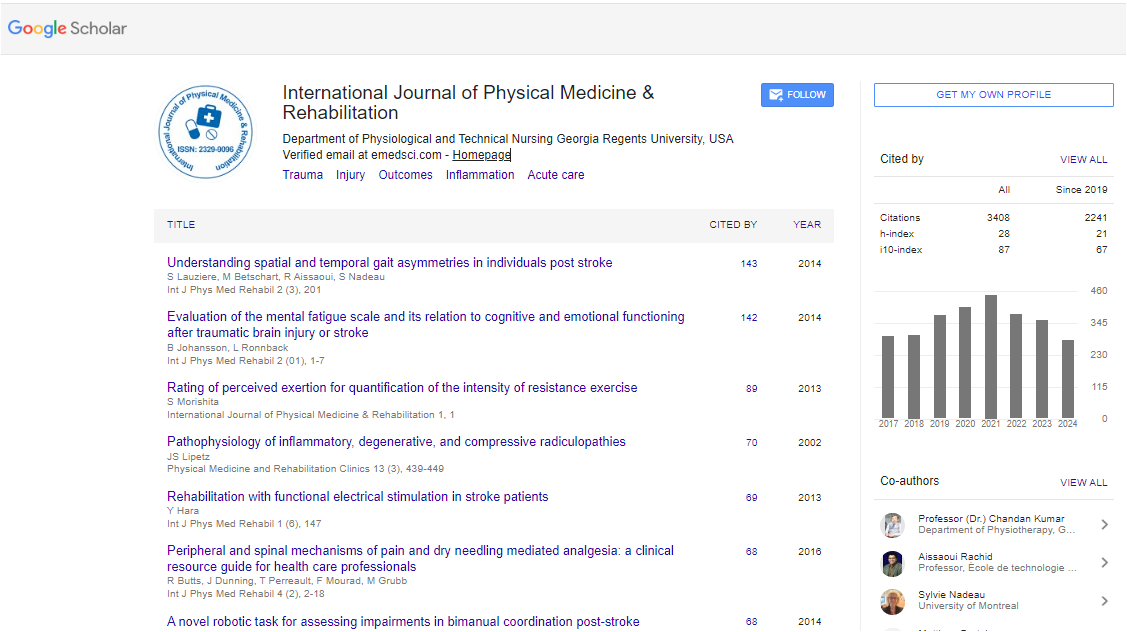
International Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation : Citations & Metrics Report
Articles published in International Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation have been cited by esteemed scholars and scientists all around the world. International Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation has got h-index 28, which means every article in International Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation has got 28 average citations.
Following are the list of articles that have cited the articles published in International Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.
| 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Total published articles |
60 | 58 | 58 | 84 | 71 | 40 | 59 | 63 | 75 | 68 | 83 | 86 |
Research, Review articles and Editorials |
17 | 29 | 51 | 82 | 58 | 22 | 48 | 52 | 58 | 50 | 72 | 53 |
Research communications, Review communications, Editorial communications, Case reports and Commentary |
29 | 29 | 8 | 2 | 13 | 18 | 11 | 11 | 17 | 18 | 11 | 33 |
Conference proceedings |
0 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 11 | 17 | 0 | 43 | 67 | 71 | 79 |
Citations received as per Google Scholar, other indexing platforms and portals |
291 | 359 | 381 | 445 | 400 | 375 | 303 | 296 | 240 | 124 | 57 | 16 |
| Journal total citations count | 3422 |
| Journal impact factor | 2.90 |
| Journal 5 years impact factor | 5.75 |
| Journal cite score | 5.25 |
| Journal h-index | 28 |
| Journal h-index since 2019 | 21 |
Important citations (390)
Pharmacoeconomic analysis of cellex® in the treatment of ischemic stroke |
|
Pharmacoeconomic analysis of cellex® in the treatment of ischemic stroke |
|
Pharmacoeconomic analysis of cellex® in the treatment of ischemic stroke |
|
Pharmacoeconomic analysis of cellex® in the treatment of ischemic stroke |
|
Clinical and psychosocial predictors of exceeding target length of stay during inpatient stroke rehabilitation |
|
Predictors of depression after stroke: a systematic review of observational studies |
|
Running to breaking point? the relationship between 1.5-mile run time and injury risk in female recruits during british army basic training |
|
Prevalence of musculoskeletal injuries in new zealand army recruits as defined by physical therapy service presentations. |
|
Epidemiology and financial burden of musculoskeletal injuries as the leading health problem in the military |
|
Using causal energy categories to report the distribution of injuries in an active population: an approach used by the u.s. army. |
|
Renovo: a sensor-based therapeutic system for brachial monoplegia |
|
Effects of modified camitz opponensplasty to restore thumb opposition for severe carpal tunnel syndrome |
|
The effects of upper limb motor recovery on submovement characteristics among the patients with stroke: a meta-analysis. |
|
Final results of multi-center randomized controlled trials of bci-controlled hand exoskeleton complex assisting post-stroke motor function recovery |
|
Abstract people around the world select their foods and meals according to particular choices based on physiological disorders and diseases, traditions, lifestyles, beliefs, etc. in this chapter, two of these particular alimentations are reviewed: those of the gourmet and the frail elderly. they take place in an environment where food is usually synonymous of body health disregarding its effects on social, cultural and psychological aspects, including emotions. based on an extensive literature review, it is proposed that the paradigm changes from food equals health to food means well-being, the latter encompassing physical and physiological aspects as well as psychological, emotional and social aspects at the individual and societal levels. the growing food and nutrition requirements of an aging population are reviewed and special nutritious and enjoyable products available for this group are discussed. |
|
Incidence, diagnosis, and risk factors of venous thromboembolism after surgery for malignant bone and soft tissue tumor of lower extremity |
|
Forward to bernstein: movement complexity as a new frontier |
|
Rehabilitation of the arm motor function in poststroke patients with an exoskeleton-controlling brain–computer interface: effect of repeated hospitalizations |
|
Combined diabetic treatment with low carbohydrate diet, exercise and music therapy |
|
Electrical, hemodynamic, and motor activity in bci post-stroke rehabilitation: clinical case study |
|