Ming Dynasty, flourished in the Qing Dynasty, and shined again in contemporary times and became famous all over the world. It includes two series: Dragon lantern dance and colored lantern dance. The dragon lantern dance mainly includes ten varieties: Big worm dragon, fire dragon, straw dragon, bamboo shell dragon, yellow wattle dragon, bench dragon, zheng long, small color dragon, bamboo dragon, and lotus dragon, among which the big worm dragon is the most distinctive and the fire dragon is the most exciting. The lantern dance mainly includes fish leaping over the dragon gate, loach eating tangyuan, three stripes, eighteen bachelors, bright lion, kaishan tiger, mussel shell essence, rhinoceros looking at the moon, pig nibbling pumpkin, gaotai dragon lion dance, wild goose tower inscription, pumpkin shed twelve varieties (Figure 1).
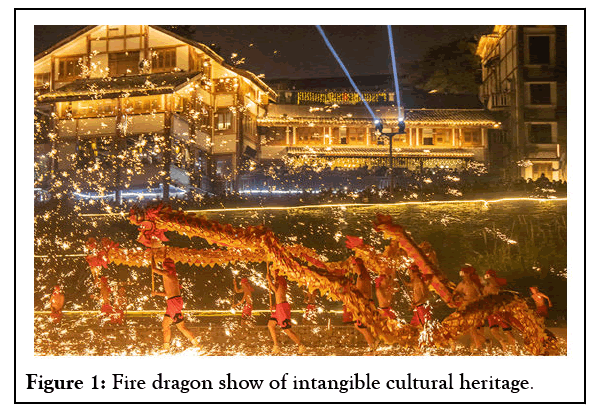
Figure 1: Fire dragon show of intangible cultural heritage.
The fire dragon dance embodies the spirit of teamwork, benefiting mankind, striving for progress, and harmony with the sky and at the same time has social functions such as entertaining people and showing power. The fire dragon performance is closely related to folk activities, rich routines, dynamic and humorous characteristics, unique accompanying music, ingenious props conception, exaggerated shape, frugal and generous costumes, free participation of dancers, convenient retreat, and strong participation of the masses, which is an important representative of the activation of intangible cultural heritage tourism.
During the festival, Chongqing will organize fire dragon performances, which have become an important part of the local cultural tourism market and an important representative of the living inheritance and effective use of intangible cultural heritage. In the warm atmosphere, the "fire dragon" dressed in golden light soared out of the "molten iron meteor" flying in the sky, constantly circling, churning, and jumping. The dragon dancers went into battle shirtless, and the "fire dragon" danced around the field, and the dragon's body flickered, emitting colorful sparks. People dance in the dragon, the dragonflies in the fire, and the scene of fire and silver flowers brings a visual feast to tourists and feels a different taste of intangible cultural heritage (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Fire dragon spurts fire of intangible cultural heritage
The tourism activation of intangible cultural heritage resources is to achieve the rise from the "material" level to the "immaterial" level, and to meet the dual prosperity of material and spiritual under the concept of common prosperity; from the level of "artifact protection" to the level of artifact makers or skill inheritors, do a good job in the inheritance and protection of people; moving from "static protection" to "living conservation" as a resource. Realize the concept of protecting intangible cultural heritage in people, seeing things and seeing life, continuously realize the effective use and sustainable inheritance of intangible cultural heritage resources in the three Gorges reservoir area, and achieve both spiritual and material prosperity in the process of common prosperity.
[Crossref]
[Crossref]
[Crossref]
[Crossref]
Citation: Li X (2023) Tourism Activation of Intangible Cultural Heritage in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area-A Case Story. J Tourism Hospit. 12:518.
Received: 13-Mar-2023, Manuscript No. JTH-23-22129; Editor assigned: 16-Mar-2023, Pre QC No. JTH-23-22129 (PQ); Reviewed: 30-Mar-2023, QC No. JTH-23-22129; Revised: 06-Apr-2023, Manuscript No. JTH-23-22129 (R); Published: 13-Apr-2023 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-0269.23.12.518
Copyright: © 2023 Li X. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.