Journal of Tourism & Hospitality
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0269
ISSN: 2167-0269
Research Article - (2019)Volume 8, Issue 5
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has inevitable impacts on different industries and their performances. The tourism industry, as the largest and fastest growing industry in the world, cannot be excluded from this technology and its huge impacts. ICT provides information about tourist attractions in different destinations before travelling and improves tourists’ satisfaction. Although Algeria has great tourism potentials, it still needs to be performed well in promoting its attractions to international tourists via ICT tools yet. This research explores the impact of ICT on foreign tourists’ satisfaction of the tourism industry and uses Algerian tourist agencies as a case study, and proposes a model for the impact of ICT on sustainable tourism. It proposes a model; namely, Al Djazaer Siyaha, for improving information quality and tourist services’ quality in the eTourism industry. Also, it is recommended that the tourism authorities should develop e-tourism infrastructures in order to keep up with the competitiveness of this field to enable the country to benefit from the global benefits of the tourism industry.
Al Djzaer Siyaha; Information and communications technology; Tourism; Tourists’ satisfaction; Sustainable tourism; Information quality
Tourism is now one of the most important industries in the world. It is also known as the fastest growing sector— the first world industry, and an important tool in promoting sustainable development. Besides, it promotes economic development through bringing important revenues of foreign currency, reducing unemployment, and upgrading areas. So, accordingly, most countries in the world rely on tourism as a pillar for their economy.
The world has already undergone too many changes, and ICT has occupied the highest position of interests of various business sectors and services. Since tourism industry is the first industry that has been associated closely with progress in information and communication technologies, tourist electronic transactions have become global outcry and an important condition for providing competitive tourist services of good quality in the new global marketing environment. So, tourism organizations should adopt an e- tourism strategy, in order to be able to compete within the era of digital economy, technology, e- commerce, electronic information sources, e-negotiation, commercial, and business services of international aspect [1].
ICT plays an important role in the application of e-tourism services in terms of activating systems and web- based applications. Providing customers with electronic services has become one of the successful elements of any economic sector, especially tourism industry, as it promotes electronic services and modern applications.
It is one of the promotional features in a highly competitive market interested in updating the tourism industry and e-marketing and all tourist services provided. As e-tourism has been the bulk of e-commerce, developing and activating the best solutions and the latest electronic systems for tourism services has been done in terms of e- marketing strategies to achieve comprehensive performance of tourism to support the competitive global tourism to attract tourists and tourism investments [2].
It is worth to mention that many countries have succeeded in using ICTs to develop their tourism industries. For example, Malaysia has been very successful in attracting many tourists through these means [3]. Islamic tourism in Malaysia is one of the important tourism segments considering its official religion. The country possesses numerous natural, religious, historical, and cultural tourist attractions. Hence, the integration of well- crafted ICT solutions, the tourism industry in Malaysia rely on ICTs and especially the internet as tool of international communication. As an important segment, Islamic tourism is also utilizing the advancement of technology by using websites as a tool in performing tourism related activities such as marketing, promoting and introducing tourism products and services to the potential tourists. As a very important reference point for potential tourists, Islamic tourism websites have become of a good quality standard, since it is the main indicator for the e-business success [4].
In 2007, Malaysia’s tourism website has been declared as a role model of e-tourism by the United Nations Conference Trade and Development (UNCTAD). Based on its superb display of marketing graphics and design, it was the beauty of this website that lead to an average of 12.3 billion hits every month [5].
It is worth to mention that eTourism market in France had reached € 6.57 billion in 2008, which represents 23% of development, compared to 2007. In this context, eBusiness in the field reached 47%, including all oprating activities. Internet users for tourism reached 17 million ; they spent 18%of their tourist budget online [6].
Although Algeria has many attractive tourist potentials which can make her rise to the ranks of the important tourist destinations in the Mediterranean Sea and the world, there are major challenges in front of Algeria to exploit the sea potentials to meet the requirements of global markets and keep up with the trends. To achieve this goal, the Algerian government adopted in 2008 a strategy to promote tourism to the very prospects of 2030 based on the support reception structures and work on improving services to international standards. Despite the natural potentials owned by Algeria, it is still far to attract tourists from different countries of the world. Many experts asserted the need to redraw the plan of developing tourism in Algeria, creating a competitive advantage, and the need for the embodiment and foundation of a strong tourism and promoted as a tourist productive and durable destination.
The material resources alone are not enough to attract tourists, but several conditions must be provided by creating excellent tourist poles that respond to international. So, in order to improve tourism and tourist destination, Algeria should give a great importance to ICTs and exploit them effectively for the sake of improving tourism industry and promote sustainable development of tourism in the country to be an excellent tourist pole in the region. This paper analyzes how ICT can be a veritable tool for tourism sustainable development in Algeria. Also, it proposes Al Djazaer Siyaha, as a web program model for improving information and tourist services’ quality in the eTourism industry.
Nowadays, with the technological revolution, ICTs have had tremendous impacts in all industries and sectors, as well as, specific businesses. The impact of ICTs on businesses relate to the facilitation of communication with organizational stakeholders, serving as an effective sales channel, providing an effective platform for engaging in marketing and others. It is not withstanding that the tourism industry has also been influenced by the integration of ICTs. This; in fact, has been largely acknowledged in the literature.
Buhalis and O‘Connor (2005) identified a number of key changes in ICT that gradually revolutionize the tourism industry. eTourism and the Internet in particular support the interactivity between tourism enterprises and consumers and as a result they re- engineer the entire process of developing, managing and marketing tourism products and destinations. They demonstrated that future of eTourism will be focused on consumer centric technologies to ensure that the new sophisticated and experienced consumers are served. Therefore, agile strategies are required at both strategic and tactical management levels to develop the ‘info structure for tourism organizations to manage their internal functions [7].
Olorunfemi and Raheem (2008) examined the benefits of tourism to local economy on its potentials in transforming the rural poor‘s life. Arising from this benefit is the security challenge which is often least discussed even among researchers on tourism. They also identified the physical security of the tourists and the psychological security of the host communities crucial for sustainable tourism development in Africa. Finally, they concluded that sustainable tourism development isvisible and possible if a mechanism exists that guarantees the security either way [8].
Alisha and Frew (2010) carried an investigative study into the use of information and communication technology for sustainable tourism development.They examined how ICT can be used in the management of sustainable tourism. They presented an array of ICT- based tools/applications for use by destination managers and discussed the opportunities in destination management for applying ICT to Sustainable Tourism Development [9].
Ogbu, Idris, and Ijagbemi (2011) analyzed how ICT can better improve the tourism sector in Nigeria. They demonstrated various ways by which ICTs have been adapted for the course in tourism. In their work, it was revealed that almost every tourism products can be sold online without the consumer necessarily visiting the place before making any choice since tourism products are not already manufactured goods. Booking of flights and hotel reservations can be done online through e-mail, telephone calls and other internet services thereby helping to reduce if not remove entirely the time wasting processes of the old system [10].
Toumi and Kherif (2011) believed that e-marketing for tourism has been of paramount importance, especially with the explosive growth in new technologies and the increasing use of the Internet. Since it has become the most competitive area in the tourism marketing environment,they illustrated the importance of the fact that organizations of tourist services should to competitiveness in the field of using new sources and news channels of tourist information to provide the best quality of services in order to achieve the satisfaction of the customers [11].
Peaseand Rowe (2005) discussed the role of ICTs in promoting tourism industry and hospitality. They asserted the fact that the increase in demand for international tourism is due to several factors, including increased income in many exporting countries for tourists; the intention of most tourist countries to promote tourism of their natural merits and tourist services so as to stimulate tourists due to the means of tourist attraction. Added to that increase in the demand for tourism is the progress in the field of information and communication technologies that lead to good communication between the countries exporting tourism and receiving countries, and also provide tourist services and hotel distinctive for tourists. So, this technology has become an important factor in pushing the tourism sector and its development [12].
Nabil Aid (2013) investigated one Tourism in Arab countries and discussed the role of ICTs in promoting and developing tourism sector. According to him, Arab governments should highly exploit ICTs to improve e-applications for tourism industry relying on e-marketing strategies to have sustainable tourism and support world tourism competitiveness to attract tourists and tourist investments [13].
Karimidizboni (2013) examined the role of information technology in the tourism industry in Iran by presenting some solutions about it. Due to popularity of internet demand, many tourist organizations, such as hotels, airplanes, and travel agencies, have changed by applying the Internet as an important part of communication and marketing strategies. Searching Information that is important part of buying decision-making process, evolved as an internet achievement. ICT not only reduces the risks of receiving and uncertainty, but also increases the quality of travel [14].
The idea of adopting the sustainable development concept in tourism appeared in the early ‘90s, which generated sustainable tourism– an area that quickly gained importance both in academia and research, and in tourism industry [15].
Tourism development refers to the "the various programs that aim to achieve an increase in tourism resources and deepen and rationalize productivity in the tourism sector." Sustainable tourism development is defined as one of the means that― meet the needs of tourists and host sites and by protecting and providing opportunities for the future. It is the guiding rules in the management of resources in a manner that achieves the requirements of economic and social issues and cultural integration is achieved and environmental factors [16].
Sustainable tourism dissociates itself as a matter of principle from mass tourism and partially associates to alternative, contemporary tourism forms. In other words, sustainable tourism is primarily the opposite of mass tourism. This is defined as “a positive approach intending to reduce tensions and frictions created by the complexity of interactions between tourism industry, tourist, natural environment and the local communities as host of tourist” [17]. Sustainable tourism is defined as: ‘… tourism and associated infrastructures that, both now and in the future: operate within natural capacities for the regeneration and future productivity of natural resources; recognize the contribution that people and communities, customs and lifestyles, make to the tourism experience; except that these people must have and equitable share in the economic benefits of tourism; are guided by the wishes of local people and communities in the host areas‘ [18].
One of the most important principles of sustainable tourism meant to serve the protection and economic development of local communities and protected areas. The primary goal of a priority of sustainable tourism development is to develop and implement effective planning measures that lead to maximize the benefits of tourist potentials of economic and environmental aspects to reduce the risk of environmental degradation [19].
Information and communication technologies are powerful tools to take part in the global market, improve the provision of basic services, and enhance opportunities for local development. According to a study of the Organization of Cooperation and Economic Development (OCDE), Information and Communication Technologies are one of the crucial and important factors in enhancing economic development, Economic Cooperation and Development and it has to be included in the economic and social fabric. It has also been reported that the tourism services currently rank first in the electronic trade [20]. Since the Internet is the basic and important backbone to implement spread of applications for information and communication technologies, the primary goal of ICT is to make the World Wide Web more meaningful through a variety of programs and services, so that business institutions can make many deals across the network. This technology provides many options and alternatives: to select tools and choose services to develop solutions that meet the need so reach institution.
Castells (2000) mentioned that "in such an era, a development that is carried/ or conducted without the Internet looks like doing manufacturing without electricity" [21]. So, this statement is a clear, eloquent reference to the crucial importance of the Internet nowadays and in the future, and this is what explains the growing speed of its spread: Internet‘s duration of deployment is estimated only about seven years. So, does the Internet have benefits in the tourism industry and hospitality to support sustainable development? What can ICTs add to the tourism sector?
Setting up a well-recognized framework for eTourism will support harmonized development of the industry. Accordingly, e-TF is alsoplaying a fundamental role in the distribution of tourism information and sales. Increasing proportion of users are buying services on–line, in this sense, online booking and reservation services have been widely accepted among both leisure and business travelers to a degree where it is true to say that "e-tourism" has taken off and the touristic sector will gain a larger and larger share of the online commerce market.
Recently, Mr. Ghouti, Adviser at the Ministry of Tourism, has revealed that an agreement was signed between his ministry and that of Post and ICT to develop ane-TF to support future economic operators, hoteliers, travel agencies to integrate tools for virtual tourism marketing [22].
This decision falls well with the expectations of the promotion of tourism sector that were proposed by JF Schmidt, university and French marketing expert, who recommended that in Algeria, etourism can be set in accommodation with tourist capabilities. He believed that "the effectiveness of the internet is the simplest tool and rich opportunities for global tourism action plan." In reviewing the data on the virtual marketing and tourism demand in France, the expert found that "60% of the French prepare their travel via the Internet. This means that the new promotional marketing virtual media has its place to "provide pallets of new tourist products" [22]. As far as Algeria is concerned, he asserted that the destination can be enhanced but only to regions that convey imaginary sites for tourists who want to get there." Best examples can be taken from Morocco, Cuba, and Australia that illustrate new data for e-tourism and contribute to the influx of tourists in these regions.
In order to implement e-TF, the three following basic necessary steps are required [22]:
• Tourism data collection (Offers, prices, maps, reports, ... etc)
• Digitization of data collected using various technological means
• Dissemination of information electronically via WAP, across multiple electronic media, and in several languages.
The quality of tourist services will only be made available through the use of ICT in various fields of tourism and hospitality; such as, planning, promotion, marketing, booking, contracts, and financial settlements. Also, the World Trade Organization (WTO) and other governments have emphasized on the importance of using ICT in the tourism sector and hospitality. It is no longer an option, but it has become a basic building block in tourism development. So, eTourism is not seen as competitor to the traditional tourism, but it is considered as a complementary to it, and necessary for the development of the tourism sector [23].
This integration can be as follows:
• Tourist services, of various kinds, rely heavily on circulation of tourist information, characterized by difference and contrast, and therefore difficult to measure its quality. So, there is the Internet which is appropriate center to them. It reduces this discrepancy by virtual visit to the tourist service so that the user can identify landmarks and areas easily through interactive images of the site and search the data and detailed information on tourist areas to be visited.
• The use of ICTs enables toreduce the cost of producing tourist services. It contributes in promoting tourism. On the other hand, ICT operates to reduce costs, especially those related to contacts, and those related to the distribution.
• Expand in the use of ICTs may lead to the emergence of potential needs that did not exist before, and this obliges workers in the tourism sector to develop a variety of new products in order to meet the needs of potential [24].
Also, among the factors which push and incite policymakers to use ICT, we can cite the followings:
• The desire of business managers in the sector to define their work, products, and services presented to tourists and how to contact them more quickly and at lower cost.
• Electronic publishing of the information concerning both tourism and hospitality institutions which the tourists want to know about without going to the tourist organization.
• Providing special services for tourists in terms of speed and ease, via the Web and e-mail
• Attract new tourists who are connected to the Internet.
• Dissemination of tourist information to the tourists in a timely manner; any delay in the publication deadlines will affect the value of information. Advertise tourist products and services online so as to attract a large number of tourists.
• Allow tourists to book via the Internet. Being present everywhere and display compatibility with the requirements of tourists.
• Being a pillar of innovation and development and creating new products, services, and markets.
• Provide a variety of services for tourists fastly [25].
Algeria, thanks to its unique location and vast area, looks very distinctive with its unique in both natural and urban components. The Algerian authorities sought by pattern to exploit these potentials to be developed. Algeria is a country that features a specific nature that made it of interest to researchers. Western writers described Algeria as a cultural mosaic and a rare masterpiece. Algeria‘s land stretches in its vast breadth on a distance of 1900 kms from the North to the South, and 1800 kms from the East to the West.
Elements of tourist attractions in Algeria
Natural and geographical sites: Algeria is located in North Africa, bordered to the North by the Mediterranean with a 1,300 km2 coastline, East of Tunisia and Libya, and West of Morocco, Mauritania, and Western Sahara, and to the South of Niger and Mali. Algeria is the largest country in Africa in terms of area, as it sits on 2,381,471 km2. It has a population of more than 41 million inhabitants.
There exist in Algeria variety of tourist facilities, both recreational and family, in different cities and regions of Algeria each with its characteristics. Some have beaches where pools and seaside resorts, and some contain highlands, where the rebound of tourist services in summer and in winter where ice skiing. Moreover, Algeria contains some cities that are best known of their historical, cultural, and religious monuments that attract tourists. The following Table 1 shows the major Algerian cities and their tourist potentials.
| Algiers | The city is characterized by its Islamic and modern European architecture. It was known as the Casbah with its narrow streets and numerous mosques and castle, which was built in the sixteenth century. The Casbah is a historically significant architectural heritage and recorded by the UNESCO in 1992. In Algiers, there are many historical and most prominent tourist sites [26] (The Casbah). The famous movie La Bataille d’Alger‘ (1966) symbolizes the historic military events that took place in the Casbah during the Algerian Revolutionary era. Among the most important tourist sites in Algiers, we can cite the followings: The Dey’s Palace in Algiers, known as Riyadh Palace, is also called the Fort 23. This palace which was the living house of the Pushas of Algiers is regarded as the most beautiful architectural groups of Algiers during the Ottoman period and one of the most important historical monuments of the city. It was built in 1750 by Dey Hussein, the Pusha of Algeria [27]. La Notre Dame d'Afrique, formerly known as "Lady Africa" or "Lella Miriam" is located in Z'Ghara and stands on 124 meters above sea level. The basilica was designed by the French architect Jean Eugène Fromageau and was completed in 1872. The exterior is built in Byzantine style, whereas its inside is designed in the Moorish architecture. It is mostly a sacred shrine to the Virgin Mary [28]. The Ketchawa Mosque is one of the most famous historic mosques in the Algiers with its unique, architectural Turkish masterpiece. It was built during the Ottoman rule in 1021 Hijri/ 1612 A. D. It was called Ketchawa relatively to the market which was held in the nearby area. However, it was turned into "St. Philip" Church during the French colonialism when Duke General De Rovigo, Supreme Commander of the French troops, burnt all versions of the Holy Quran in the nearby market square. He also killed more than 4 thousand Muslims who held fast as a means of protest against converting the mosque into church. It was demolished on Dec. 18, 1832, but in the dawn of Algeria's independence, the mosque was rebuilt on Nov. 2, 1962 [29]. |
| Tipaza | It is a wonderful site that features Phoenician and Roman ruins. It contains now places of tourist services evolving from luxury hotels, tourist villages, and luxury restaurants. Among the attractive tourist cities in Tipaza is Cherchell [30]. |
| Constantine | Commonly known as Cirta, this famous city is an outstanding tourist destination as well as being a meeting place for all roads and the center of activity and movement of the city. It is recognized as being one of the centers of Andalusian music. Also, it is well known of its delicious traditional meals in addition to its products from traditional crafts and embroidery with gold threads, known as Alguendourah. The Old City is built on a rock of hard limestone, giving it a unique view that is impossible to find across the world in any city. In Constantine, there are some important tourist sites of which we can mention the followings: The Massinissa Mausoleum (tomb) is located in El Khroub city, 16 km south-east of Constantine, and is a square tower built in three rows of stones filled and are carved in a manner inspired by the Greek style. This shrine is attributed to Massinissa (238 BC- 148 BC), the founder of the Numedian state and ruled this area for 60 years. He contributed to the promotion of urbanization and the development of agriculture in the region, and founded a strong army [31]. The Ahmed Bey Palace is among the most important architectural masterpieces in Constantine. Ahmed Bey was influenced the Islamic architecture in Mecca and inspired the idea of translating this fascinated architecture in building his palace. It was established in 1835. It extends to 5600 m2 [32]. The Suspended Bridges: Because of the location of the city and the rift valley crossing it, height huge bridges were built to facilitate the people’s movements within the city. |
| Oran | It is mostly known as Al Bahia, the second largest city in Algeria, and the capital of the Algerian West. It is located on the Mediterranean. Oran is a very old city that was founded generally due to the Andalusian and Moroccan traders in the tenth century (937 AD). It was occupied by the Spaniards in 1509 that were later expelled by the Ottomans in 1792. The French later occupied the city of Oran in 1838 until the independence. Oran combines two architectural models: one is modern built by the French, and the second Old Spanish Andalusian style. The city is surrounded by vineyards; its nice weather and living prevails an atmosphere of calm, and it is a city which full of movements and activities. Oran contains some tourist sites such as the Derb, an ancient street, Medine Jdida (The New City), Place d’Armes, and Al Basha Mosque (1796). In Oran, there is a wonderful tourist site of Ain El Turk which contains hotels and the tourist complex of Andalusia overlooking Mediterranean. Also, there is Santa Cruz Tower which was founded by the Spaniards [33]. |
| Annaba | It was settled by the Phoenicians who labeled it Hippone in the 12th B. C. The city is located in the far east of Algeria and is best known as the Pearl of the Algerian East. Among its tourist highlights the Grand Mosque and the Cathedral of St. Augustine, a philosopher born and brought up in Algeria. At the heights of Annaba, there are currently tourist facilities including a complex for recreation and exercise of Seraidi [34]. |
| Bejaia | The city is located on the Mediterranean coast and its coast overlooking the bay in a scene high of beauty combines lush forests and sea water. Tourist services flourish there where swimming pools, beaches, and restaurants offering delicious meals from sea fruit [35]. |
| Tlemcen | The city is best known of being subjected and ruled by some many dynasties; such as, The Moravides, The Meridinides, and The Zianides. It contains some important tourist destinations which contain landscaped facilities and best quality services including: bathroom stations of Bougherara and shsiger for treatment with hot mineral water. There are also “Lourit” waterfalls with its fresh waters, in addition to several where several green oases and fertile plains [36]. Al Machwar Castle is a historical and archaeological site that shows the ancient successive civilizations in city of Tlemcen. It was set up by Yagmura Ben Ziane, the founder Al Ziaanide State, in the 12th century A. D. It was built with an authentic architecture and was an impregnable fortress palace of the Zianides rulers. The Castle is built on an area of 4 hectares, surrounded by fortified walls of five meters tall [36]. Another important site in the city is the Mosque of Sidi Boumediene who was a famous solemn in the twelfth century. His tomb remains one of the most attractive features of the visitors. The mosque was built with a pure architecture in the 14th century by the Black Sultan, Sultan of Fez, during the 2nd Meridinide invasion. Its minaret is decorated by brick and polychrome pottery of the Andalusian style [36]. |
| The Hoggar | It is located in the far South of Algeria. It is famous of its annual festival tourist area, which is a tradition that highlights the heritage and culture of the Sahara. This occasion has become attractive to many tourists who want to experience the airspace lively cultural and artistic activities, such as folk and camels‘ competitions. There is also, in the Hoggar, the ‗Alasekam‘ which is a famous passage is one of the nicest places for the tourists and especially for those who want to enjoy the unique scenery for sunrise and sunset there [37]. |
| Timgad | It is an ancient Roman city in Batna which was built by Emperor Tarjan in the year 100 A. D. so as to protect their people from the attacks of Aouras people. Tourists can notice its great organization and harmony of both economic and cultural life during the Roman era. The city currently holds the most important international and festival of Timgad [38]. |
Table 1: Major Algerian cities and their tourist potentials.
The Algerian coastline stretches on 1200 kms and is characterized as being high and containing rocks. It has some important touristic spaces; such as, El Kala (El Taref), Tigzirt(Bejaia), Sidi Fredj (Tipaza), Tnes (Chlef), Beni Saf (Ain Témouchent), Ain El Turk (Oran), and Mersa Ben M‘hidi (Tlemcen).
The highlands contain the Atlas Mountains of both Northern and Saharan areas. They contain such touristic areas as El Chréa and Tikejda Mountains. Since Algeria is a rich country with its fabulous nature and tourist capabilities, it is also rich in mineral springsabout 202 sites, which are characterized with therapeutic feature.
They are locayed in the North of Algeria. Among these, we can cite: Hamam Righa (Ain Defla), Hamam Bouhnifia (Mascrara), Hamam Righa (Ain Defla), Hamam Guergour (Setif), Hamam Es-Salhine (Médea), and Hamam Al Maskhoutine (Guelma).
The Algeria Sahara stretches over 2 million kms which comprises the regions of Adrar, Tindouf, Tamanrasset, Ourgla, and Ilizi. It is mostly characterized by camels‘ breeding, especially in Tindouf, Béchar, Laghouat, Ghardaia, Ouargla, Tamanrasset, Oued Souf, and Ilizi.
This practice is still inherited by the people of the countryside; they are greatly attached to it due to multiple reasons despite the changes of modern life sweeping the various aspects of life. For these inhabitants, it is a symbol of pride and prestige and related to the history and mysterious legends of the Sahara.
Camel is truly a useful animal. According to the traditions, camel‘s dander is always used for making beautiful traditional clothing style; such as Kachabiya, Gelaba, and Barnous that protect people against hard and bad weather in winter. Its skin is used in manufacturing some traditional tools and such as Gerba that is used for collecting drinking water to be cooled in the desert climate. Camel‘s meat is rich in vitamins and fat-free so that the residents use to cure some common diseases, including mullein hepatitis, and its hump serves in treating respiratory diseases and problems.
What is most significant in a camel is its milk. There has been found that camel’s milk has the following features. Regarding the chemical composition of camel's milk, it is similar to mother's milk. It contains a small amount of lactose (sugar‘s milk), saturated grease, and a large amount of vitamin C, Calcium, and iron, which makes it more appropriate for children who are not breastfed. Camel‘s milk protects the gums and strengthens teeth because it contains a large amount of vitamin C which helps to restore and protect the body's cells. It has been proven that the said milk is effective in the treatment of some diseases, such as, Tuberculosis, asthma, cancer, and anemia.
Algeria’s national parks: The total number of Algerian national parks 10 of which 8 are recognized in the north and occupies a total area of approximately 165 362 hectares. These parks contain prestigious, rare plants and animals, and thus they are subjected to strict protection by the authorities. They are built as reserves to protect the samples from the scenery, forests, plants and animals, and for the development of activities that have a relationship with nature, together with the investment in projects related to scientific research. We can cite here the three most important parks of:
• The National Park of Djurjura is a natural park located in the mountains of Djurjura in Tizi Ouzou, Northern Algeria. It was founded (18,500 hectares) in 1983 o as to be protected from extinction because it is one of the most beautiful tourist areas in Algeria, especially in winter because of the snow and the high peaks are filled with snow from September to May; as well as forested dense spaces, valleys, and lakes. The animals that the park contains almost exist in the national territory, and it is so varied and rich. There exists in the park a kind of a special bird in Algeria known as a Kabilyan nut breaker [39].
• The National Park of El Kala is one of the most attractive and magnificent protected areas in the Mediterranean Sea. It attracts many migratory birds in the winter, crossing the desert and the Mediterranean Sea. This ecological system of plants and animals has attracted the attention of local and international scientists a long time ago. The park was established in 1983 and is located in the north-eastern side of Algeria at 87 km from Annaba city. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, on the east by Tunisia, from the south by Souk Ahras city, and from the West by El Taref city.
• The park sits on an area of 76 438 hectares. Geographically, it is located between longitudes 36 and 43 north latitude and 08 and 37 to the east. The park contains 850 plant species, about 1/3 varieties of plants in Algeria. Among the plants, there is angiospermes, as well as a gemospermes. In addition to 30 species of ferns, there exist 100 species of fungi, and 40 species of algae, and 50 species of lichen. The said park is rich with diversity of animals, both vertebrates and invertebrates, such as, main legs ferry species (gasteropodes), as well as many legs (myriapodes). There are also 45 varieties of rare insects, 23 categories of amphibians, reptiles, and mammals [40].
• The National Park of Tlemcen was founded in May 1993. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea and Ain Temouchent city to the North, Sidi Bel Abbes city from the East; the Kingdom of Morocco from the West, and the city of Naama from the South. It is an area of approximately 8225.04 hectares and there is a project to extend it to 80,000 hectares. The park contains different kinds of oak trees, and there are about 850 categories of plants, including 22 protected, 31 original, 38 rare and 27 very rare. The park also contains about 174 animal species, including 49 protected like cheetah, squirrel, and hedgehog of North Africa. Also, it includes about 100 species of birds, including 38 protected; such as the Royal Eagle, Owl, and Wildcats, and about 18 species of reptiles, and 33 species of insects [41].
Algeria’s national feasts: Algeria's local feasts, in all regions, reflect the country’s enjoyment throughout the year. From north to south, each region celebrates its own feast with lot of happiness. There are about 256 feats held annually across the different regions of the country. The most important ones are (Table 2):
Tavissit Feastival |
It is held in Tamanrasset where the residents of the Hoggar meet for three days to celebrate the coming of spring in a varied festive atmosphere. Folkloric reviews are being organized through the city main streets, and many locals and foreigners are frequently participating in this feast where traditional crafts occupy a special place. Also, fashion shows, selecting "Miss Hoggar", and the best “Targui” are organized in this day [42]. |
| Sabibah Feast | It is held in Djanet, the capital of the Hoggar, during the religious day of Ashura. The Touareg meet to renew the peace agreement which they held for almost three thousand years, and to re-new their alliances. During the celebration, the celebrants represent scenes of fighting, the mouthpiece of the last battle preceding the peace holding, and permeate these songs reviews and joy reluctance of women to encourage the belligerents [44]. |
| Al Mawlid Al Nabawi Feast | It is held in Timimoun, South of Algiers, to celebrate the birth of Prophet Mohammad (PBUH). The celebration lasts for seven days, and on the last day, people from the nearby villages meet in the Zawiya of Sheikh Haj Belkacem in which they raise the banners, sing popular songs, settle disputes, and hold new alliances [42]. |
| Waada of Sidi Ahmed Al Majdoub | It is held in the end of the second week of October in Asla village, situated in Naama city, in memory of the holy man Sidi Ahmed Majdoub who lived in the fifteenth century in the region. The Majadbh tribe celebrates this feast to preserve the customs and traditions where couscous is served for all the invitees. During the ceremony, knights’reviews are held, poetry competitions are celebrated, and a huge trade fair, containing lot of goods, is made [42]. |
| Knights Omdukal Festival | It held in Aures region during the first weekend of May in the palm trees and palaces of the city of Omducal. During this feast, the region witnesses the signed reviews of horsemen dressed in traditional costume and viewing beautiful horses. During the three days of this feast, traditional songs, such as Issa Jermoni‘s, are being sung and traditional poetry competition is being held [43]. |
| Silver Aith Winnie Festival | It is held from 27 July to 4 August of each year in the village located in Djurjura region. Women of this region wear their silver jewelry decorated with coral and painted yellow, green, and blue. This tribal jewelry has won several awards in Canada and the United States [42]. |
| Coral Festival | It is held in El Kala city where fishermen, artisans, and merchants meet in the Coral Feast in August. Algerian coral, which is synthesized immediately after fishing, is import- oriented. The latter is best known for its quality and scarcity of pink colors [42]. |
| Strawberry Feast | It is held in May 23- 4 in the city of Skikda [42]. |
Table 2: Algeria’s national feasts.
How can ICT be a veritable tool for sustainable tourism development in Algeria?
Information and communication technology is a driving force in the current information driven society. It facilitates trading partnership with other industries, provide facilities, distribution of product and services, provide information online to consumers in order to plan their trip, create a new business environment and also help tourism professionals to define the boundaries of the proposed tour site and its surroundings. It gives information on weather, altitude and other information to pilot on board. It helps tourist on air to communicate during emergency and also to other pilot on airplanes with traffic control station. Information is very important at every stage in the sales cycle of the tourism product [44]. Information must be able to flow quickly and accurately between the client, intermediaries and each of the tourism suppliers involved in servicing the client‘s need.
The amalgamation of computer and telecommunications has become an almost universal feature of the tourism industry [45]. Its power allows information to be managed more effectively and transported worldwide almost instantly [46]. As a result, it had and continues to have a major effect on the methods of operation in the tourism industry. However, it has not affected all functions and sectors equally. As Poon (2003) pointed out, it is having the greatest impact on the marketing and distribution functions. Airlines use technology to manage and streamline their operations and gain strategic advantage. Information technology has reshaped our commerce and society in general [47]. Goods and services are provided to the consumers online (e-commerce, e-governance, ebanking) to mention but few.
McGuffie asserted that tourism enterprises need to understand, incorporate and utilize ICT strategically in order to serve their target markets, improve their efficiency, maximize profitability, enhance services and maintain long-term profit [48].
As far as Algeria is concerned, it is still, like most Arab countries, suffering from a lack of tourists due to several reasons; such as, security problems, poor technological Telecom Infrastructure, and the banking financial system is still crisp and closed; these are causes are weakening tourism in Algeria, as indicated by reports of World Tourism Organization.
Within the Algerian web tourism portal, there are a number of sites, belonging to both public and private sector, including the leading tourism portal called ‗www.algeriantourism.com‘ which provides direct contacts and bookings with several travel agencies, airlines, and hotels. The website also displays all the information relating to tourist trips organized successively in Algeria. Moreover, the National Office of Algeria (ONAT) provides information about tourist sites classified by UNESCO. It also contains contact information of national tourist agencies, and to other tourist enterprises in the country- hotels, restaurants, camps, museums, and tourist hangars. However, despite all these information, the web portal is not dynamic and lacks interactivity and linking the various actors in the tourism sector, especially hotels, and travel agencies.
According to international reports, Algeria has recorded the lowest percentage of the tourist destinations in the Mediterranean countries in the year 2006, despite the availability of multiple tourist areas of coastal, mountain, and Saharan nature. Algeria also counts for capabilities represented in the important traditional industry which give a strong boost to the tourism sector. So, in order to improve the Algerian tourism sector, the authorities have to improve the security situation, which is considered the most important factor to bring tourist internally and externally, in addition to the rehabilitation of the labor force in the sector, and work to raise awareness and promote using various means of ICTs to be made available for tourists. So, the application of information technology and communication has a crucial, effective impact in improving the tourism industry in the country. Through ICT, we can communicate directly with tourists, provide them with information and tourist offers, and enable them with the possibility of both online booking and payment.
This is a non- experimental and explorative study, which focuses on Information and Communication Technology (ICT) with particular concern on its effects on tourism development in Algeria. The main aim of this work is for appreciation of how ICT and tourism influence one another. On the other hand, it also hopes to highlight the need for stakeholders in tourism to take this rampaging technology into cognizance and see the need to harness it for sustainable tourism in the country. Specific attention is being focused on internet-based Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs).
Al Djazaer Siyaha: A proposed model for improving information and tourist services’ quality in the eTourism industry: eTourism comprises a number of services provided by information and communication technology for the completion and promotion of tourism services and hotel across different networks, depending on the principles and foundations of e-commerce. In fact, the term goes further to include tourism mobile (m-tourism) that is used for electronic devices; such as, mobile phones. Thus, ICTs have been exploited in the construction and establishment of tourist entities which require a certain degree of technological know- how knowledge of patrons [49].
It contributes in a large volume to the electronic commerce where profits in this sector have exceeded $ 89 billion in the world in 2004. In France, for instance, e-tourism reached 45% in 2005 of the e-commerce volume. According to reports of the Arab Tourism Organization, 40 percent of the total numbers of tourists, globally 938 million tourists, have used electronic tourism services to either inquire or purchase travel and reservation services. The number of visitors to Orbitz.com amounted to 35 million, Yahootravel.com 80 million visitors, and expedia.com 50 million visitors.
Besides, it acquires 24% of the proceeds of various online electronic ads. According to Forrester Research, the e-tourism revenues of air and maritime travel tickets, online hotel reservations, and car rental for the year 2008 reached $ 32.8 billion, compared to $ 16.4 billion in hotels revenues [50].
Taking into account these data about the importance of e-tourism in promoting the tourism industry in Algeria, the authorities should be aware of the necessary use of ICT in tourism sector to improve tourism and make a dynamic sector in the economy. Therefore, Algeria should develop an eTourism Framework (e-TF) which is a market driven project with a balanced consortium of ICT professionals and tourism professionals whose expertise allows analyzing market needs, issue jobs and tourism training guidelines.
In order to fulfill the needs and demands of foreign tourists who intend to visit Algeria, the proposed model of Al Djazaer Siyaha (Algeria Tourism), which is an eTourism Internet program, must consider all relevant touristic factors. The proposed model for eTourism is divided into two sections. The first comprises web portal with online business services provided by the Ministry of Tourism, tourist agencies, and tourist enterprises to foreign tourists. The second section contains five variables of information quality leading to tourists’ satisfaction and trust of the tourist online services. The Figure 1 below illustrates the proposed model.
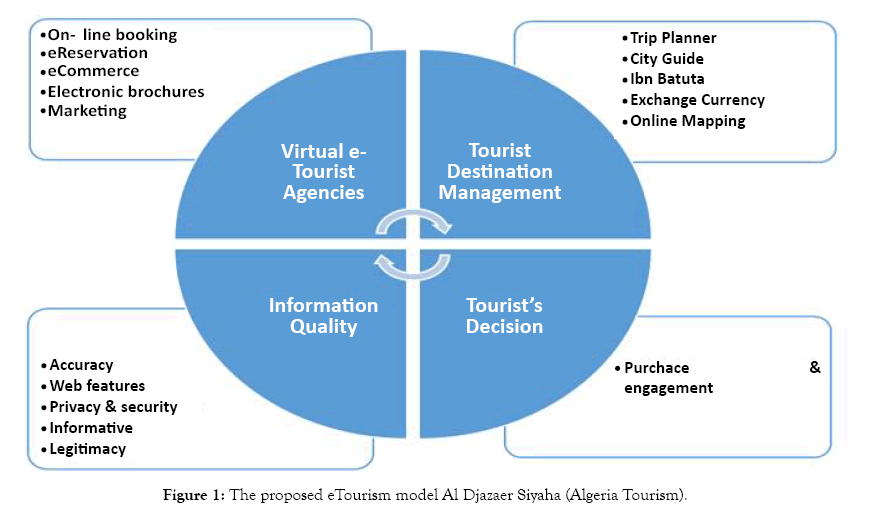
Figure 1: The proposed eTourism model Al Djazaer Siyaha (Algeria Tourism).
As seen above in the figure, the web program acts as tourist product provider. Tourist agencies exist primarily as intermediaries between suppliers of travel services; such as, airlines and hotels, and customers. The way of doing business in the tourism industry has been changed dramatically due to the development of information technology [51]. The rapid growth in the size of the e-travel service business is clear evidence of this. The Internet has become one of the most important platforms for travel-related service entrepreneurs to provide services and communicate information with their target customers. The number of travel-related websites has grown rapidly during the past decade, and the competition has become more intensive than ever. To survive, or even succeed, entrepreneurs need to be customer-orientated. An e-service company should see things through customers’ eyes, realize their needs, and design an online service system that can meet customers’ expectations [52].
For instance, ICTs have revolutionized the business of travel in Spain. Booking 5.8 billion euros ($ 7.9 billion) in online reservation in 2008, virtual travel agencies accounted for roughly one-third of the overall travel sector's revenues. Rather than losing ground during the economic downturn, online agencies managed to maintain revenue growth, albeit at a modest 2.7%. The data for virtual travel agencies in Spain are very positive: More than half of the money spent on travel and hotel reservations is via Internet transactions, according to a 2008 report by DBK, a consulting firm. In addition, 53% of people are buying online reserve their travel, lodging and tickets for special events [53].
In Algeria, traditional tourist agencies should make investments relating to technologies to ensure their long-term strategic viability. Besides, since traditional tourist agencies have created unique values on their significant co-specialized assets and provision of value-added services for customers, thus competitors or new entrants might not be able to follow these.
A) Virtual eTourist agencies
Al Djazaer Siyaha provides tourist agencies with several business approaches to get on the Internet:
• Alliance with technology provider: This is a one-stop solution for those traditional tourist agencies without any experience in electronic commerce technology. eCommerce applications will be developed by one technology provider. This enables tourist agencies to acquire the most desirable ICT assets, and then combine them with their own expertise assets for assuring the success of its online products.
• Portfolio partnering: One technology provider may not be able to suit the needs of a tourist agency, especially for those who have various range of products and business in global market. In this case, it is more flexible to have partnership with different technology providers to get all the advantages of their IT assets.
• Develop eCommerce technologies: Traditional tourist agencies may invest to build their own electronic commerce technologies, and get patent on it.
• Develop interactive virtual e-tourist agencies in Algeria with useful services such as:
a) Photos: In the virtual web site, the travel agency should post much updated photos about the country: tourist sites, places of destinations that the Algerian e-tourist agencies tend to transport tourists to. This will promote eagerness in in both foreign and domestic tourists to travel and see the magnificent tourist places.
b) Webcasts: A webcast is a media presentation distributed over the Internet using streaming media technology to distribute a single content source to many simultaneous listeners/viewers. A webcast may be distributed either live or on demand. Essentially, webcasting is―broadcasting over the Internet. The Algerian e-tourist agencies should benefit from this streaming technology by posting live videos about the different tourist locations and sites in Algeria as way of introducing the country to tourists. The videos should not only focus on the geographical sites, but also should include customs and traditions, such as marriage, wedding, fiancée and festival celebrations. However, the videos should not only concentrate on these customs and traditions, but should also focus on other tourist potentials in Algeria; such as, national parks discussed above and the different activities that can be practised there so that to fully attract the visitors and introduce the culture of the country. These videos will attract most tourists.
c) Electronic brochures: Electronic brochures provide the ideal mechanism for delivering detailed information via e-mail and the Web. They are especially useful for providing more comprehensive information than you might want to show on a Web page. Electronic brochures have many advantages, including:
• Design fidelity is maintained across computer platforms.
• Information is delivered to customers instantly.
• Recipients can view or print documents.
• Your printed branding standards are fully maintained.
• Electronic brochures can be indexed by most search engines, extending their reach and value.
As far as Algerian e-tourist agencies, they should give more importance to electronic brochures. These should include every information regarding the services- provided by the tourist agency, tourist sites, and activities in Algeria to make tourists more interested in visiting our country.
d) eBookings and eReservations: eBooking means making a reservation for a service via the Internet. It is also known as computer reservations system which is used to store and retrieve information and conduct transactions related to travel. Algerian e-tourist agencies can benefit from the eBooking system to help tourists book for their airline tickets or for their hotel reservations. So, via eBooking system, they should rely on data base information of gateways for airlines, hotel, rental cars, and other services as well as airline tickets so that consumers will be accessible. Through this online system, tourists can interact with the travel agent, book online, and pay online also and get the receipt of their payment. They can pay online through credit cards, or through money transfer system.
B) Tourist destination management
A local tourism destination is a physical space in which a visitor spends at least one overnight. It includes tourism products; such as, support services and attractions, and tourism resources. It has physical and administrative boundaries defining its management, images and perceptions defining its market competitiveness. Tourism destinations incorporate various stakeholders, including a host community, and can nest, and network to form larger destinations.
Buhalis defined the term as “... a unique entity, with a political and legislative framework for tourism marketing and planning” 53. Tourism destination management systems are considered to play an increasingly important role in achieving and maintaining tourism sustainability. Tourism destination management can be regarded as a collection of multi-agent processes involving a wide range of stakeholders. It can apply many techniques, strategies and processes to shape the development and daily operation of tourism related activities. In the context of Al Djazaer Siyaha, the Algerian eTourism web program, tourism destination management can provide foreign tourists with various methods and applications to organize their trips successfully. These can be cited below as follows:
a) Trip planner: This tool has been available on the web since 1998. When used in Al Djazaer Siyaha, it offers foreign tourists with immediate pricing for complex international itineraries without rule restrictions, limited standard routes or the need to articulate dates for every flight on your trip while you are in the planning stage. In addition, Trip Planner helps tourists with the ability to organize their trips by assembling database of special services and fares available exclusively and offered by tourist agencies. This; in fact, creates a competition between tourist agencies to attract most of foreign tourists. Meanwhile, foreign tourists will find it easier to plan their trips, while visiting Algeria, in collaboration with tourist agencies.
b) City guide: It is a book of information about a place designed for the use of visitors or tourists. In the case of the Algerian eTourism web program, City Guide usually includes information about sights, accommodation, restaurants, transportation, and activities. Maps of varying detail and historical and cultural information are often included.
c) Ibn Batuta: Working as tourist guides in tourist agencies, they are made visible, through their online profiles, to foreign tourists. In case a foreign tourist needs a tourist guide for his tour in Algeria, it is up to him to choose one from the list the most available, appropriate, and convenient to him. In this case, Ibn Batuta. i. e. the tourist guide, chosen by the foreign tourist will assume the success of the trip through his knowledge and management skills.
d) Exchange currency: As foreign tourists need money to exchange in the visiting country, the web program will provide them with this ability through daily updates of currency exchange.
e) Online mapping: Algerian e-tourist agencies should also focus on online mapping which is a way of using maps online to provide a number of functions. They should provide maps about locations of the different tourist sites, their locations, the roads, the cities, the villages, and places of different activities conducted. They should turn to the Internet for more personalized information. So, through online mapping, tourist agencies will be able to make maps for individuals based on their particular needs. Thus, the map is much more than a graphic of roads; it is a custom-made printing specifically based on a desired route.
C) Information quality
There are five crieteria that comprise the information quality level of Al Djazaer Siyaha, eTourim Web Program, to determine its validity. These are as follows :
• Accuracy: It is an important principle in tourism industry that promotes trustworthiness, honesty, sincerity, and truthfulness. Information accuracy depends on content reliability and validity, which leads to users’ trust on the web program.
• Web features: The use of web design, functions, and languages improves the usability of the website that attract users. The graphic used, colors, the way information arranged in the website are the important elements that can attract visitors; in addition to the design that should represent the content’s theme. It should be interactive, have easy navigation features, and promote relevant hyperlinks to motivate users, and; therefore, lead to engagement decision. Therefore, the Djzaer Siyaha should be of a quality, a very good structure, interactive, provide search engine with quick option and downloadable audio, video, and documents. In addition, it should support visitors with customer oriented decision support system to help them make choices to increase the success of the business.
• Privacy and security: Customer has right to ensure that data that provided to the e-tourism website while performing any transaction are protected from any potential harm. Privacy policy, information protection policy, clear payment and refund procedures must be included in the website in order to gain visitors’ trust.
• Informative: Customer purchase and engagement decision should be enhanced by the fact that quality of the information contains all necessary information and linked to the relevant source of information. The information must be up-todate, complete and useful to the web visitors.
• Tourist decision (purchase and engagement): Tourist decision in e-commerce is highly depending on the information quality of the website. Therefore, the aforementioned factors of information accuracy, web features, security and privacy, and informative characteristics will directly influence tourists’ decision in eTourism web portal.
ICT evolves constantly by providing new tools for improving the tourism industry. It promotes interactivity between tourism enterprises and consumers, and as a result, it contributes in developing, managing, and marketing tourism products. This paper has discussed the situation of Algerian tourism and proposed ways of improving sustainable tourism in the future. The key change resides in investing and exploiting the huge potentials of ICT by Algerian tourist agencies to improve tourism industry and turn it into a productive sector. Through ICT, tourist agencies can be in full interactivity with tourists: providing them with data and special offers, and helping them with eBooking and online payment. Tourist facilities through the internet are useful to tourists and help them to better plan for their trips.
Therefore, ICT will raise opportunities and provide huge advantage for tourist agencies to enhance their innovation and competitiveness; the future of eTourism will be focused on ICT that will enable organizations to focus on their profitability through a network of partnerships. Therefore, ICT will bring some important changes in the tourism industry such as:
• eTourism will replace traditional tourism
• tourists will give more importance to eBookings and eReservations
• Interactive multimedia will be the key element in tourism marketing
• Webcasts and electronic brochures will raise eagerness in tourists and motivate them to organize tours to visit the different tourist sites and destinations they saw in live cameras.
• Tourist products will be available online through ICTs.
• ICTs will raise competitiveness among tourist agencies in Algeria in providing the different services and the best special offers.
Citation: Guemide B, Benachaiba C, Maouche S (2019) Integrating ICT- Based Applications for Sustainable Tourism Development in Algeria. J Tourism Hospit 8:415. doi: 10.35248/2167-0269.19.8.415
Received: 03-Sep-2019 Accepted: 30-Oct-2019 Published: 06-Nov-2019
Copyright: © 2019 Guemide B, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.