Poultry, Fisheries & Wildlife Sciences
Open Access
ISSN: 2375-446X
ISSN: 2375-446X
Mini Review - (2021)Volume 9, Issue 8
Coronavirus which is an infectious disease commonly called as COVID-19 causes illness in the respiratory system in the humans. It is the new virus that is Impact in the whole world badly or it is spreading primarily through contact with the person. Every segment of the society is going to remember this year. In 2020, all this time I remember reading a quote by ‘Alvin Toffler’ that "Technology is a great growing engine of change". Well, during this pandemic there is no need of a further explanation of this remark. It has overwhelmed the entire world and India also has borne the brunt of the same. The Spread was so colossal that WHO had to declare it as a pandemic.
Coronavirus; Pandemic; Technology; Lockdown
"Silver coating of a destructive pandemic" this sounds like a confusing expression, however it's actual with regards to Coronavirus. Despite the fact that the Coronavirus pandemic has unleashed destruction all throughout the planet and carried the world economy to a close to stop, there is one angle on the planet where it's having a positive effect on climate. During the Coronavirus lockdown, pictures of the Himalayas being noticeable from Punjab and the more clear waters in the channels of Venice became famous online via web-based media. Recordings of creatures like deer, mountain goats, peacock and surprisingly wild felines meandering through the abandoned roads in metropolitan regions were likewise various. Because of limitations in fishing exercises, dolphins were accounted for to have come much nearer to shore than they had already. Nature has been the large champ during the Coronavirus pandemic.
COVID has become overall sickness and all countries of the world are confronting it. Because of which populace of the world is compelled to live inside their home. Business exercises in the nation additionally influenced because of COVID. As a we whole know COVID has taken existence of a many individuals all over the globe. To forestall the spread of COVD-19, legislatures of various countries are finding a way numerous ways to control the spread of this infection. Taking everything into account, it is appreciating the positive effect of this infection. Before the beginning of the Coronavirus pandemic, the air around us had been considered extremely poisonous to take in because of the measure of ozone harming substances that had been produced throughout the long term. The Earth confronted rising temperatures, which thusly prompted the softening of icy masses and ascending of ocean levels. Natural corruption was occurring quickly because of the exhaustion of assets like air, water and soil.
However, after the COVID lockdown initiated, there have been slight changes in the climate. After the lockdown was set up in numerous nations, there was lesser voyaging done by individuals, regardless of whether it be by their own vehicles, or via prepares and flights. Indeed, even businesses were shut down and not permitted to work. This thusly prompted the contamination noticeable all around dropping essentially, as there was a stamped decrease in nitrous oxide outflow. Again where fish is concerned, the lockdown has seen a decrease in fishing, which implies that the fish biomass will increment after over-fishing nearly drained it. Despite the fact that COVID-19 does not damage fish and is not caused by fish eating, the fish industry is nevertheless vulnerable to indirect effects of the pandemic due to changing customer expectations, market access, or logistical issues linked to shipping and border restrictions. This, in turn, will have a negative impact on the livelihoods of fishermen and fish growers, as well as on food security and nutrition. The FAO (Fisheries and Aquaculture Department) created a COVID-19 Task Team to coordinate Departmental activities in response to the pandemic and offer coordinated assistance to measures and interventions addressing the effect of COVID-19 on fisheries and aquaculture. This team's communication and information sharing is one of its functions. Aside from that, creatures have been spotted moving about openly where once they would not challenge to go. Indeed, even ocean turtles have been spotted getting back to regions they once kept away from to lay their eggs, all because of the need human obstruction. Today, when the creation of nearly everything is on the end and producing plants are no longer as dynamic as they used to be, the emanation of smoke has decreased which has brought about clear sky. Not just this, the usage of vehicles on the street is diminished. This has contributed towards brought down CO2-outflows. The emanation of nitrogen dioxide has likewise decreased. Plants are becoming better in light of the fact that there is cleaner air and water, and in light of the fact that once more there is no human impedance. With everything at a halt, plants are permitted to flourish and develop and create more inclusion and oxygen. Less litter additionally implies lesser obstructing of stream frameworks, which is acceptable over the long haul for the climate. To battle COVID, organizations have requested that labourers telecommute. This has decreased vehicles on street. Moreover, the utilization of plastic has additionally decreased as individuals at this point don't have tea or espresso in expendable glasses (Figure 1).
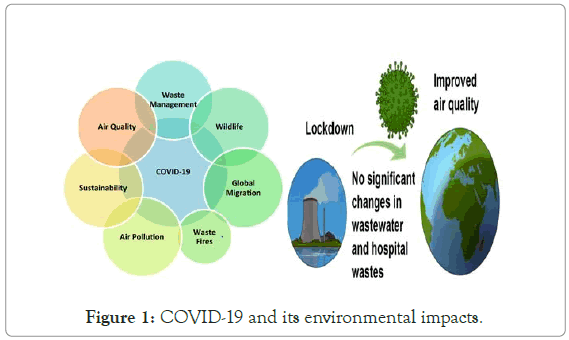
Figure 1: COVID-19 and its environmental impacts.
Food is not responsible for the disease's spread to humans. The World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Organization for Animal Health (OIE) both believe that the COVID-19 pandemic is being sustained through human-to-human transmission rather than international commerce in animals and animal products. Currently, there is no proof that individuals can get COVID-19 through food. Lockdown and physical separation tactics have disproportionately harmed disadvantaged small-scale and artisanal workers and communities in developing nations with substantial informal sectors. Many of these employees do not belong to producer groups that represent their collective interests, making it difficult to obtain government assistance. Coverage of the fisheries and aquaculture sectors is adequate. Since the episode of COVID-19, clinical waste age is expanded universally, which is a significant danger to general wellbeing and climate. For test assortment of the suspected COVID-19 patients, conclusion, therapy of colossal number of patients, and sterilization reason bunches of irresistible and biomedical squanders are produced from clinics [1]. For example, Wuhan in China created in excess of 240 metric huge loads of clinical burns through consistently during the hour of the episode, which is just about 190 m tons higher than the typical time [1,2]. To shield from the viral contamination, as of now people groups are utilizing face cover, hand gloves and other security hardware, which increment the measure of medical services squander. It is accounted for that, in USA, rubbish sum has been expanding due to expanded PPE use at the homegrown level. Since the flare-up of COVID-19, the creation and utilization of plastic based PPE is expanded around the world. In any case, because of absence of information about irresistible waste administration, the vast majority dump these (e.g., face cover, hand gloves and so on) in open spots and at times with family squanders. Increment of city squander (both natural and inorganic) age has immediate and roundabout consequences for climate like air, water and soil contamination. Because of the pandemic, isolate strategies set up in numerous nations have prompted an increment in the interest of internet looking for home conveyance, which at last increment the measure of family squanders from sent bundle materials [1]. Be that as it may, squander reusing is a viable method to forestall contamination, save energy, and save normal assets [3]. Yet, because of the pandemic numerous nations delayed the waste reusing exercises to diminish the transmission of viral disease (Table 1) [1,2,4-10].
| Authors | Purpose | Sample | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data 1: COVID-19 and the environmental degradation | |||
| Zambrano-Monserrateet al.(2020) | To study the indirect effect of COVID-19 on the environment | China, USA, Italy, and Spain | a. COVID-19 improved air quality, beaches and reduced noise levels. b. It increased the bulk amount of domestic and medical waste and reduced initiatives to recycle waste. c. GHGs reduction is for a shorter time period. |
| Saadat et al. (2020) | To explore the environmental aspect of COVID-19 | Global | a. Improve air and water quality worldwide. b. Generate bulk amount of medical waste. |
| Chakraborty and Maity (2020) | To examine the consequences of COVID-19 on environment and society | Global | a. COVID-19 helps to recover the environment and create a positive effect on the environment. |
| Data 2 : COVID-19 and climate/meteorological factors | |||
| Qi et al. (2020) | To examine the influence of metrological factors, such as temperature and humidity on COVID-19 cases | 30. Chinese provinces | a. Significant negative influence of temperature and humidity on daily cases of COVID-19. b. Interaction effect of temperature and humidity is robust in case of daily COVID-19 cases. |
| Sobral et al. (2020) | To explore the impact of meteorological factors on COVID-19 transmissions | International sample | a. Negative relationship between temperature and COVID-19 transmission. b. Positive relationship between precipitation and COVID-19 transmission. c. Countries that have higher rainfall experience an increase in COVID-19 transmission. d. There is no relationship between temperature or precipitation on COVID-19 mortality. |
| Data 3: COVID-19 and air pollution | |||
| Abdullah et al. (2020) | To examine the impact of MCO of Malaysia on air quality | Malaysia | a. Find a significant influence of MCO of Malaysia on reduction of PM. |
| Dantas et al. (2020) | To consider the consequences of partial lockdown of COVID-19 on air quality | Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | a. CO decreases significantly during lockdown period. b. NO2 decreases due to lockdown. c. PM reduced to a low level. d. O3 increased due to reduction in NO2. |
| Tobías et al. (2020) | To inspect the air pollution level of Barcelona during COVID-19 lockdown | Barcelona, Spain | a. NO2 and BC reduced by 50% during lockdown. b. PM reduced. c. O3 increased by more than 50% during lockdown. |
Table 1: Summary of articles in research data [1,2,4-10].
So for the better conservation of our Mother Nature we can do and conduct many things, first and foremost everything in a sustainable manner.
Sustainable industrialization
Industrialization is crucial for economic growth and also for a wealthy nature.
To reduce the emission of carbon to the atmosphere, use bicycle in a short distance travel, and public transport systems.
Properly treat both municipal and industrial waste water before introducing into the main water sources.
Waste recycling and reuse, make compost from food waste, prepare time-oriented policies, arrange international conventions (Figure 2).
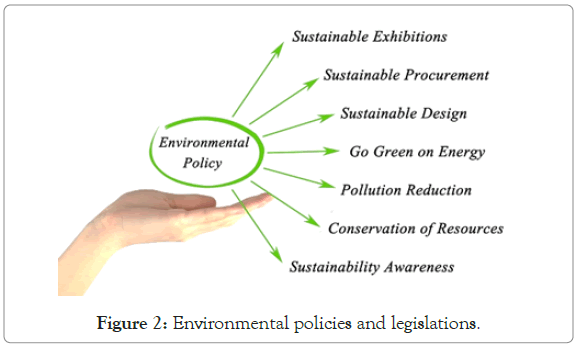
Figure 2: Environmental policies and legislations.
Despite the fact that the beneficial outcome the lockdown has had on the climate may not keep going long, it is still educational to perceive how people have abused nature and the manner in which Mother Nature attempts to recuperate when people let her be for quite a while. Ideally, world pioneers, tree huggers and strategy producers have seen the inspiring visuals of nature recovering during the lockdown and will attempt to find more grounded ways to secure the climate later on. The COVID-19 pandemic is a threat to human society, both for risking human life ensuring economic distress and for its invisible emotional strains. Definitely these changes can be reversed with a long run only. Because we are human beings, once you face a fearful condition, it is difficult for us to return to the original state easily. May be for a few people only, I think, but it's a fact. Well, anyways take COVID-19 era as an opportunity to grow, learn and advance in every way, especially in the shopping industries. Every coin had two faces, with the bad comes the good we are a race of survivors, and we're going to win this too.
Author wish to thank the family members and Department of Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies, Panangad, 682506 Kerala for giving the essential facilities, and their thoughtful support and direction throughout the investigation.
There is no funding source available.
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Citation: Ajay VS (2021) Impact of COVID-19 on Environment: Reimagine, Recreate, Restore our Mother Nature: A Critical Review. Poult Fish Wildl Sci. 9:221.
Received: 09-Aug-2021 Accepted: 23-Aug-2021 Published: 30-Aug-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/2375-446X.21.9.221
Copyright: © 2021 Ajay VS. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.