Journal of Tourism & Hospitality
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0269
ISSN: 2167-0269
Research Article - (2023)Volume 12, Issue 1
Regional tourism cooperation can bring about a multi-win pattern for tourism destinations, such as complementary advantages, overall promotion, economies of scale, improvement of comprehensive competitiveness, economic restructuring and tourism culture prosperity. Climbed from 2016-2018 by travel notes and official news two dimensions of text data, based on social network theory from the perspectives of both the government and tourists explore tourism cooperation between the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration of 26 city network structure characteristics, on the basis of the space of tourist flows from the perspective of tourists put forward the structure of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation development mode and countermeasures, rectification and navigation for government policy. The results show that there is an unbalanced core-edge structure in the tourism cooperation network, and the network structure of government cooperation is looser than that of tourists. The network structure of tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration needs to be optimized according to the needs of tourists. The optimum path of Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation should pay attention to policy focus and governance, route planning and reconstruction of multi-dimensional measures, on the basis of resources, take the market as the guidance, through the knowledge sharing, communication and other aspects to achieve complementary synergy, promoting regional tourism cooperation, construction of barrier-free tourism zone, promote the healthy development of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism continued.
Tourism cooperation; Network structure; Dual Government and Tourist perspectives
Background analysis
In the context of all-region tourism, tourism destinations have changed from the construction and management of single scenic spots to the comprehensive and integrated development, which promotes the quality and efficiency of the local tourism industry and approaches the concept of innovation, coordination, green, development and sharing. Regional tourism cooperation has achieved the goal of mutual benefit and win-win development through market interaction, information sharing, and product and brand co-creation. The development of China's tourism industry has basically stepped into the stage of regional competition and cooperation from the competition of scenic spots, routes and cities pointed out that the sustainable and healthy development of tourism industry cannot be separated from the cooperation between regions, and the regional tourism cooperation between cities is the manifestation of the latest business form of tourism [1]. The increase of residents' economic income and the improvement of living standards promote multi-destination tourism to become a trend, analyzed the reasonable setting and arrangement of tourist routes is the common focus of both supply and demand in the tourism market [2]. Tourists are usually the most important and active factor in the tourism destination system. Different tourism destinations are connected through self-selected tourism behavior and tourism flow. The cognition and emotion of tourism products promote the purchase decision-making behavior of tourists, which is an important influencing factor of regional tourism cooperation.
In addition, due to the instant effectiveness and convenient interaction of network communication, tourists are keen to share their travel experience on tourism websites pointed out that government departments can release official news, policies and regulations more conveniently through official websites, so that public opinion information related to tourism can be widely disseminated and effectively exchanged [3,4]. Tourism, as a special industry, involves various fields such as economy, society and cultural life, so it is necessary for the government to intervene in the development of tourism. The coordinated and balanced development of regional tourism requires the government to make targeted policies and make reasonable plans according to the needs of tourists. Studies on regional tourism cooperation mostly focus on the role of government suppliers in tourism destination policies and related development. For example, the government uses different websites to release official news to plan and promote tourism products, and overall shaping and marketing of destination images to improve the tourism competitiveness among regions [5]. However, in the practical sense, regional tourism cooperation is closely related to the passenger flow. As the demander, tourists' spatial choice behavior affects the form, scale and structure of cooperation between different tourist attractions. Tourism destinations are interdependent to a large extent, which is manifested as a group of nodes and a group of ties representing a certain relationship and embedded together in a cooperative structure, finally forming a tourism destination network [6]. In this network, each destination will share information, jointly innovate tourism products and interact with the tourist market, so as to realize the regional tourism development goal of "1+1>2".
Therefore, inter-regional cooperation has formed a diversified and complex network structure, and inter-city tourism interaction and cooperation have blurred regional boundaries, which is of strategic significance for the construction of tourism cooperation network [7,8]. In recent years, big data analysis has been more and more applied in tourism management research, especially in tourism supply, destination, policy system and tourists' spatial behavior pattern. Big data analysis is of great significance for understanding regional tourism cooperation. Through big data analysis, investigated the structure of regional tourism cooperation [9], studied the relationship between regional tourism cooperation and tourism flow [10], and confirmed that tourist mobility affects the form, scale and structure of regional tourism cooperation [11]. Relevant studies show that network text data is an important data source for regional tourism cooperation analysis. From the perspective of regional tourism cooperation research, the existing studies tend to "pay more attention to the government than to tourists", and mostly ignore the internal relationship between tourism policy and tourists' spatial choice behavior. From the perspective of analysis methods of regional tourism cooperation, some scholars at home and abroad have begun to try to analyze the strategic cooperative relationship between tourism destinations from the perspective of organizational network. However, researches seldom discuss the internal characteristics of network structure in depth, but pay more attention to external appearances such as network density and centrality [12,13]. The perspective of destination selection of regional tourism cooperation, most existing studies focus on macro-regional environment analysis, and relatively few small-scale studies on tourism city cooperation [14]. From the data sources of research on regional tourism cooperation, many literatures are obtained through traditional means such as questionnaire survey, data access, thematic communication, conference communication, etc., with limited information obtained. At present, highly developed Internet informatization, massive data information mining on the network platform is not sufficient [15,16].
The Yangtze River Delta is one of the regions with the highest level of urbanization and the most active economic development in China. At the same time of its economic prosperity, the regional cooperation and development of tourism should be further strengthened and transformed into a new economic growth point and innovation point, so as to promote the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration to move forward into a high-quality development regional cluster. Due to past "top-down" government level tourism cooperation may suppress the development of the tourism market, tourism destination of unfair competition and produce the negative phenomena such as local protectionism, so from the perspective of government supply and tourist demand, using the theory of "core-edge", and the theory of social network analysis knowledge construction of Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation network structure, the relationship between node further to explore the overall situation of regional tourism cooperation network and internal development, on the basis of the space of tourist flow from the perspective of tourists put forward the structure of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation development mode and countermeasures and Suggestions, as a government policy for rectification and navigation, Explore the path of regional tourism cooperation, optimize and adjust the network structure of tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta city group and promote the healthy and sustainable development of regional tourism.
Data sources and research methods
Overview of the study area: The Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is one of the regions with the highest degree of openness and the most dynamic economy in China, and plays an important role in the all-around opening pattern. In 2003, the "Yangtze River Delta Tourism Cities Summit Forum" expanded the number of participating cities from 16 to 26 at present. It is committed to advocating the construction of a barrier-free tourism circle and setting up a model of regional tourism cooperation. At the same time, in order to optimize the cooperation mechanism of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration and give play to its leading and exemplary role, a number of documents have been formulated, such as the National New Urbanization Plan (2014-2020), the Outline of the Development Plan of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, the National Plan for Major Functional Zones, and the National Plan for Major Marine Functional Zones.
Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration contained in parts of jiangsu and anhui Shanghai three provinces and one city, belong to two of three longitudinal pattern of urbanization of the key development area, including Shanghai, nanjing, wuxi, changzhou, suzhou, nantong, yancheng, yangzhou, zhenjiang, yangzhou, taizhou, hangzhou, ningbo, jiaxing, huzhou, shaoxing, jinhua, zhoushan, taizhou, hefei, wuhu, maanshan, tongling and anqing, chuzhou, chizhou, 26, xuancheng city, through the city circle all-round construction of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration integration of high quality and development. With the advent of the era of mass tourism, the diversification of tourism product supply and tourism demand weakens the inter-regional hierarchical correlation structure, enhances the inter-city tourism cooperation, and promotes the inter-regional tourism cooperation to become normal. The Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is in a critical stage of transformation, promotion and innovative development. It must fully explore the network structure of regional cooperation in combination with tourists' demand and government supply from multiple perspectives and levels, so as to realize the leap-forward development of regional tourism.
Data sources: The Internet has the advantages of timely interaction and information sharing. This paper studies the structural differences of the tourism cooperation network in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration by crawling the data text of tourism diaries expressing tourists' wishes and official news conveying the attitude of the government. Use Python climb in Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration 26, 2016-2018, three years of text data, travel diaries from trip, where to go, way and so on three big website crawl 28369 articles, 9310 travel diary, effective travel reflect tourists Angle for the trend of the Yangtze river delta tourism cooperation, the municipal government's official website of the dynamic and the policies and regulations, a total of 13784 articles, news text effective 3871 articles. The tourism diaries and official news collected by each city are screened according to the following principles: the text content is more than 500 words, and the news trends, policies and regulations related to the cooperation and intercommunication of 26 cities in the Yangtze River Delta are screened; The selected text is the narrative text, and the general science text which only has pictures or mainly introduces the scenic spot is excluded. Replace similar text with agreement.
The completeness of the sample content is conducive to the comprehensive and in-depth content analysis of regional tourism cooperation and provides a foundation for the network structure of regional tourism cooperation. Will have access to "travel diary" and "official news" text to EXCEL in the table, and use the Python programming is transformed into matrix form, including "line" on behalf of the tourist destination of the matrix (26), the "column" representing each tourists or official news coding sequence, if the tourists visiting the city or official news content contains the city, down to 1, otherwise 0; The initial matrix of "26 rows × 9310 columns" and "26 rows × 3871 columns" were established according to the ranking of tourist spots or cities included in official news. The initial 2-module matrix is transformed into two "26 rows × 26 columns" multi-valued adjacency matrices, and the attribute data is transformed into relational data. Due to the large gap between the number of travel diaries and official news collection, in order to ensure the validity and comparability of the data analysis, the binocular data was transformed by using UCINE-cross/product-minimum Size method. Using Ucinet 6 to Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration travel diary and official news matrix of the cooperation between cities in the network structure of the visual display, through the comparative analysis between the tourist flow space and government attention and in-depth discussion network structure of Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation, and provide feasibility countermeasures to the balanced development of regional tourism.
Research methods
Social network analysis: Social network analysis is a new economic sociology research method based on social measurement to deeply study the relationship between social network and actors, mainly including individual node analysis and whole network analysis. The indicators such as network density, core-edge and cohesive subgroup were selected to analyze the overall spatial characteristics of the tourism cooperation network structure of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, and the individual spatial characteristics of the tourism cooperation network structure of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration were selected to analyze the individual spatial characteristics of the tourism cooperation network structure of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration by selecting the indicators such as point-centricity, near-to-centricity and middle-centricity [17,18]. Network density aims to measure the tightness of tourism cooperation network structure. The higher the network density is, the closer the connection between nodes is. The formula is as follows,
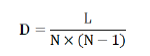
In the formula, D is the network density, L is the number of relationships actually owned, and N is the number of regions.
The core-edge model is to clearly divide the core area and the fringe area of a city in the tourism cooperation network structure and discuss their internal relations. Coagulant subgroup aims to find inter-city groups and factions that interact and cooperate with each other in the tourism cooperation network, so as to provide reference for the development of inter-city tourism cooperation. The point centrality reflects the central position of an individual city in the overall correlation network. The higher the point centrality is, the more the connection between the city and other cities in the spatial correlation network of tourism development is, and the more the city is in the central position of the network. The degree of proximity to the center reflects the degree to which an individual city is "not controlled by other cities" in the overall network. The higher the degree of proximity to the center, the more direct correlation exists between the tourism development of an individual city and other cities, and the city is the central actor in the network. The intermediate centrality reflects the degree to which an individual city controls the correlation relationship between other cities. The higher the intermediate centrality is, the stronger the ability of the individual city to control the tourism development relationship between other cities will be, and the city will be more at the center of the network.
Text content analysis: Qualitative research methods can be in-depth excavation of the tourists for the tourist destination and all-round manner, through content analysis of travel diaries and official news text profound perspective and objective analysis, understand the tourist's perception of the tourism cooperation of Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration and the government's attitude for cooperation between the two cities, to delve into the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation network structure. Using Rost CM software functional analysis of text mining and graphics and text processing tools, to deeply understand the Angle of the government and the tourists similarities and differences of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation, and for the development of regional tourism cooperation traced back, through comprehensive analysis and comprehensive grasp reasonable regional development strategy and way of thinking, promote the healthy and sustainable development of Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation.
Analysis of differences in network cooperation structure
Overall network morphological characteristics: Visitors view cooperation of the structure of the whole network density is 3.7577, the standard deviation is 5.3158, and the government network structure of the whole network density is 1.4797, the standard deviation is 1.3732, to facilitate observation, according to government repeated experiments and visitors view the tourism cooperation network structure are selected as thresholds, 1.56 visitors view a total of 382 cable (Figures 1 and 2), city cooperation basic city such as Shanghai, hangzhou, nanjing, hefei is given priority to, the network structure is relatively close, relatively high level of cohesion, directly or indirectly to the tourism cooperation between cities space correlation, The spatial structure of tourism cooperation development is relatively mature, which benefits from the building of tourist destination brand image, the improvement of transportation infrastructure and the degree of opening to the outside world. And perspective of the government only 204 cables, due to the geographical conditions, economic development and resource endowment of tourism cooperation between the government network structure is relatively loose, the low level of cohesion, of a smaller network standard constraints of individual tourism cooperation links are mainly concentrated in Shanghai, zhejiang and jiangsu, give priority to with provincial tourism cooperation within the contact, the hierarchical characteristics of the network structure. Network density and gradation of differences shows the complexity of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation network, at the same time, regional cooperation between tourists intensity is bigger than intensity of the cooperation between the government, so government departments to improve space is large, to strengthen cooperation, we should according to the demand of tourists in the supply side of the appropriate reform, promote the development of Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism integration continues to deepen, build strong active tourism growth pole (Figures 1 and 2).
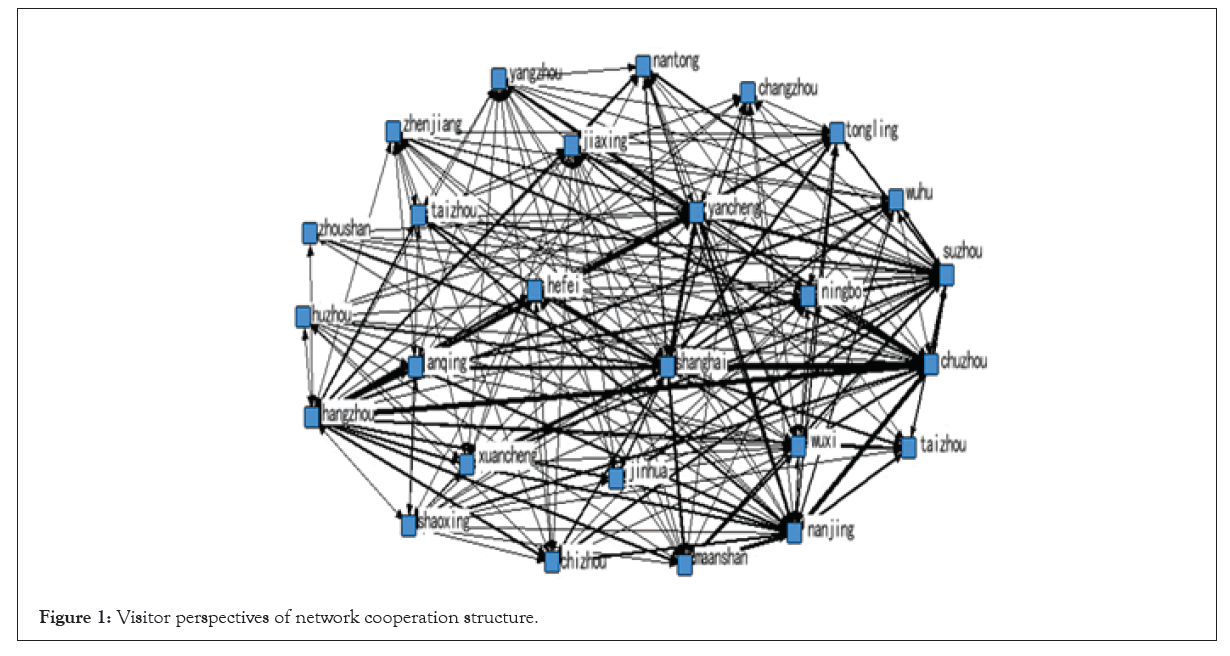
Figure 1: Visitor perspectives of network cooperation structure.
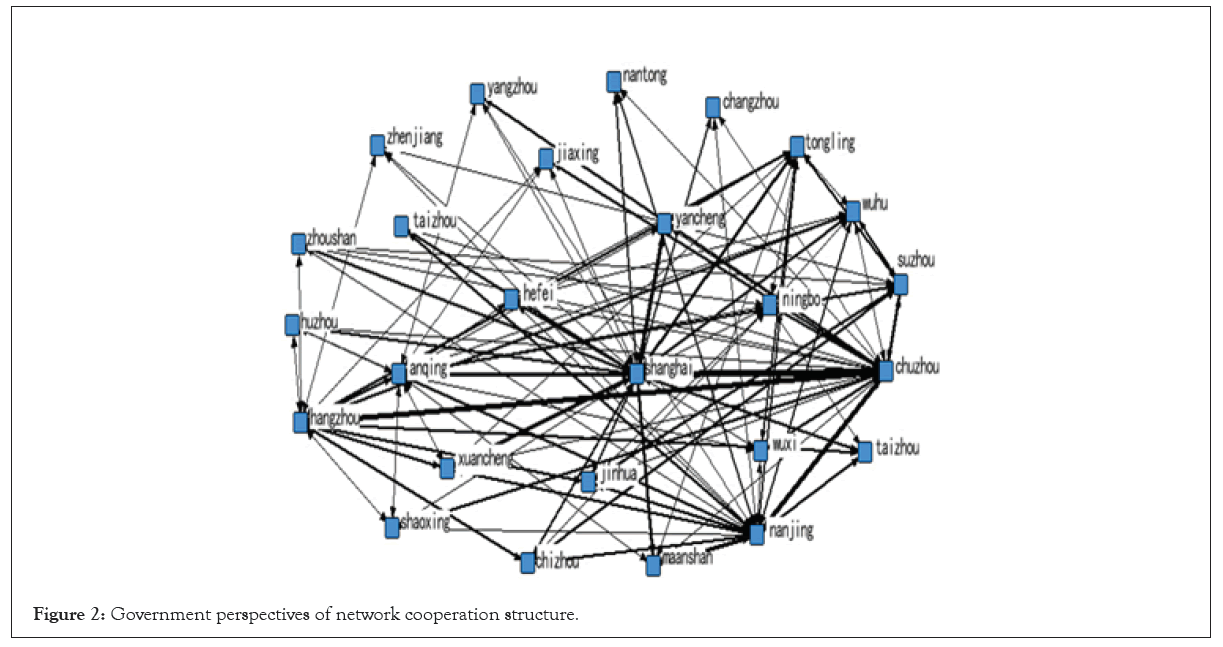
Figure 2: Government perspectives of network cooperation structure.
Core edge structure: Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation links overall network density is low, the network structure is relatively sparse, unbalanced development and overall structure has obvious characteristics of "core-edge" (see Table 1), the perspective of tourists has 10 nodes city belongs to the network core members, and the government only 7 nodes from the perspective of network core members, Shanghai for tourists and government departments, the hot focus areas, all belong to occupy a key position in Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation. In nanjing, jiangsu province and changzhou in the tourists and the government perspective, all belong to the network core shows that the two cities for tourism development and regional cooperation between have booster and the connection effect, and suzhou, nantong, yancheng in the perspective of tourists also belong to the network core of tourism cooperation, due to its geographical advantages, resources endowment and traffic conditions, the tourists to such high attention of the city. Wuxi, Changzhou and other 7 cities are on the edge of the network from the perspective of the government, indicating that the cooperation between cities of the government departments needs to be improved. It is urgent to promote the cooperation between cities and strengthen the connection between cities by formulating relevant policies and carrying out tourism activities and other measures. Only hangzhou of zhejiang provincial government and visitors view in the core network, other 9 city fringe area is located in the network, restricting the development of city network, shows that zhejiang need to strengthen the cooperation between the inter-city, between the city through resources colliding, strengthen infrastructure and government policies conducive to the development of tourism and other measures to vigorously promote cooperation between the city and improve the dilemma in many cities in the network edge. From the perspective of the government and tourists of Anhui Province, its provincial capitals Hefei and Wuhu are located in the core area of the network. It can be seen that from the perspective of tourists and government departments, Anhui Province's attention to tourism and development validity need to be strengthened, especially Hefei needs to enhance the leading role of its provincial capitals. At the same time, all cities should strengthen cooperation and exchanges, and jointly promote the development of urban tourism cooperation, so that the core area of the network can drive, influence and promote the development of tourism nodes in the fringe areas of the network, and actively strengthen the interaction of the overall network between cities, so as to promote the sustainable and healthy development of tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta city group (Table 1).
| Provinces /cities | Travel notes | Official news | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core area | Edge area | Core area | Edge area | |
| Shanghai | Shanghai | - | Shanghai | - |
| Jiangsu | Nanjing, Changzhou, Suzhou, Nantong, Yancheng | Wuxi, Yangzhou, Zhenjiang, taizhou | Nanjing, Suzhou | Wuxi, Changzhou, Nantong, Yancheng, Yangzhou, Zhenjiang, Taizhou |
| Zhejiang | Hangzhou | Ningbo, Jiaxing, Huzhou, Shaoxing, Jinhua, Zhoushan, Taizhou | Hangzhou | Ningbo, Huzhou, Jiaxing, Jinhua, Zhoushan, Taizhou |
| Anhui | Hefei, Maanshan, Wuhu | Anqing, Chizhou, Xuancheng, Tongling, Chuzhou | Hefei, Wuhu | Maanshan, Chizhou, Xuancheng, Tongling, Anqing, Chuzhou |
Table 1: Marginal structure core of tourism cooperation network in Yangtze River delta urban.
Coagulate subgroups: Based on the analysis of the relationship between subgroups and the entire network, and between subgroups and subgroup cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, it can be seen that there are no isolated points in the three levels of factions from the perspective of government and tourists. There are four sub-groups at the second level and eight sub-groups at the third level. At the secondary level, the perspective of tourists in Shanghai, nanjing, wuxi, suzhou-hangzhou-ningbo-yangzhou belongs to the first subgroup, due to the resources endowment, economic level and geographic conditions makes its dominance in the tourism cooperation network, radiating and driving play to the surrounding city, the largest extender to form the development of tourism. The second subgroup in zhenjiang-jiaxing-shaoxing, the third subgroup for changzhou-huzhou-zhoushan, hefei fourth subgroup of taizhou-yancheng-tongling-chuzhou-nantong-wuhu-ma on shan-chizhou, anqing-xuancheng-taizhou, jinhua, four large area space stronger self-organizability, according to the tourist's preference for spontaneous with a certain brand image of tourism city. From the perspective of the government, Shanghai-Nanjing-Suzhou-Ningbo-Hangzhou is the first subgroup, and the provincial capital cities or cities with high economic level form the first subgroup due to the regional conditions, historical development and policy support among the cities. The second subgroup is Xuancheng-Wuxi-Ma 'anshan-Yangzhou-Yancheng-Hefei, the third subgroup is Changzhou-Taizhou-Nantong-Huzhou-Shaoxing-Jiaxing, and the fourth subgroup is Chuzhou-Tongling-Anqing-Zhenjiang-Chizhou-Huzhou-Taizhou-Jinhua-Zhoushan. Therefore, in the first subgroup, cities from the perspective of government and tourists are roughly the same, but there are more cities in the subgroup from the perspective of tourists. In the fourth subgroup, Taizhou and Jinhua are both from the perspective of government and tourists, but other cities such as Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Anhui are also included in the perspective of government. In the second subgroup and the third subgroup, the city consistency from the perspective of government and tourists is low, indicating that the tourism cooperation development from the perspective of government and tourists has great differences due to location conditions, economic level and external openness. At the same time, the division of agglomerated subgroups crosses provincial boundaries and breaks through previous barriers between provinces. Instead, urban subgroups are formed according to the similarity or difference of location proximity, transportation convenience and resource endowment. The government should appropriately adjust the policy mechanism according to the sub-group division of tourists' perspective to meet or appropriately guide the needs of tourism consumers, so as to promote the development of regional tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. From the perspective of tourists, the division of cities in the sub-group level can be aggregated to build several city factions that can be freely spliced, so as to provide suggestions for the government to formulate tourism spatial planning and tourism enterprise product design, so as to maximize tourist satisfaction, minimize cost and enhance regional tourism attraction. In addition, the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation contact group development model, according to the government and the tourist groups, faction of two angles between the city's tourism resources integration, regional cooperation and development in the process of the feasibility of the government departments need to take corresponding measures to promote regional tourism cooperation, promoting the healthy sustainable development of tourism industry of avoiding the phenomenon of regional development imbalances, to keep closely linked to the regional tourism and stable and coordinated development (Figures 3 and 4).
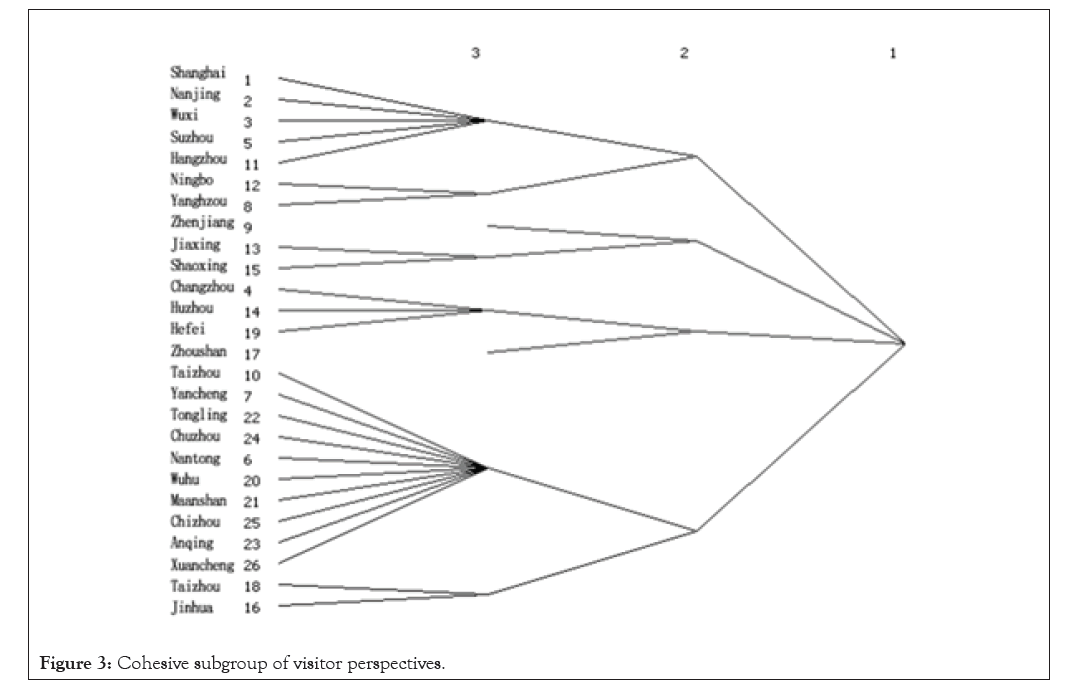

Figure 3: Cohesive subgroup of visitor perspectives.
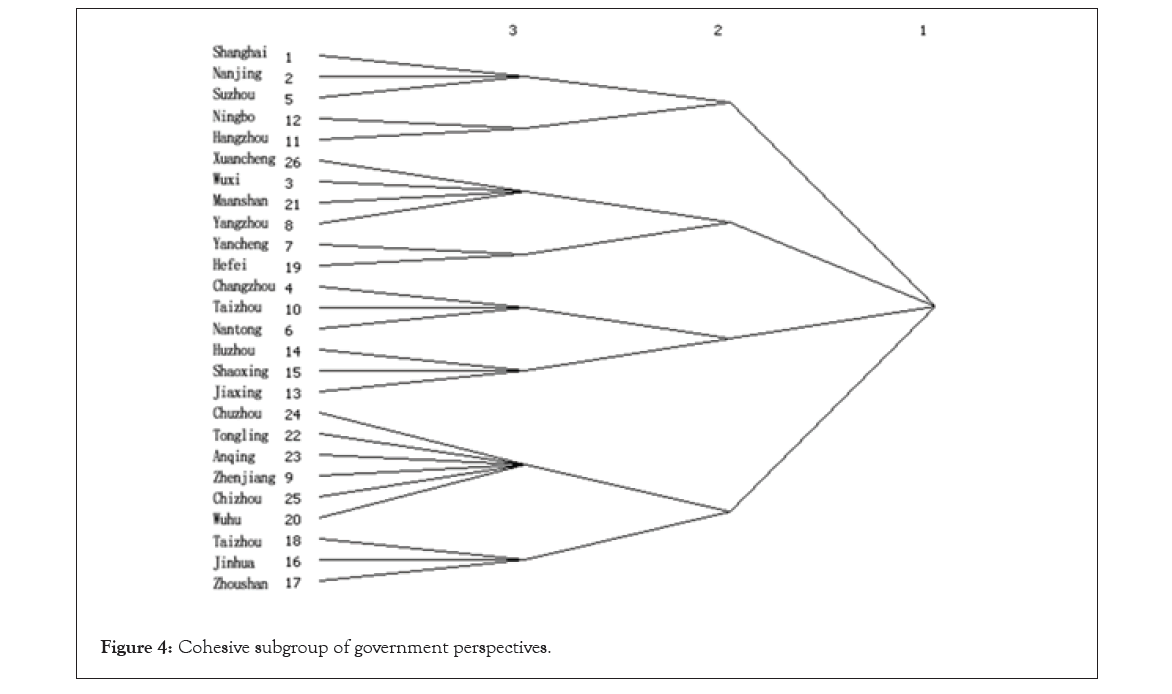
Figure 4: Cohesive subgroup of government perspectives.
Comparative analysis of city centrality
Point degree center degree: From Table 2, the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration of 26 city visitors view point center degrees mean value is 34.530, higher than the average of only Shanghai, nanjing, suzhou, yancheng city, ma on shan, hefei, hangzhou and wuhu, suggests that the tourists in the city visiting rate is high, the city with its resource endowment, economic geographical won the favour of tourists, etc. Shanghai, Hangzhou and Wuhu have the point degree center degree greater than 70, which indicates that the city occupies an important position in the tourist attractions and has a great radiation influence on the surrounding cities, forming the economic growth pole of inter-regional tourism development. The highest value of Shanghai is 100, while the lowest value of Zhoushan is 14.654, which indicates that due to the regional advantages, the degree of opening to the outside world and the level of economic development, the two levels of differentiation in the network of each node city are significant, and each city plays a different role in the spatial correlation of tourism cooperation. The government point of view center degrees numerical generally lower in cities and a significant difference was found in space, the effect of radiation and driving ability is limited, the mean value of 37.473, higher than the average city only Shanghai, nanjing, suzhou, hangzhou, ningbo, hefei, anqing and wuhu city of 8, indicates that the city government to the attention of tourism is higher, have more resources and power, strong communication skills, and other cities to the radiating and driving play in other cities. Shanghai and Wuhu have the point degree center degree greater than 70, indicating that the two cities have a higher status in the spatial association network of tourism cooperation development, and receive strong support and attention from governments, which have a greater impact on the development of tourism cooperation in the surrounding areas. Therefore, Shanghai, nanjing, suzhou, hangzhou, hefei and wuhu city 6 is the key member of the tourism space cooperation network status, the for the leadership of the region surrounding city tourism benefit and promote tourism development mode, makes the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration development increasingly tend to be balanced, but such as zhoushan, taizhou, nantong city arrested development is restricted the development of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration integration of tourism cooperation important influencing factors. Differences from the perspective of the government and the tourists, the government should according to the tourist level adjustment policies for the city's attention, in addition to Shanghai, nanjing, suzhou city, such as attention to steadily push forward, also should pay attention to the tourists visiting rate higher, ma on shan, yancheng city, to strengthen the policy support of the city to meet the needs of the tourists, promote healthy sustainable balanced development of Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation.
Proximity to center: The Table 2 shows that tourists Angle close to center in Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration, 26, peaks at 100, low of 67.568, with a mean of 90.465, as a whole is relatively balanced, shows that due to factors such as geographical advantages, resources complementary, the transportation is convenient, from the point of the tourists 26 cities in the space of the development of the tourism cooperation network all has a different correlation networks. Shanghai, Zhejiang, Jiangsu and other provinces have the highest degree of near centrality, which indicates that the cities in Jiangsu and Zhejiang provinces have obvious central actor status in the spatial network of tourism cooperation. However, some cities in Anhui Province restrict the comprehensive development of their tourism industry due to geographical conditions and economic level. The degree of proximity to the center of Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou and other cities is 100, which indicates that such city nodes are closely connected with other cities, have strong accessibility, are not controlled by other node cities, and are at the center of the tourism cooperation network. The highest, lowest and average value of the degree of proximity to the center of the government perspective is 96.154, 54.348 and 72.113. The overall network structure is relatively balanced. Due to the advent of the era of mass tourism, the attention of government departments and the marketing promotion of each city, cities are relatively closely connected. Shanghai, nanjing, wuxi, hangzhou, ningbo, hefei, close to city center is greater than the average, show that the contact area between the city closely, less controlled by other nodes of the city, and jinhua, chizhou and chuzhou degree value is relatively low, close to city center, suggests that high dependence and to other cities in the region between the small influence. Perspective of the government closer to the center of the overall perspective is relatively lower than tourists close to the center degrees, Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration in the resource advantage, economic level and on the basis of the traffic is convenient, also should according to the difference between tourists and the government perspective, to strengthen the government's policy to promote integrated marketing, city key measures, such as play a leading role, the influence of key city of edge city location, concerted drive the development of regional tourism cooperation, promote the evolution of cooperation process balance, prompting, Yangtze river delta tourism is balanced, coordinated and sustainable development to enhance the regional influence of the city.
Intermediate centrality: The Table 2 shows that tourists perspective in the middle of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration of 26 city center degree value is 38.997, the top 10 cities of Shanghai, nanjing, wuxi, suzhou, yangzhou, hangzhou, ningbo, shaoxing, zhenjiang, hefei, the sum is 28.546, accounted for 73.2% of the total, the city in the tourism cooperation network structure, strong control of plays a powerful intermediary and bridge role. Other cities generally have a low value of median centrality, and Taizhou's market value is 0, which indicates that it does not play an intermediary role in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration due to its remote geographical location or low level of economic development. The total value of intermediate centrality from the perspective of the government is 46.001, the highest value is 8.145 in Shanghai, which has a strong control ability in the tourism cooperation network structure, while the lowest value is 0 in Chizhou, which indicates that the development structure of the cooperative connection network is relatively unbalanced and the polarization situation is serious. In addition, Shanghai, Suzhou, Hangzhou and other cities form high-value regions, which have a high control over other cities in the tourism cooperation network and form an important channel for the development of tourism cooperation. However, Taizhou, Jiaxing and other cities have a low degree of intermediate centrality, which is highly controlled in the tourism cooperation network. However, the value of intermediate centrality of Chizhou is 0, which indicates that it cannot control other cities and has no ability to control resources. From the perspective of government and tourists, although most cities play an intermediary role, the overall value is low, and the resource control ability of cities in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is weak as a whole. The government should give strong support to intermediary and bridge cities such as Shanghai, Nanjing and Wuxi according to the tourism flow direction from the perspective of tourists, promote the function of inter-city tourism distribution and promote the development of regional tourism. In addition, the government should also identify potential intermediary cities, find new bridge cities for the development of tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, open up new growth poles for the integrated development of regional tourism, and promote the coordinated and balanced development of regional tourism (Table 2).
| Provinces /cities | Travel notes | Official news | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree centrality | Proximity centrality | Betweenness centrality | Degree centrality | Proximity centrality | Betweenness centrality | |
| Shanghai | 100 | 100 | 2.973 | 84.764 | 96.154 | 8.145 |
| Nanjing | 69.047 | 100 | 2.973 | 64.211 | 80.645 | 1.333 |
| Wuxi | 28.03 | 100 | 2.973 | 29.689 | 80.645 | 1.978 |
| Changzhou | 18.027 | 86.207 | 0.323 | 23.177 | 73.529 | 1.248 |
| Suzhou | 58.263 | 100 | 2.973 | 45.465 | 92.593 | 6.527 |
| Nantong | 22.383 | 92.593 | 1.9 | 21.732 | 83.333 | 3.621 |
| Yancheng | 47.315 | 69.444 | 0.154 | 24.073 | 78.125 | 2.283 |
| Yangzhou | 21.966 | 100 | 2.973 | 23.258 | 73.529 | 1.403 |
| Zhenjiang | 17.855 | 96.154 | 2.674 | 30.952 | 69.444 | 0.139 |
| Taizhou | 24.538 | 67.568 | 0.071 | 21.772 | 89.286 | 6.706 |
| Hangzhou | 73.393 | 100 | 2.973 | 56.012 | 86.207 | 3.494 |
| Ningbo | 21.439 | 100 | 2.973 | 39.308 | 80.645 | 2.07 |
| Jiaxing | 19.351 | 96.154 | 1.933 | 26.766 | 64.103 | 0.024 |
| Huzhou | 17.831 | 96.154 | 1.933 | 26.238 | 75.758 | 1.902 |
| Shaoxing | 18.506 | 100 | 2.973 | 25.903 | 67.568 | 0.074 |
| Jinhua | 22.05 | 89.286 | 0.855 | 29.359 | 56.818 | 0.133 |
| Zhoushan | 14.654 | 86.207 | 1.687 | 30.616 | 65.789 | 0.251 |
| Taizhou | 20.698 | 69.444 | 0 | 27.181 | 55.556 | 0.056 |
| Tongling | 19.365 | 96.154 | 0.095 | 33.821 | 80.645 | 3.117 |
| Chuzhou | 25.116 | 89.286 | 0.371 | 35.647 | 54.348 | 0.061 |
| Maanshan | 38.725 | 86.207 | 0.145 | 26.088 | 67.568 | 0.305 |
| Hefei | 37.385 | 83.333 | 2.088 | 50.959 | 59.524 | 0.181 |
| Anqing | 29.991 | 86.207 | 0.145 | 59.976 | 60.976 | 0.317 |
| Wuhu | 75.43 | 89.286 | 0.371 | 81.131 | 62.5 | 0.062 |
| Chizhou | 28.161 | 86.207 | 0.323 | 32.693 | 55.556 | 0 |
| Xuancheng | 28.261 | 86.207 | 0.145 | 23.512 | 64.103 | 0.633 |
Table 2: Centrality analysis of spatial association network of tourism cooperative development in Yangtze River delta urban agglomeration.
Optimizing the tourism cooperation structure of the Yangtze River delta city group
Through the travel diary and official news text high-frequency word analysis, Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration travel diary of high frequency words in scenic areas, attractions, food, celebrity anecdotes, folk customs and experience is given priority to, the official news of the high frequency words in publicity, promotion, joint, ecology, LvYouWei, opening speech, the scenic area and development. Thus the emphasis of the government and tourists to the tourism perception, tourists tend to own the tourist accommodation environment, diet atmosphere, tourist experience, transport infrastructure and tourism services and all-dimensional, multi-layered perception, and mainly focus on the affection and kid around ska, conform to the sightseeing tourism to the development of leisure tourism, tourist experience, focus on the evaluation and perception of tourist attractions. Government departments focus on the transformation and improvement of tourist destinations, development and innovation, and the improvement of tourist satisfaction. They focus on the image publicity and promotion of tourist destinations, the maintenance of scenic spots, and the cooperation and promotion between regions. The semantic analysis of tourism diaries and official news in social networks can reveal the relevance and difference of semantic words from the perspective of government and tourists. The semantic words perceived by tourists include Jiangnan, ancient town, scenery, history, culture, architecture and accommodation, covering natural resources, human resources, tourism environment and atmosphere, and tourism facilities and services. And the government's point of keywords have service, organization, communication, host, development, promotion and cooperation, localization level of official news and attention from the global level of overall regional level, paying more attention to the scenic spot and image communication and cooperation between the region linkage, and promote tourism in promotion, market development and promotion, etc., aims to lead the scenic spot and the benign development of tourism between the two cities. Tourists comprehensive perception of tourism destination and official news attention due to its starting point, there are certain differences, different levels and Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration of regional tourism cooperation of the differences between supply and demand, the government should according to the objective demand of tourists, in-depth excavation of the tourism destination image and regional joint promotion, to provide reasonable policy support, make products meet the demand of tourists, driving tourists punters routing point to the line of change, all-round, multi-dimensional promote regional tourism cooperation, create a Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration barrier-free tourism zone. According to the current situation of "core-edge" and centrality difference between the government's supply side and the tourists' demand side, in order to promote the coordinated, balanced and sustainable development of tourism in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, the following optimization paths are proposed.
Policy focus and governance: Market is a basic means for the allocation of tourism resources, but the market mechanism is not everything, in the process of promoting tourism development has obvious failures, based on the health of the tourism market and tourism industry continues to develop, must want to have the government's intervention, to the invisible hand of the market and the visible hand of government to play a dual role of government-led tourism industrial development pattern is clear about the government in the main body position in the industry development. According to the whole network analysis shows that the government pay more attention to provincial capital cities such as Shanghai, hangzhou, nanjing and suzhou, chuzhou dense, economic level of tourism resources, such as the developed city, the government should undertake corresponding rectification according to wh-what tourist city promotion measures, in order to satisfy the demands of tourism consumers, improve supply quality. According to individual network analysis shows that the government's point of the cooperation and tourists demand for tourism city level slightly different, so the government should be based on node cities such as Shanghai, hangzhou, nanjing, suzhou, ningbo, hefei and other intermediary and Bridges the development of the city to develop targeted measures to promote the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration multidimensional and multifaceted integrated development of the tourism industry. Governments in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration play a leading role in shaping regional joint marketing and brand image and promoting the sustainable and healthy development of tourism by formulating tourism industry policies, carrying out inter-city and regional tourism promotion and holding leadership meetings. At the same time, the ability and level of the government's official website and search engine in spreading information and stimulating tourists' interest should also be improved and timely optimization and adjustment of regional tourism cooperation policies should be made. Based on the response of tourists to government policies, policies or development strategies can be formulated to provide a starting point for the renewal of regional tourism cooperation concept, the establishment of cooperation platform, the innovation of cooperation mechanism and the reform of cooperation system. In addition, the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration governments should reasonable use of the advantages of the resources advantage, economic level and traffic location is reasonable on regional governance, to speed up the management of city construction, public services and industry to achieve barrier-free tourism, promote the urban construction of hard and soft environment, to provide convenient services at the same time make the tourists get more happiness and satisfaction, steady progress was made in Yangtze river delta regional tourism cooperation, and promote the development of regional tourism integration.
Line planning and reconstruction: According to the analysis of the network centrality of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration from the perspective of tourists' demand, Shanghai, Nanjing, Hangzhou and Suzhou are regional tourism centers, hubs or distribution centers, which are suitable to be set as starting points or stopping points in tourist routes. According to the agglomeration subgroup analysis, tourists prefer to "Shanghai-Nanjing-Wuxi-Suzhou-Hangzhou", "Ningbo-Yangzhou" and other cities for joint travel based on the emotional tone and travel atmosphere of the city. Therefore, the tourism network of the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration should be constructed from the perspective of tourists' demand according to the resource endowment, supporting facilities and market positioning between cities. Enterprises can assemble tourist cities through product design and repackaging, and governments should consciously adjust and reconstruct the structure of tourist city network. In order to meet the psychological needs of tourists seeking novelty and novelty, enterprises or governments should plan the routes with various types of tourism products to meet the differentiated needs of tourists. In order to gain market share, tourist attractions should carry out market segmentation for tourists, create targeted and specific tourism products, attract tourists to come and improve their popularity. At the same time, the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration should respond to strategic measures such as "toilet revolution" and "cultural and tourism integration" in the tourism industry, improve the infrastructure and resource connotation of scenic spots, so as to meet the needs of tourists and improve its reputation effect. In addition, by virtue of favorable factors such as location advantage, resource endowment, information sharing and transportation development, and trans-city tourism cooperation opportunities are organized to break through the barriers of local tourism protectionism and promote the steady improvement of regional tourism cooperation. Homogeneity and heterogeneity in the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism scenic area, there is also a positive strategic cooperation relationship between through active marketing promotion and the scenic area, to attract more customers with high quality, each other between each city to tourism, each group, in order to get the development of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration theory strategic advantages, promote the development of tourism coordination equilibrium.
Brand promotion and marketing: Differentiated tourism market is the key to realize the sustainable development of regional tourism cooperation. Combined with the needs of tourists, the Yangtze River Delta city group should dig deeply into the characteristics of tourism resources and form differentiated and personalized tourism supply. For example above should strive to create history and the modern Shanghai intersection of tourism image, focused on historic or tourist attractions has contemporary feeling extremely, the above key launch hangzhou jiangnan water, the characteristics of ancient town tourism products, the above on the basis of history and culture, nanjing integrated museum, former residence, old street, garden construction and other tourism resources, hefei above can highlight this ancient village, rural tourism and other tourism products, the corresponding form personalized travel supplies, create a batch of market prospect and potential of tourism projects meet the diverse needs of the tourists, Promote the sustainable development of regional tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta city group. In regional tourism cooperation, local governments should change their thinking. The government should not only be the policy maker, the facility builder and the concern of regional interests, but also undertake the public function of regional brand marketing. It should do a good job in regional tourism service and marketing from the perspective of tourists' demand. On the above the depth of cooperation, to actively promote the government in the sharing of tourism information platform should be built, the realization of the maximum area of each corresponding cooperation and sharing of resources, information, market, more tourists will bring double more opportunities of employment, income and region will eventually to promote the realization of the interests of the whole area. At the same time around the important media platform in official news websites, should strengthen the important scenic spots and the propaganda, using weibo, WeChat, websites and other diversified marketing platform, to build influential festival events, events, etc., continuously strengthen the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism brand in the tourist's perception of the heart, pull the tourist flow in the distribution and promote sustainable development of the Yangtze river delta tourism coordination equilibrium, jointly promote the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation.
This study only intercepts the tourism diaries and official news from 2016 to 2018 for discussion. Long time, small area and multi-dimension are the important research directions of tourism spatial structure and regional tourism cooperation development in the future. In addition, the overall network and individual network of regional tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration need to be deeply discussed, and the measurement of regional tourism cooperation also needs to be made by using the measurement method, which needs to be further studied and judged by combining the tourism cooperation with the directed data of tourism flow. There are some limitations in this study. First of all, the study mainly focuses on static analysis and lacks dynamic diachronic analysis. Secondly, the data is mainly based on the network text, and the data source is relatively single, lacking the support of multi-source data such as questionnaire survey. In addition, the research scope is mainly 27 cities in the Yangtze River Delta region, and the research on other tourist destinations in the Pan-Yangtze River Delta region is relatively lacking. Therefore, the follow-up research can explore the dynamic study of relatively large tourist destinations under multi-source data, and conduct directional analysis on the visiting order of tourist scenic spots for specific groups such as self-drive travel and group travel, as well as conduct micro-discussion on the characteristics of tourists to study the corresponding tourist routes. At the same time, in-depth integration of GIS spatial data, metrological methods, tourism group image design and other issues are the next focus of the Yangtze River Delta region tourism destination cooperation research.
There is a disequilibrium phenomenon in the tourism cooperation network, and the structure of the tourism cooperation network from the perspective of government is looser than that from the perspective of tourists. In terms of the whole network, the Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation in the network due to the unequal status between city form the core-edge of the resources, information and interest structure, the core city due to their level of power, influence and dominance in the network, and part of the edge of the city in a passive position in the regional tourism cooperation, the city needs the government and enterprises to give high attention and promote coordinate the balanced development of regional tourism. Government and visitors view of condensing subgroup analysis showed that there are multiple factions in Yangtze river delta urban agglomerations tourism cooperation network, there are informal urban complexes, so the government and enterprises should be based on the similarities and differences between the factions on tourist destination image, the tourism product marketing promotion be used for reference. In terms of individual network, from the perspective of the government and tourists, there are differences in the degree of centrality of each city, but Shanghai, Hangzhou and Nanjing are in the central position and are the core members of the tourism cooperation network, and they have certain influence and dominance over the surrounding cities. The degree of intermediate centrality indicates that Shanghai and Suzhou play the role of intermediary, which has strategic significance for information transmission and cooperation communication in the tourism cooperation network. Therefore, attention should be paid to the sound development of tourism cooperation network, the cooperation between non-neighboring cities, the barriers of regional protectionism should be broken, the network governance should be strengthened, and the stable development of regional tourism cooperation should be promoted.
The Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration is at an important moment of quality upgrading, innovation and transformation. It is in urgent need of optimizing and upgrading according to the existing differences between supply and demand based on the regional status quo, promoting the coordinated promotion of regional tourism and forming an international competitive advantage. Based on the regional advantages, resource endowments, economic strength and complete urban system of the Yangtze River Delta city group, and combining with the comparative analysis of the connection degree of the tourism cooperation network, the whole network and the individual network from the perspective of the government and tourists, this paper puts forward the spatial development model of the tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta city group. Based on a comprehensive transportation network play a role of the core of Shanghai radiation, combination of nanjing, hangzhou, hefei, suxichang metropolitan area of the city development, strengthen the coast, along the Yangtze river, shanghai-nanjing, shanghai-hangzhou hangyong gold development belt of polymerization, build "four with a nuclear five circles" tourism cooperation network spatial pattern, and thorough going efforts to promote the construction of the Yangtze river delta urban agglomeration of regional tourism cooperation.
To optimize the structure of regional tourism cooperation in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, we should pay attention to policy focus and governance, route planning and reconstruction, and brand promotion and marketing. Based on resources and oriented by the market, government departments should formulate corresponding policies and regulations and provide certain financial support according to the needs of tourists. In addition, in order to meet the needs of tourists, according to the tourists' perspective of urban small groups to replan and lead the development of new tourist routes, according to the market positioning to shape new tourism products; At the same time, the differentiated tourism market is the key to realize the sustainable development of regional tourism cooperation. Combined with the needs of tourists, the Yangtze River Delta city group should dig deeply into the characteristics of tourism resources to form differentiated and personalized tourism supply. We should give full play to the initiative of multiple subjects, strengthen the tourism cooperation and connection in the Yangtze River Delta city group, optimize the structure of the tourism cooperation network, and realize the coordinated and balanced development of barrier-free tourism in the Yangtze River Delta city group.
Citation: Wu X, Song H (2023) Research on the Differences in the Tourism Cooperation Network Structure of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration from a Dual Perspective. J Tourism Hospit.12:512.
Received: 22-Dec-2022, Manuscript No. JTH-22-21106; Editor assigned: 26-Dec-2022, Pre QC No. JTH-22-21106; Reviewed: 09-Jan-2023, QC No. JTH-22-21106; Revised: 16-Jan-2023, Manuscript No. JTH-22-21106; Published: 23-Jan-2023 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-0269.23.12.512
Copyright: © 2023 Wu X, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.