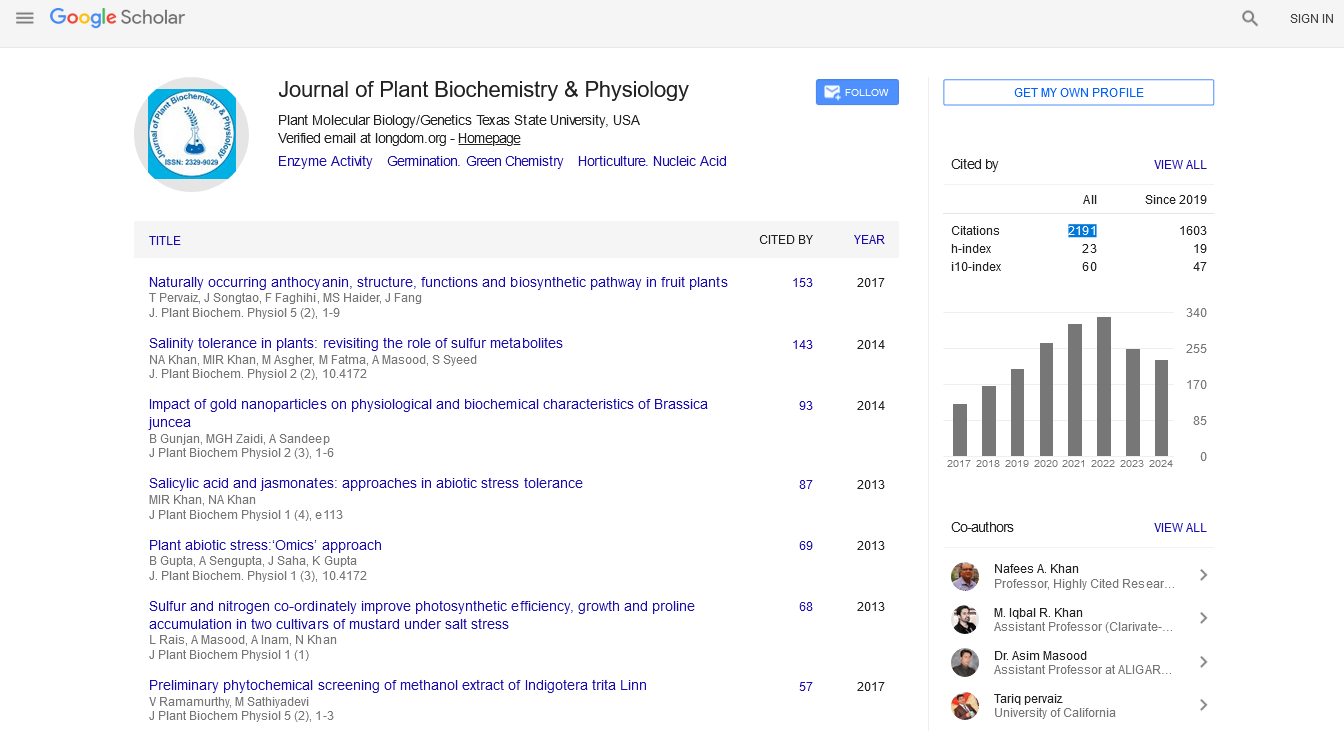
Journal of Plant Biochemistry & Physiology : Citations & Metrics Report
Articles published in Journal of Plant Biochemistry & Physiology have been cited by esteemed scholars and scientists all around the world. Journal of Plant Biochemistry & Physiology has got h-index 29, which means every article in Journal of Plant Biochemistry & Physiology has got 29 average citations.
Following are the list of articles that have cited the articles published in Journal of Plant Biochemistry & Physiology.
| 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Total published articles |
44 | 30 | 60 | 36 | 14 | 17 | 23 | 29 | 11 | 24 | 30 | 35 |
Research, Review articles and Editorials |
10 | 4 | 32 | 13 | 2 | 17 | 23 | 28 | 6 | 23 | 28 | 29 |
Research communications, Review communications, Editorial communications, Case reports and Commentary |
0 | 26 | 24 | 23 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
Conference proceedings |
15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Citations received as per Google Scholar, other indexing platforms and portals |
219 | 254 | 327 | 314 | 269 | 208 | 166 | 123 | 128 | 101 | 39 | 0 |
| Journal total citations count | 2191 |
| Journal impact factor | 4.25 |
| Journal 5 years impact factor | 5.03 |
| Journal cite score | 4.78 |
| Journal h-index | 29 |
| Journal h-index since 2019 | 19 |
Important citations (595)
drought and salinity alter endogenous hormonal profiles at the seed germination phase |
|
the intricacy of silicon, plant growth regulators and other signaling molecules for abiotic stress tolerance: an entrancing crosstalk between stress alleviators |
|
plant-microbe interactions in adaptation of agricultural crops to abiotic stress conditions |
|
acetylsalicylic acid enhance tolerance of phaseolus vulgaris l. to chilling stress, improving photosynthesis, antioxidants and expression of cold stress responsive genes. |
|
the difference in n metabolism between nad(p)h-specific nr-deficient mutant and wild-type barley (hordeum vulgare l.) |
|
sulfur nanoparticles mediated improvement of salt tolerance in wheat relates to decreasing oxidative stress and regulating metabolic activity. |
|
photosynthetic differences in mustard genotypes under salinity stress: significance of proline metabolism |
|
mycorrhizal fungi and thiobacillus co-inoculation improve the physiological indices of lallemantia iberica under salinity stress. |
|
photosynthetic and cellular responses in plants under saline conditions |
|
interplay between selenium and mineral elements to improve plant growth and development |
|
evaluating the importance of proline in cadmium tolerance and its interaction with phytohormones |
|
coordinated role of nitric oxide, ethylene, nitrogen, and sulfur in plant salt stress tolerance |
|
antioxidant enzymatic activities and growth response of quinoa (chenopodium quinoa willd) to exogenous selenium application |
|
ethylene supplementation combined with split application of nitrogen and sulfur protects salt-inhibited photosynthesis through optimization of proline metabolism and antioxidant system in mustard (brassica juncea l.). |
|
it takes two: reciprocal scion-rootstock relationships enable salt tolerance in 'hass' avocado. |
|
modified gold nanoparticles for efficient delivery of betulinic acid to cancer cell mitochondria. |
|
sulfur-mediated control of salinity impact on photosynthesis and growth in mungbean cultivars screened for salt tolerance involves glutathione and proline metabolism, and glucose sensitivity |
|
salicylic acid changes morpho-physiological attributes of feverfew (tanacetum parthenium l.) under salinity stress |
|
the key roles of salicylic acid and sulfur in plant salinity stress tolerance |
|
green synthesis of sulfur nanoparticles using ocimum basilicum leaves and its prospective effect on manganese-stressed helianthus annuus (l.) seedlings |
|