Medicinal & Aromatic Plants
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-0412
ISSN: 2167-0412
Research Article - (2019)Volume 8, Issue 2
The inhabitants of Laspur valley of Chitral have always been used plant resources for medicine, human and other animals food, vegetable, housing, timber, condiment, facial mask, fuel, ornamental and other multi purposes, from many years ago. A total of 212 species belonging to 55 families including 2 gymnosperms families (4 species), 5 monocots families (24 species) as well as 48 dicots families (184 species) have been recorded from the research area during 2013-2014. Family Asteraceae contributed the greatest number of species (30), after that Fabaceae (20 species), Poaceae (15 species), Brassicaceae (14 species), Rosaceae (12 species), Apiaceae (9 species), Solanaceae, Ranunculaceae and Salicaceae (each with 7 species), Lamiaceae (6 species), Polygonaceae (5 species), Amaranthaceae and Malvaceae (each with 4 species) and Cupressaceae, Boraginaceae, Caryophyllaceae, Chenopodiaceae, Cucarbitaceae, Grossulariaceae, Cyperaceae and Alliaceae (each with 3 species). All the other families are represented by less than 3 species. Ethnobotanically 155 plants were used as fodder including gymnosperms with one species and angiosperms with 154 species (135 dicots and 19 monocots), medicinal 100 species including 2 species of gymnosperms and 98 species of angiosperms (89 dicots and 9 monocots), fire wood 47 species including 4 gymnosperms and 43 angiosperms, vegetables 36 species of angiosperms, ornamental 31 species among which gymnosperms have one species and 30 species in an angiosperms (27 dicots and 3 monocots), timber 17 species including one species of gymnosperms and 16 species of angiosperms, fruit 10 species of angiosperms, facial mask/facial cream 10 species (9 angiosperms and 1 gymnosperm). Habit wise 157 plant species are recorded as herbs, 32 species as shrubs while 23 species trees. Totally 85 plants are cultivable and 127 plants are wild. During collection most of the plants are uprooted due to unawareness among communities. So there is a crucial need of conservation and protection of flora.

Medicinal; Economic; Laspur valley; Fodder, Medicinal; Wood
Generally, animals feed on the grass species and various dicot plants. Inhabitants of mountainous areas of Pakistan use plants for multi purposes, e.g., medicines, shelter, fuel, food and fodder for animals etc [1]. People rely on different medicinal plants for treatment of diseases in different areas of pakistan as well as outer world [2-6]. With the arrival of human civilization, numerous systems of therapy have been established mainly on the basis of plants. Our traditional systems of medicines like Ayurveda, Homeopathy, Sidda, Unani, etc continue to deliver the primary health care to greater than threequarters of population of the world (Table 1). Treatment of diseases through medicinal plants dates back to 5000 years in India [7]. Utilization of natural plants medicines by conventional methods gives potential indicators for biological actions [8]. Much of the species were found in Mallam Jabba are used for versatile [9]. The folks of district Swat collect medicinal plants during different seasons and sell them in the native market to make some money [10]. Juniperus excelsa is one of the best timber woods of Mastuj [11]. Previous record about uses of medicinal plants explored that poor folks of Hattar of District Haripur favor folk medicine just because of low rate, occasionally it is a part of their cultural values [12]. The folks of Central Punjab depend relies on plants for several regular necessities [13]. About 20,000 medicinal plants are used throughout the world [14]. Acacia nilotica contains volatile oils, phenolic glycosides, alkaloids, gums, oleosins, steroids, tannins and terpenes [15]. In Azad Kashmir plants has diverse habitat [16]. Above the 60 years old people of Kashmir have valuable information about the use of the indigenous medicinal vegetations, which should be conserved through conduct of surveys [17]. The quinine is obtained from the bark of Cinchona tree found in Southern America is used to cure malaria [18]. The plants have been used to keep homes warm in winter seasons (Figures 1-5). It can also use to make musical instruments to pass spare time [19]. Women of rural areas still use wild barriers, flowers and stem decoctions as valuable facial masks to keep their face, hand and feet protected against microbes, infections, ultraviolet light and cold [20-22]. International organization (WHO) has revealed that about 75%-90% of the rural inhabitants of the world and local herbalists are attending medicinal problems. Hamirpur district is also well known region of the west Himalaya which is surrounded by thick forest having rich floral diversity [23,24]. Juglans regia plant is used for multi purposes such as timber wood, fire wood and dyeing agent etc [25] (Table 2). In 75 species collected from Booni Chitral, which are used for multipurposes [26]. 50 plant species of 29 families were recognized which are being used by local residents of District Gujrat, Pakistan [27]. Survey studies were conducted in North Waziristan which recorded about 88 medicinal and aromatic plants belonging to 53 families [28]. Totally 50 plant species were documented from Margalla Hills National Park, Islamabad [29-32]. Totally 29 plants having 20 families were described from Mirpur, AJK [32-34] (Tables 3-8) .
| Name of Families | Medicinal uses | Fodder | Fruit | Ornamental | Facial mask | Firewood | Timber |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cupressaceae | 1 species | - | 1 species | 3 species | 1 species | ||
| Ephedraceae | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 | 1 | - |
| Total | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 |
Table 1: Traditional uses of gymnosperm plants.
| Families | Medicinal use | Fodder | Ornamental | Timber | Condiment | Firewood | Thatching |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alliaceae | 2 species | 1 species | - | 2 species | - | - | |
| Cyperaceae | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Iridaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | |
| Poaceae | 6 | 15 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Xanthorrhoeaceae | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 9 | 19 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
Table 2: Traditional uses of monocot plants.
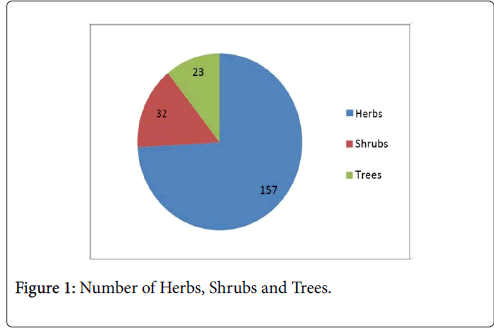
Figure 1: Number of Herbs, Shrubs and Trees.
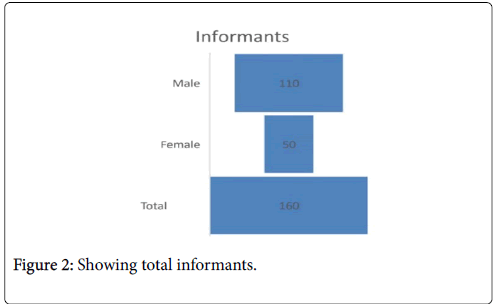
Figure 2: Showing total informants.
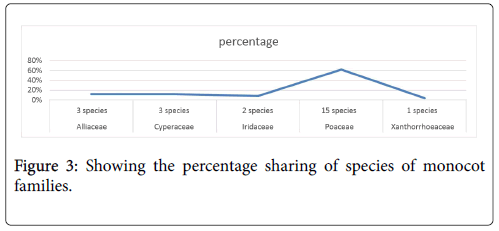
Figure 3: Showing the percentage sharing of species of monocot families.
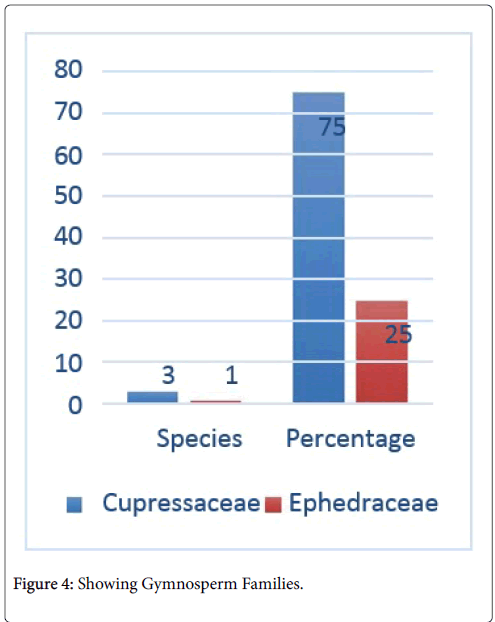
Figure 4: Showing Gymnosperm Families.
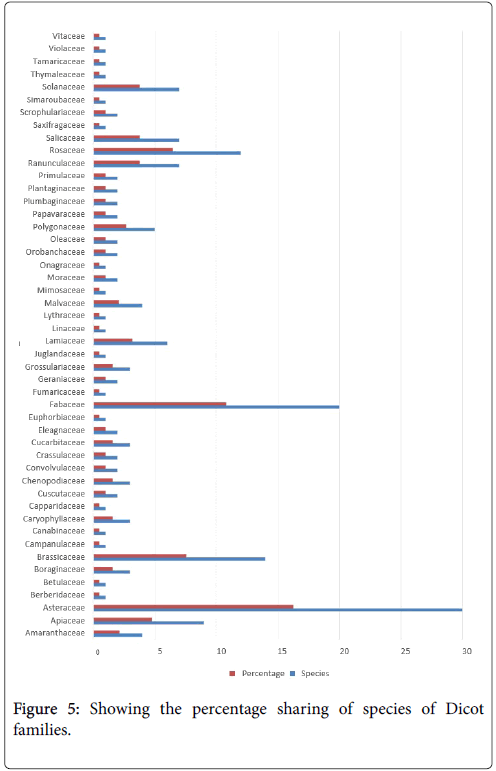
Figure 5: Showing the percentage sharing of species of Dicot families.

Figure 6: Questionnaire.
| S. No | Plants | Gymnosperm | Monocot | Dicot | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cultivable plants | 1 | 11 | 73 | 85 |
| 2 | Wild plants | 3 | 13 | 111 | 127 |
| Total | 212 |
Table 3: Total amount of cultivable and wild plants.
| Plants | Amount | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Gymnosperns | 4 | 1.88% |
| Monocots | 24 | 11.32% |
| Dicots | 184 | 86.79% |
| Total | 212 |
Table 4: Percentage of gymnosperm and angiosperm.
| Uses | Monocot | Dicot | Gymnosperms | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medicinal uses | 9 | 89 | 2 | 100 |
| Fodder | 19 | 135 | 1 | 155 |
| Firewood | - | 43 | 4 | 47 |
| Ornamental | 3 | 27 | 1 | 31 |
| Timber | - | 16 | 1 | 17 |
| Fruits | - | 10 | - | 10 |
Table 5: Plants used for multipurposes.
| Plants | Dicot | Monocot | Gymnosperm | Total | %age |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbs | 133 | 24 | 0 | 157 | 74.05% |
| Shrubs | 30 | 0 | 2 | 32 | 15.04% |
| Trees | 21 | 0 | 2 | 23 | 10.84% |
| Total | 212 |
Table 6: Total amount of herbs, shrubs and trees.
| Families | Medicinal uses | Fodder | Fire wood | Ornamental | Timber | Fruit | Facia mask | Vegetable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amaranthaceae | 2 | 3 | 2 | |||||
| Apiaceae | 8 | 4 | 1 | |||||
| Asteraceae | 9 | 17 | 5 | 9 | 4 | |||
| Berberidaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Betulaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Boraginaceae | 1 | 3 | ||||||
| Brassicaceae | 5 | 11 | 1 | 7 | ||||
| Campanulaceae | 1 | |||||||
| Canabinaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Caryophyllaceae | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Capparidaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Cuscutaceae | 2 | |||||||
| Chenopodiaceae | 1 | 3 | 1 | |||||
| Convolvulaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Crassulaceae | 2 | |||||||
| Cucarbitaceae | 3 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| Eleagnaceae | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Euphorbiaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Fabaceae | 5 | 19 | 3 | 1 | 6 | |||
| Fumaricaceae | 1 | |||||||
| Geraniaceae | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Grossulariaceae | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||||
| Juglandaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Lamiaceae | 5 | 3 | 1 | |||||
| Linaceae | 1 | |||||||
| Lythraceae | 1 | |||||||
| Malvaceae | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| Mimosaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Moraceae | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||
| Onagraceae | 1 | |||||||
| Orobanchaceae | 2 | |||||||
| Oleaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Polygonaceae | 3 | 5 | 1 | 2 | ||||
| Papavaraceae | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Plumbaginaceae | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| Plantaginaceae | 1 | 2 | ||||||
| Primulaceae | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||
| Ranunculaceae | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Rosaceae | 8 | 10 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 1 | |
| Salicaceae | 1 | 7 | 7 | 5 | ||||
| Saxifragaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Scrophulariaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Simaroubaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Solanaceae | 5 | 5 | 1 | 3 | ||||
| Thymaleaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Tamaricaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Violaceae | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Vitaceae | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Total | 89 | 135 | 43 | 27 | 16 | 10 | 9 | 36 |
Table 7: Traditional uses of dicot plants.
| S.No. | Botanical name | Family | Local name | Habit | Habitat | Part used | Herbal recipe and medicinal uses | Other uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Juniperus communis L. | Cupressaceae | Olin sawrooz | Shrub | Alpine region | Whole plant | -------------------- | Only used as Firewood. |
| 2 | Juniperus excelsa M. Bieb | Cupressaceae | Sawrooz | Tree | Hills | Whole plant | Aqueous extract from leaves and corns are anthelmintic. | Timber wood and fire wood. |
| 3 | Cupressus sumpervirens L. | Cupressaceae | Sadabahar | Tree | Garden | Whole plant | -------------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 4 | Ephedra gerardiana Wallich ex C. A. Meyer | Ephedraceae | Sumani | Shrub | Hills | Whole plant | Boiled in water, crushed and aqueous extract is obtained, called Gholja in Khowar language, which is used to treat facial sun burn pneumonia, and gastric problem. | Woody part is used as fire wood while leaves are served as fodder for animals. |
| 5 | Allium cepa L. | Alliaceae | Threshtu | Herb | Field | Bulb & leaves | The bulb is wormed and oily like secretion is obtained which is use for cough refluxing purpose and lower blood pressure. | As a foodstuff they are usually served as a part of a prepared dish, but can also be eaten raw or used to make salad, condiment and pickles or chutneys. |
| 6 | Allium neapolitanum Cirillo | Alliaceae | White garlic | Herb | Garden | Leaves & flowers | ------------------ | Ornamental plant. |
| 7 | Allium sativum L. | Alliaceae | Wrezhnu | Herb | Field | Bulb | Paste of bulb is mixed with meal to decreases hypertension and blood pressure. It strengthens nails when it is applied on nails. | Bulb of this plant is used in cooking as flavouring agent, spice, aromatic and condiment. |
| 8 | Carex divulsa Stokes | Cyperaceae | Narigass | Herb | Plain areas | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder. |
| 9 | Cyperus esculentus L. | Cyperaceae | Narigass | Herb | Plain areas | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder. |
| 10 | Carex shortiana Dewey & Torr. | Cyperaceae | Narigass | Herb | Plain areas | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder. |
| 11 | Iris ensata Thunb. | Iridaceae | Karyzma | Herb | Near field | Leaves | ------------------ | Fodder. |
| 12 | Iris germanica L. | Iridaceae | Sosun | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | The shoots are dried turned into a poltice and placed on the inflamed parts of the body. | The plant also has ornamental value. |
| 13 | Aristida cyanantha Steud. | Poaceae | Ishpur | Herb | Hills | Whole plant | ---------------- | Whole plant serves as cattle fodder both in fresh and dried condition. |
| 14 | Avena fatua L. | Poaceae | Shashar | Herb | Wheat field | Whole plant | ------------------ | This weed is a common unwanted invader of wheat fields, if allowed to grow and mature it may cause largely reduce wheat crop. Leaves serve as fresh fodder for animals. |
| 15 | Cynodon dactylon L. | Poaceae | Triangular grasses | Herb | Fertile areas | Whole plant | Bare footed walk on the lawns of this plant early morning is recommended for people with burning sensation on their feet. | |
| 16 | Deschampisa caespitosa (L.) P. Beauv. | Poaceae | Gass | Herb | Plain areas | Whole plant | ----------------- | Fodder. |
| 17 | Hordeum distichon L. | Poaceae | Ishpersiri | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Seeds are grinded, floured and used to make bread which is efficient for hepatitis, jaundice and appetizer. | Hay is mixed with clay plaster as an anti-cracking agent. Stem and leaves are consumed as cattle fodder. |
| 18 | Hordeum murinum L. | Poaceae | Meadow barley | Herb | Fertile area | Whole plant | ----------------- | Fodder. |
| 19 | Hordeum vulgare L. | Poaceae | Siri | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Its flour is used in bread making also recommended as stomachache, asthma, anemia and indigestion. | Its leaves are served as fodder for animals. Hay is mixed with clay plaster as an antic racking agent. |
| 20 | Panicum miliaceum L. | Poaceae | Olin | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Its flour is efficient stomach ache. | Leaves are used for animals while seeds are eaten by hens and birds. |
| 21 | Phragmites karka (Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. | Poaceae | Shoal | Herb | Field | Leaves & stem | ------------------ | Generally used for thatching purpose, fodder for animals, making baskets and Writing pen for school children. |
| 22 | Pennisetum typhoideum (Burm. f.) Stapf | Poaceae | Grass | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Flour is grinded from its seeds to make bread which is useful to treat stomach ache, cough and flu. | Straw is used as fodder for cattle while seeds serve as fodder for hens. |
| 23 | Saccharum spontaenum L. | Poaceae | Shol | Herb | Lower pasture | Leaves & stem | ---------------------- | The edges of mature leaves are quite sharp and they can cut fingers when harvest them. They are also served as fodder for cattle. |
| 24 | Setaria viridis L. | Poaceae | Grassec | Herb | Field | Whole plant | ---------------------- | Fodder |
| 25 | Secale cereal L. | Poaceae | Lachgandm | Herb | Field | Whole plant | ---------------------- | Fodder |
| 26 | Triticum aestivum L. | Poaceae | Gom | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Triticum aestivum also known as bread wheat. These crops provide food for human so it is a source of energy and domestically important. | The dried stem and leaves serves as cattle fodder. It produces the main bulk of straw. There are four varieties of wheat in the study area which are locally named as Tuh gom, Safidek, Zhakht gom and Bakhtawar gom. |
| 27 | Zeamays L. | Poaceae | Juwari | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Seeds are grinded, powdered or made flour which is used to make bread to treat jaundice and stomach pain. The delicious cobs are cooked directly in fire and are eaten | It is a main ingradiant of human food. Stems and leaves are used as fresh and dry fodder for cattles |
| 28 | Hemerocallis fulva L. | Xanthorrhoeaceae | Juwari gamburi | Herb | Garden | Flowers | ------------------ | Ornamentally used. |
| 29 | Amaranthus cruentus L. | Amaranthaceae | Kruishakhu | Herb | Maize field | Leaves & stem | Young leaves are used as vegetable which are laxative. | Fodder |
| 30 | Aerva lanata (L.) Juss. ex Schult. | Amaranthaceae | Knotgrass | Herb | Fertile land | Whole plant | ------------------ | The plant provides grazing field for chickens and other livestock. |
| 31 | Amaranthus retroflexus L. | Amaranthaceae | Ganari | Herb | Field | Leaves | ------------------ | Fodder |
| 32 | Beta vulgaris L. | Amaranthaceae | Lablabu | Herb | Field | Corm and leaves | Sugar beet is cultivated as vegetable which is said to be increase blood level. | Leaves are used as fodder for cattle. |
| 33 | Carum carvi L. | Apiaceae | Hojoj | Herb | Field | Seeds | Seeds are boiled; herbal tea is made and is used in nausea and stomachache. | ------------------------------ |
| 34 | Carum copticum L. | Apiaceae | Shunjmuk | Herb | Field | Seeds & flowers | The flowers, seeds and leaves of this plant are boiled in milk containing a small amount of salt. The mixture is used againt bronchitis, cough, throat infections and diarrhea. | ------------------ |
| 35 | Cuminum cyminum L. | Apiaceae | Safed zira | Herb | Field | Seeds & leaves | Seeds and leaves of this flavouring plant are mixed with meal to increase appetite and improve taste. | Used as condiment |
| 36 | Coriandrum sativum L. | Apiaceae | Danu | Herb | Field | Leaves & fruits | Seeds are mixed with vegetables which are carminative and diuretic agent. | Aromatic in nature therefore used as condiment. |
| 37 | Daucus carota L. | Apiaceae | Kheshgum | Herb | Field | Whole plant | This vegetable is employed in the Improvement of eyesight and blood increased production. Tea made from its seeds is used for curing abdominal pains. | Carrot root is edible and is used as salad. Gajar's halwa can be made from the plant roots. Leaves are served as a fodder for cattle. |
| 38 | Ferula narthex L. | Apiaceae | Rauw | Herb | Hills | Whole plant | Young stems are cut resulting in oozing out of milky exudate. It which is locally called Hing and used as stomachache and against diabetes and tootache. | Leaves are used as fodder for animals. |
| 39 | Foiniculum vulgare Mill. | Apiaceae | Bodioung | Herb | Field | Seeds & leaves | Seeds and fresh leaves are chewed for cough, abdominal pain and pneumonia | Used as spice and condiment. |
| 40 | Heracleum maximum Bartram | Apiaceae | Phorol | Herb | Fertile area | Whole plant | Peels from stems, called Khaf, are placed in burnt condition to treat rheumatism. | It is mostly used as fodder for cattle especially in dry condition to thicken the milk of cattle. In addition, floral escape is edible. It is also used to make flutes for children. |
| 41 | Prongus ferulacea L. | Apiaceae | Ribbed Cachrys | Herb | Upper pasture | Leaves& fruits | ----------------- | Fodder |
| 42 | Artemisia biennis Willd. | Asteraceae | Busith | Herb | Every where | Leaves& stem | ----------------- | Fodder |
| 43 | Artemisia bigelovii A. Gray | Asteraceae | Thaspuk | Shrub | Hills & sandy area | Whole plant | Inflorescence and leaves are grinded into powder; this is used against gastric problems and as stomach ache. | It is used fodder, firewood and also used for soil erosion control. |
| 44 | Artemisia ludoviciana Nutt. | Asteraceae | Shothing | Shrub | sandy area | Whole plant | ------------------- | Firewood |
| 45 | Artemisia dracunculus L. | Asteraceae | Maxhini | Herb | Field | Shoot & leaves | Plant body is used as broom for sweeping lawns. | Fodder |
| 46 | Aster amellus L. | Asteraceae | Aster | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ----------------- | Ornamental plant |
| 47 | Artemisia maritima L. | Asteraceae | Dron | Shrub | sandy area | Whole plant | ---------------- | Branches are used as broom while leaves are used as fodder for animals. |
| 48 | Artimesia absinthium L. | Asteraceae | Kharkhalich | Herb | Arid ground | Seeds | One teaspoonfull of seeds (powdered) are taken with sufficient water for curing diabetes, abdominal pain and high B.P. | --------------- |
| 49 | Artemisia rutifolia Stephan.ex Spreng. | Asteraceae | Zom thasphuk | Shrub | Hills | Whole plant | ------------------ | Firewood and fresh fodder for animals. |
| 50 | Artemisia scoparia Waldst. & Kit. | Asteraceae | Zha | Herb | scare watery area | Shoots | The aqueous extract obtained from its flowering axis is called Zhawogh which is used in the treatment of malaria. | Plant body is also serves as fodder for cattle and making broom. |
| 51 | Carthamus tinctorius L. | Asteraceae | Poam | Shrub | Field | Dried floret and seeds | The orange/reddish florets are collected, dried, powdered and mixed with milk to cure itching of body rashes. Herbal tea made from seeds cures cough and tonsillitis. | ------------------ |
| 52 | Chicorium intybus L. | Asteraceae | Khasti | Herb | Fertile area | Roots & leaves | The root of this plant is dugout, washed, Chopped and boiled with water. These aqueous extract is useful for cardiac. Problem, malaria, vomiting and typhoid. | It is used as vegetable. It also serves as fodder for cattles. |
| 53 | Chrysanthemum segetum L. | Asteraceae | Shadongi | Herb | Field | Flowers amd leaves | Inflorescence and leaves are collected,crushed, boiled condiment to increase flavour and taste of vegetable. | |
| 54 | Cirsium arvense L. | Asteraceae | Chamchirik | Spiny shrub | Every where | Leaves | ----------------- | Fodder. |
| 55 | Circium vulgare (Savi) Ten. | Asteraceae | Blansirik | Spiny shrub | Every where | Leaves | The weed after hervest losses turgidity. It is used as both fresh and winter fodder to thicken the milk of animals. | Fodder. |
| 56 | Cosmos bipinnatus Cav. | Asteraceae | Jangali gamburi | Herb | Fertile area | Whole plant | --------------------- | The flowers of this ornamental plant attract honey bees, birds, butterflies and other insects. |
| 57 | Conyza bonariensis (L.) Cronquist. | Asteraceae | Horse weed | Herb | Every where | Whole plant | --------------------- | Fodder. |
| 58 | Calendula officinalis L. | Asteraceae | Bodoki | Herb | Field | Leaves and flowers | -------------------------- | Florets and leaves of this ornamental plant are used as condiment and vegetable. |
| 59 | Centaurea cyanus L. | Asteraceae | Blue bottle | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ------------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 60 | Erigeron asper Nutt | Asteraceae | Rough fleabane | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | --------------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 61 | Echinops echinatus Roxb. | Asteraceae | Ishperuzoakh | Spiny shrub | Exposed area | Whole plant | --------------------- | Fodder and firewood. |
| 62 | Helianthus annus L. Echinops echinatus Rox | Asteraceae | Yorghereyak | Herb | Field | Whole plant | ---------------- | Leaves are used as fodder for animals while seeds are eaten by hens. It has also an ornamental value. |
| 63 | Inula rhizocephala Schrenk | Asteraceae | Herb | Herb | grassy area | Leaves | ------------------- | Fodder. |
| 64 | Lactuca sativa L. | Asteraceae | Kileem | Herb | Field | Leaves | Leaves are served as vegetable which are act as appetizer and cooling agent. | Salad. |
| 65 | Matricaria camomilla L. | Asteraceae | Shirisht | Herb | Exposed area | Flowers | The floral axes are collected and dried. Then water boiled and the decoction is used against jaundice, abdominal pain, indigestion and fever. | Its leaves are used as fodder for livestock. |
| 66 | Sonchus arvensis L. | Asteraceae | Chirnisak | Herb | Every where | Whole plant | ----------------- | Fodder. |
| 67 | Tagetes minuta L. | Asteraceae | French marigold | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ------------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 68 | Tagetes erecta L. | Asteraceae | Gulsambar | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ------------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 69 | Tagetes tenuifolia Cav. | Asteraceae | Gulsambar | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ------------------- | Ornamental plant |
| 70 | Tragopogon pratensis L. | Asteraceae | Chiron | Herb | Upper pasture | Whole plant | ------------------- | Fodder. |
| 71 | Taraxacum officinale F.H. Wigg | Asteraceae | Phovow | Herb | Agricultural land | Leaves and shoot | Leaves and young shoot are served as vegetable to treat constipation, liver and kidney disorder. | Fodder. |
| 72 | Berberis vulgaris L. | Berberidaceae | Chounj | Shrub | Exposed area | Whole plant | Leaves and fruits are collected, juice is extracted and filtered which can be taken orally for the treatment of typhoid, jaundice, dyspepsia, blood purification and muscular pains. | This plant is used as fencing agent agaist th grazing animals. also used as packing papers, which is mostly used as basket for the storage of butter and cheese. Stem is used as fire wood and leaves as animal fodder. |
| 73 | Betula utilis D.Don | Betulaceae | Bulee | Tree | Laspur gol | Whole plant | Bark of this plant is warmed and wrapped around boils. | The water proof thin bark was used as paper for writing in the past. Bark is |
| 74 | Anchusa arvensis (L.) M. Bieb. | Boraginaceae | Small bugloss | Herb | Every where | Leaves | --------------- | Fodder. |
| 75 | Arnebia euchroma (Royle) Johnst | Boraginaceae | Phusook | Herb | Sandy area | Roots and leaves | The roots of this plant are dug out; outer bark is removed, dried, crushed and mixed with some mustard oil which turns into bright red and used to avoid and stop hair loss. | Leaves are used as fodder for livestock. |
| 76 | Solenanthus apenninus L. | Boraginaceae | Solenanthus | Herb | Every where | Leaves | ----------------- | Fodder. |
| 77 | Brassica compestris L. | Brassicaceae | Sarson | Herb | Field | Leaves | ----------------- | Vegetable and fodder. |
| 78 | Brassica rapa var.perviridis L. | Brassicaceae | Hazgar | Herb | Field | Leaves | ----------------- | Vegetable is excellent source of calcium. |
| 79 | Brassica napus var.napobrassica | Brassicaceae | Kalam | Herb | Field | Whole plant | ----------------- | Vegetable and fodder. |
| 80 | Brassica oleracea var.capitate L. | Brassicaceae | Band ghobi | Herb | Field | Leaves | ----------------- | Vegetable is good source of vitamin K, and vitamin C. |
| 81 | Capsella bursa-pastoris (L.) Medikus | Brassicaceae | Shatara | Herb | Field | Whole plant | ----------------- | Fodder. |
| 82 | Descurainia Sophia L. | Brassicaceae | Tansy mustard | Herb | Plain areas | Whole plant | Fodder. | |
| 83 | Lepidium ruderale L. | Brassicaceae | Palak khardachi | Herb | Field | Leaves | Leaves are used as salad for dyspepsia and stomach upset. | Salad. |
| 84 | Lepidium draba L. | Brassicaceae | Gordoghjoshu | Herb | Around field | Leaves | Fodder. | |
| 85 | Nasturtium officinale W.T. Aiton | Brassicaceae | Toqjoshu | Herb | Wet area | Leaves and stem | Leaves serves as vegetable which is used against dyspepsia and hepatitis. | Stem and leaves are also used as livestock fodder. |
| 86 | Raphanus sativus var. longipinnatus L.H.Bailey | Brassicaceae | Muli | Herb | Field | Corm and leaves | Corm is used to make salad which is efficient for hepatitis and jaundice. | Leaves are served as fodder for cattle. |
| 87 | Raphanus caudatus L. | Brassicaceae | Trupakosh | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Fodder. | |
| 88 | Raphanus sativa L. | Brassicaceae | Tipor | Herb | Field | Corm and leaves | Radish crops are grown for their swollen roots which have pungent scent. Corm is used to make vegetable and salad in case of jaundice. | It can also be eaten raw. Leaves are served as fodder for cattle. |
| 89 | Sisymbrium irio L. | Brassicaceae | Khelikheli | Herb | Field | Leaves and seeds | Seeds are grinded, powdered and mixed with few drop of water to make rounded ball like structure, which can be rubbed at flate stone and applied as mask on face to protect face from sunburn and facial pimples. | Leaves are served as fodder for animals. |
| 90 | Thalpi arvense L. | Brassicaceae | Field pennycress | Herb | Field | Whole plant | ---------------- | Fodder |
| 91 | Codonopsis clematidea Schrenk. | Campanulaceae | Marghon | Herb | Grassy area | Whole plant | ---------------- | Fodder. |
| 92 | Canabis sativa L. | Cannabaceae | Boung | Herb | Around fields | Whole plant | The leaves are dried, grinded and powdered called garda. Garda is mixed with wheat flour and is given to cattle against flatulence, abdominal pain and as sedative. Seeds are fed to hens to enhance egg lying. | Canabis sativa is also used as firewood and fodder for cattle. |
| 93 | Lepyrodiclis holosteoides (C.A.Mey.) | Caryophyllaceae | Birghal | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Young leaves are used to make vegetable which are laxative. | Plant is used as fodder for cattle. |
| 94 | Stellaria littoralis Torr. | Chick weeds | Herb | Marshy places | Whole plant | ----------------- | Fodder. | |
| 95 | Silene conoidea L. | Apupar | Herb | Wheat field | Whole plant | A paste is prepared from the dried young leaves and seeds and applied on pimples affected skin also used in case of backache. | Plant is also used as fodder animals. | |
| 96 | Capparis spinosa Linnaeus. | Capparidaceae | Kaveer | Shrub | Bare places | Flowers and fruits | Floral buds are collected, dried, mashed with wheat flour and cooked to prepare aquous extract called Kavirough, which is efficient for abdominal pain, malaria and typhoid. | Leaves are used as fodder while fleshy fruits are applied as face cosmetics. |
| 97 | Cuscuta epithymum L. | Cuscutaceae | Umbool | Herb | Every where | Whole plant | ------------------ | The plant is firscollected, dried, powdered, mixed with water and then coloured wools and white threads |
| 98 | Cuscuta reflexa Roxb | Cuscutaceae | Umbool | Herb | Every where | Whole plant | ------------------ | Dyeing agent. |
| 99 | Chenopodium album L. | Chenopodiaceae | Kunakh | Herb | Maize field | Leaves | Leaves are served as vegetable in the disorder of bowels, as laxative for Constipation.. | Fodder. |
| 100 | Chenopodium botrys L. | Khodur | Herb | Field | Leaves | ------------------ | Fodder. | |
| 101 | Chenopodium murale L. | Gangali kunakh | Herb | Every where | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder. | |
| 102 | Ipomoea indica (Burm.f.) Merr. | Convolvulaceae | Nazuk badan | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ------------------ | Ornamental plant. |
| 103 | Convolvulus arvensis L. | Mish | Herb | Maize field | Whole plant | In young condition leaves are used to make vegetable to treat constipation. | It grows as a weed in maize crop and serves as cattle fodder. | |
| 104 | Rhodiola rosea L. | Crassulaceae | King’s crown | Herb | Hills | Whole plant | ----------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 105 | Aeonium canariense Webb & Berthel. | Crassulaceae | Ghepjoshu | Herb | Alpine areas | Whole plant | ----------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 106 | Cucarbita maxima L. | Cucarbitaceae | Alok | Herb | Field | Seeds, leaves & fruits | Seeds are boiled and filtered to prepare an herbal tea to cure pneumonia and cough. | Flowers and fruits are used as vegetables. Leaves are used as food for cattles. |
| 107 | Cucurbita pepo L. | Kadu | Herb | Field | Seeds, leaves & fruits | Vegetable is used to lower blood pressure, | Leaves are eaten by cattle. Anticancerous and diuretic agent. | |
| 108 | Cucumis sativus L. | Badrangh | Herb | Field | Leaves & fruits | |||
| 109 | Eleagnus angustifolia L. | Elaeagnaceae | Shounjur | Tree | Foresty area | Whole plant | Fruits are dried and powdered to treat asthma and cough. The gummy stem and branches resin is dried then powdered and used as shempoo as tonic for long, healthy and silky hair. | The branches are cut by the formers to give out along the edges of cultivated fields to protect them grazing of animals. It is a best timber, firewood and animal fodder. |
| 110 | Hippophae rhamnoides L. | Elaeagnaceae | Mirghinz | Shrub | Foresty area | Whole plant | The juice obtained from its berries called Buringogh is used against high blood pressure and eye diseases. Barries are also applied on face as face mask agaist sunburn. | Its branches are employed in thatching materials, animal fodder and firewood. It is also used as barbed boundary marker around field and along path to keep away cattle. |
| 111 | Euphorbia nicaeensis All. | Euphorbiaceae | Ano chirnisk | Herb | Hilly area | Latexs | When it is cut, bleed a milky white sap called latex which is applied externally on face to treat eczema and acne but over dose cause swelling on skin. | Leaves are used as fodder for animals. |
| 112 | Astragalus tragacantha L. | Fabaceae | Garmezu | Shrub | Hilly area | Whole plant | ------------------ | Thatching purpose and fire wood. |
| 113 | Astragalus sesameus L. | Orchokuchun | Herb | Hilly area | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder. | |
| 114 | Asrtagalus solandri Lowe. | Doderokuchun | Herb | Hilly areas | Whole plant | ---------------- | Fodder. | |
| 115 | Astragalus adsurgens Pall. | Crown vetch | Herb | Hilly area | Leaves | Increase milk productivity of cattle. | Leaves and branches are served as fodder. | |
| 116 | Cicer microphyllum L. | Qaquchun | Shrub | Hill slope | Whole plant | Used as firewood and fodder for cattle and also used in making edges of mud roofs. It prevents mouse passage because of its spiny stem. | ||
| 117 | Cicer arietinum L. | Chola | Herb | Field | Leavesand seeds | The seeds are sweet and are used as anti diuretic, bronchitis and skin diseases | Leaves are used as fodder for cattle while seeds are consumed as pulse. | |
| 118 | Coronilla varia L. | Like rub | Herb | Grazing land | Whole plant | Fodder. | ||
| 119 | Lathyrus odoratus L. | Jangali kuchoon | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | Ornamental plant. | ||
| 120 | Lens culinaris Medikus | Sirju | Herb | Field | Leaves and fruits | Pulse and animal fodder. | ||
| 121 | Meliotus officinalis L. | Bisus | Herb | Fertile places | Whole plant | Fodder. | ||
| 122 | Medicago minima L | Small medick | Herb | Fertile places | Whole plant | ------------------- | Fodder. | |
| 123 | Medicago sativa L. | Mushich | Herb | Fertile area | Leaves & stem | The plant in fresh and dried condition is a fodder, which fattens the cattle. | Fodder | |
| 124 | Pisum sativum L. | kuchoon | Herb | Field | Whole plant | Seeds are rich in proteins which are used as vegetable. | Stem and leaves are given to animals. Seeds are also edible without cooking | |
| 125 | Phaseolus lunatu L. | Lobia | Herb | Field | Whole plant | The young pods are used as vegetable and seeds are eaten as pulse. Its leaves are served as fodder for cattle. | ||
| 126 | Sophora tomentosa L. | Khakhart | Shrub | Bare places | Whole plant | Decayed leaves provide good fertilizer and it is also served as fodder and firewood. | ||
| 127 | Trifolium prantense L. | Shaftal | Herb | Field | Whole plant | It thickens the milk of animals. | It increases soil fertility. | |
| 128 | Trifolium repens L. | Shabluki | Herb | Fertile area | Leaves & flowers | Increases the milking capacity of animals. | It has a good fragrance. It increase soil fertility and cultivated as crop rotation | |
| 129 | Trifolium resupinatum L. | Shaftal | Herb | Field | Whole plant | It is preferred as best fodder for cattle because it increases the milk yielding capacity. | It is generally grown as a fodder crop, important for its nitrogen fixation which increases soil fertility. | |
| 130 | Vicia faba L. | Andalu | Herb | Field | Seeds & leaves | Seeds are boiled, added small amount of salt and eaten to treat chest burn and hepatitis. | Young pods and seeds are important source of pulse. Leaves and stem are used as fodder for domestic animals. | |
| 131 | Vicia sativa L | Fabaceae | Kharashek | Herb | Wheat field | Whole plant | ----------------- | Fodder. |
| 132 | Corydalis aurea Willd. | Fumaricaceae | Golden corydalis | Herb | Alpine area | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder. |
| 133 | Geranium carolinianum | Geraniaceae | Zarkari | Herb | Grassy areas | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder. |
| 134 | Geranium wallichianum Oliv. | Geraniaceae | Garden Geranium | Herb | Alpine areas | Whole plant | ----------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 135 | Ribes grossularia L. | Grossulariaceae | Ghangu | Shrub | Upper pasture | Whole plant | ----------------- | Fruits/barriers are much liked by the children. Leaves are used as fodder and stem is used as firewood. |
| 136 | Ribes aureum Pursh | Qalahure gamburi | Shrub | Garden | Whole plant | ----------------- | Ornamental plant having good aroma. | |
| 137 | Ribes oxyacanthoides L. | Grossulariaceae | Chilanju | Shrub | Upper pasture | Whole plant | ----------------- | Firewood and fodder. |
| 138 | Juglans regia L. | Juglandaceae | Birmough | Tree | Every where | Whole plant | Bark and leaves are used for gums and tooth diseases and sparkling of teeth. It has warm nature and can cause jaundice. Decoction of leaves is given in eczema. Seeds can be eaten to lower blood pressure. | Seeds yield cooking oil. The plant is used in agricultural tools, green manure fodder, and firewood and dyeing agent. Pericarp of fruit is used as hair dye. |
| 139 | Lamium amplexicaule L | Lamiaceae | Greater henbit | Herb | Grassy areas | Leaves & stem | ----------------- | Leaves are given to cattle. It is an important nectar and pollen plant for bees |
| 140 | Mentha arvensis L | Podina | Herb | Garden | Stem & leaves | It is stomachache and anthelmintic agent when used as salad. | This herb has a beautiful fragrance therefore its leaves and young stem are used as condiment. | |
| 141 | Mentha longifolia (L.) Huds. | Ben | Herb | Bank of canal | Whole plant | Herbal tea, made from roots, called Benough, which cures fever, jaundice and indigestion.The fresh and dried leaves are also eaten as digestive and as stomachache agent. | In early spring, the fresh leaves are collected and used as salad. It is used as fodder in dry condition. | |
| 142 | Nepata cataria L. | Mutrich | Herb | Grassy areas | Whole plant | Seeds pastes are applied to injuries and backache. | It is a weed of cultivation and fodder for cattle. | |
| 143 | Mentha spicata L. | Suspru | Herb | Field | Whole plant | The leaves and flowers meshed with wheat flour, are cooked to prepare Suspruough, which is eaten as febrifuge and appetizer and to cures dyspepsia, typhoid and stomach pain. | It is also used as salad and condiment. | |
| 144 | Thymus serphyllum L. | Lamiaceae | Siew | Herb | Alpine pastures | Seeds & leaves | The plant having good smell and locally green tea is made from its leaves and flowers which are considered as medicine for fever, cough, cold and headache | ----------------- |
| 145 | Linum usitatissimum L. | Linaceae | Shintiki | Herb | Field | Seeds & fruits | Seeds are grinded and fried then a paste is made from it which is use full for toothache and lumbago. | ----------------- |
| 146 | Lawsonia inermis L. | Lythraceae | Shorang | Herb | Field | Leaves& flowers | Grinded leaves and flowers are used as mehndi for foot crack, boil and for split skin near nails. Leaves are mixed with the Brassica oil and made into paste which is externally applied to athlete foot to relieve. | Leaves ground and made into powder applied for hair dyeing. |
| 147 | Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench. | Malvaceae | Bhindi | Herb | Field | Leaves & fruits | Fruit is nutritious and diuretic in case of dysentery. It is very effective against urinary and skin diseases. | Leaves are served as fodder for animals while fruits are used as vegetable. |
| 148 | Alcea rosea L. | Layn | Herb | Garden | Leaves & Petals. | The dried petals are grinded, powdered and poultice is made which is applied to the boils to draw out the puss. After two to three times application the patient should be rid of the boil | Ornamentally used. | |
| 149 | Malva neglecta Wallr. | Suwachal shakh | Herb | Field | Leaves & seeds | Leaves are used as vegetable to treat constipation and other digestive problems and also act as cooling agent. | ------------ | |
| 150 | Malva sylvestris L. | Malvaceae | Suwachal gamburi | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | The young leaves are served as vegetable to cure joint pain. | Ornamental plant. |
| 151 | Acacia arabica (Lam.) Willd | Mimosaceae | Kiker | Tree | Foresty area | Whole plant | -------------------- | Hard wood is durable and is used for the construction of homes, fuel wood and other purposes while leaves are fodder for animals. |
| 152 | Morus alba L | Moraceae | Mrach | Tree | Garden | Whole plant | Fruits are directly used in jaundice. | Leaves are used as fodder for cattle while branches and stem are used as firewood. |
| 153 | Morus nigra L | Moraceae | Shamrach | Tree | Garden | Whole plant | Black mulberry can be cultivated for its edible fruit which are used in jaundice, dyspepsia and as blood purifier. | Stem and branches are served as a fodder, timber and firewood. |
| 154 | Epilobium angustifolium L. | Onagraceae | Telibashu | Herb | Foresty area | Leaves | ------------------- | Fodder |
| 155 | Euphrasia officinalis L. | Orobanchaceae | Eyebright plant | Herb | Marshy places | Fodder | ||
| 156 | Pedicularis sceptrum-carolinum L. | Orobanchaceae | Charachari | Herb | Around field | Leaves & stem | ------------------- | Fodder |
| 157 | Fraxinus excelsior L. | Oleaceae | Toor | Tree | Laspur gol | Whole plant | The aqueous extract from boiled bark is given orally to pregnant women to deliver premature baby provided where it is feared that the infant has died within the foetus of mother. | Stem and branches are used as firewood, in making agricultural tools and as thatching purposes; while leaves are served as fodder for animals. |
| 158 | Jasminum officinale L. | Oleaceae | Chambeli | Shrub | Garden | Whole plant | -------------------- | Ornamental plant |
| 159 | Atraphaxis pyrifolia Bung. | Polygonaceae | Ishpen | Shrub | Upper pasture | Whole plant | -------------------- | |
| 160 | Oxyria digyna (L.) Hill | Polygonaceae | Shutshakhu | Herb | Upper pasture | Leaves & stem | The leaves have a fresh bitter taste and are rich in vitamin C; they can be used to prevent and cure scurvy. | Leaves are used to make vegetable and also eaten raw. The plant is important for both insects and larger animals that feed on it in cold and alpine regions where it occurs. |
| 161 | Poligonum persicara L. | Spoted lady thumb | Herb | Field | Leaves | Increase milk productivity in animals. | Fodder | |
| 162 | Rheum emodi L. | Ishpar | Herb | Hills | Floral scape & leaves | Floral escape is edible and eaten raw. This is used for treatment of flue and cough. | Fodder | |
| 163 | Rumex longifolius DC. | Polygonaceae | Chirkonzu | Herb | Damp grassy places | Leaves | The fresh leaves are collected, boiled, cut, and the past are mixed with tomato, onion, ginger, garlic, salt (as required) and then fried in oil, this gravy is used as laxative when eaten as vegetable. | Vegetable and fodder |
| 164 | Papaver somniferum L. | Papaveraceae | Koknar | Herb | Field | Capsule & latex | Latex is extracted from the popy capsule called affune. Opium is taken in small doses orally or smoked neat as pain killer for scorpion bite. It is used by some as an aphrodisiac; as it stimulates the sense of pleasure and increase physical vigor. Seeds are mixed with tea and are given to patients having nasal and chest congestion, bronchitis and sunstroke | --------------- |
| 165 | Papaver rhoeas L. | Papaveraceae | Poppy plant | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | It contains alkaloid Rhoeadine which is sedative and narcotic in nature. | Ornamental plant |
| 166 | Acantholimon ulicinum (Willd.ex Schult) . | Plumbaginaceae | Plis tholpak | Shrub | Hill | Whole plant | --------------- | Firewood and fodder |
| 167 | Acantholimon bracteatum var. capitatum BOISS. | Plumbaginaceae | Tholpak | Shrub | Hill | Whole plant | ----------------- | Firewood. |
| 168 | Plantago lanceolata L. | Plantaginaceae | Boikoligini | Herb | Grassy area | Seeds & leaves | ----------------- | Fodder |
| 169 | Plantago major L. | Plantaginaceae | Ispaghol | Herb | Grassy area | Leaves | The seeds are soaked in milk/water and used against diarrhea, loose motions and constipation | Leaves serve as cattle fodder |
| 170 | Primula rosea Royle. | Primulaceae | Bulisqar | Herb | Bank of canal | Whole plant | ----------------- | This ornamental plant usually grows in spring season. |
| 171 | Primula macrophylla D.Don. | Punar | Herb | Upper pasture | Whole plant | The white powdery deposition from ventral sides of leaves and flowers stalks is used to cure irritation, redness and other eye diseases. | ||
| 172 | Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux | Ranunculaceae | Zharojosh | Herb | Upper pasture | Roots | Roots are peeled, dried, powdered and mixed with hair oil to remove dandruff and lice by strengthening and cleaning hair. Roots are very poisonous when eaten, cause death. | --------------- |
| 173 | Clematis orientalis L. | Chountrouk | Shrub | Sandy area | Whole plant | A paste is prepard from the crushed leaves and used against eczema. | It is also used as firewood and fodder for animals. | |
| 174 | Ranunculus cymbalaria Pursh. | Chiririjosh | Herb | Equatic | Leaves | ---------------- | Fodder | |
| 175 | Delphinium brunonianum Royle | Makuti | Herb | Upper pasture | Whole plant | Seeds and leaves roots decoction act as healing, anthelmintic and insecticidal and antilice agent. It is very poisonous plant and used for destroying maggots in animals wounds, particularly in sheeps and goats. | The flowers are considered harsh, bitter and unpleasant. | |
| 176 | Trollius europaeus L. | Globe flower | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ------------------ | Ornamental plant | |
| 177 | Ranunculus equatilis L. | Oowough gass | Herb | Equatic | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder | |
| 178 | Ranunculus millefoliatus vahl | Ranunculaceae | Buttercup | Herb | Upper pasture | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fodder |
| 179 | Cotoneaster nummularia Fisch.et Mey. | Rosaceae | Mikini | Shrub | Forestry area | Whole plant | The edible fruits are blood purifier. | Firewood and fodder for cattle |
| 180 | Crataegus songarica K.Koch | Ghooni | Tree | Foresty area | Whole plant | An aqueos extract called Ghuniogh is obtained from the bark soaked for few hours in waters. A glass of this extract is used to reduce labour pain in women. | It is timber wood, firewood and also used as fodder for animals. | |
| 181 | Potentilla anserina L. | Silverweed | Herb | Moist soil | Leaves | ----------- | Fodder. | |
| 182 | Prunus armeniaca L. | Zhuli | Tree | Everywhere | Whole plant | The ripe fruits are dried, soaked in water to obtain sweet syrup; this syrup is used against constipation and cough. Bark of Khubani is cut, soaked with water, mixed with gummy substances and rubbed at flate stone which is called Togholi and is applied on faces to protect faces from sun burn. | Its leaves are served as fodder while stem is used as timber and firewood. Fruits of Prunus armeniaca are edible. | |
| 183 | Prunus avium L. | Cherry | Tree | Lower Laspur | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fruits are eaten and leaves are given to animals while wood is used for sports items as well as for fuel purpose. It is a best plant for shade. | |
| 184 | Prunus persica (L.) Stokes | Gherwalogh | Tree | Garden | Whole plant | The powdered seeds, mixed with water, are usually applied on hands during winter. | Fruits are edible and delicious to eat. The leaves are served as fodder and stem is used as firewood. | |
| 185 | Pyrus communis L. | Toung | Tree | Garden | Whole plant | ----------------- | Pear is grown for their edible fruit which is rich in vitamins. Leaves are used as animal fodder, while branches and stem are used used as firewood | |
| 186 | Pyrus mallus L. | Palough | Tree | Garden | Whole plant | Fruits are good source of energy and stomach ache. | The dried fruits are called Palavushto and are used during winter. Branches and stem are efficient for firewood. There are four varieties of apples in the area: Isdob (Sweet and juicy), Shout palough (sour), Basoti (larger and sweeter) and Shokorpalough (sweetest and smallest) | |
| 187 | Rosa alba L. | Gulab | Shrub | Bare area | Flowers & leaves | Juice of petals is used to cure eye disease (opthalmitic) and abdominal pain. | Ornamental plant. | |
| 188 | Rosa indica L. | Gulab | Shrub | Garden | Flowers & leaves | Petals are crushed; juice is extracted, which is important for blood purification | Ornamental plant. | |
| 189 | Rubus fruticosus L. sens.str. | Atchu | Shrub | Foresty area | Whole plant | Fruits are carminative and are also used for diarrhoea and looseness of intestine. | Stem and branches are mostly used as firewood while leaves are served as fodder for animals. | |
| 190 | Rosa webbiana Wall ex. Royle. | Rosaceae | Throny | Shrub | Bare area | Whole plant | The petals of these plants are collected, petals are dried, crushed and powdered; this powder in one tea spoon is poured into tea, due to which herbal tea is made for stomach ache. | In Laspur, people enclose poplars and other trees with thorny bushes of these plants, willow branches or erecting stone and mud walls to control free grazing of animals |
| 191 | Populus nigra L. | Salicaceae | Terek | Tree | Entire valley | Whole plant | ------------------- | The bark peels are used in basketry. The plant yields timber of good quality. People have started using poplar timber widely for construction of houses. |
| 192 | Populus trichocarpa Torr. & A.Gray. | Romenu | Tree | Entire valley | Whole plant | --------------- | Timber wood, fire wood and fodder | |
| 193 | Salix candida Flüggé ex Willd. | Bubahak chikar | Tree | Foresty area | Whole plant | --------------- | Mud supporter and prevent soil erosion. | |
| 194 | Salix acomphylla Boiss. | Chikar | Tree | Entire valley | Whole plant | The extract obtained from fresh leaves is taken orally to regulate menses. | Young shoots are used in basketry and as thatching material for houses. It is a best timber wood and firewood. | |
| 195 | Salix alba L. | Teli | Tree | Entire valley | Whole plant | ------------------ | The stem barkes and young branches are used in basketry, thatching material and it is also highly appropriate for cricket bats, toy bats and artificial limbs. It serves as a shade tree. | |
| 196 | Salica exigua Nutt. | Narrowleaf willow | Tree | Foresty area | Whole plant | ------------------ | Fire wood and fodder. | |
| 197 | Salix arctica Pall. | Salicaceae | Arctic willow | Shrub | Hilly area | Whole plant | ------------------ | The arctic willow is a food source for several arctic animals. |
| 198 | Bergenia stracheyi (Hook.f. & Thorns.) Engl. | Saxifragaceae | Besabur | Herb | Hill | Whole plant | Seeds, leaves, roots and latex are used for eczema, tooth ache and bleeding gums. Roots of the plants are crushed; boiled and aqueous extract is obtained called, Bisabur pooru, which is used as face cream (sun block) | Leaves are used as fodder for cattle. |
| 199 | Linaria vulgaris Mill. | Scrofulariaceae | Toadflax | Herb | Garden | Whole plant | ---------------- | Ornamental plant. |
| 200 | Verbascum Thapsus L. | Scrofulariaceae | Gordoghkaru | Herb | Sandy area | Leaves & stem | The leaves are used for dish washing especially effective in cleaning some oily and greasy utensils. Leaves are given to cattle as fodder to treat abdominal swelling. | Fodder |
| 201 | Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle | Simaroubaceae | Bakayini | Tree | Forestry area | Whole plant | Its leaves are stomach ache for cattle. | Stem is used as fire wood and branches are used for sheltering purpose. |
| 202 | Datura stramonium L. | Solanaceae | Bangedivana | Herb | Dry plains | Stem & branches | The peel from dried stem and branches, called khaf, are placed over affected parts of the body and burnt to treat rheumatic diseases. Seed smoke is considered as evil repellent and protects from evil sight | --------------- |
| 203 | Hyocyamus niger L. | Ispandur | Herb | Dry plains | Seeds and branches | Flowers, fruits and stems are heated for pan and used against backache. Its dried seeds are burnt and fumigated for the protection from evil eyes. | ---------- | |
| 204 | Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. | Patingel | Herb | Field | Leaves & fruits | ------------------- | Condiment | |
| 205 | Nicotiana tobaccum L. | Tamaku | Herb | Field | Leaves | Leaves are used as anthelmintic agent. The dried leaves are used in making snuff. | ------------- | |
| 206 | Solanum nigrum L. | Pirmilik | Herb | Field | Barries & leaves | Ripened fruits are collected to extract its juice. It is effective against eyes irritation and against sunburn. The fruits are eaten as stomachache. | It is also used as fodder for animals. | |
| 207 | Solanum tuberosum L. | Alu | Herb | Field | Whole plant | It increases fatness. The raw tuber juice is applied on burns externally. | Potatto tubers are used as vegetable; and are also the source of starch. Potatto is one of the best sourse of income. | |
| 208 | Solanum melongena L. | Solanaceae | Patigan | Herb | Field | Leaves & corm | ---------------- | Vegetable and fodder. |
| 209 | Daphne mucronata Royle. | Thymeleaceae | Lovomikini | Shrub | Upper pasture | Whole plant | Fruits/barries are grinded, paste in water and used for treatment of lumbago and backache. Barries are also used as facial cream to protect face from sunburn. | Stem is used as firewood while leaves are eaten by animals. |
| 210 | Myricaria elegans Royle | Tamaricaceae | Phaphaki | Shrub | Sandy area | Leaves & stem | Flowers are collected, dried, powdered and its paste is used in backache. | Leaves are used as fodder while stem as firewood. |
| 211 | Viola rupestris F.W.Schmidt. | Violaceae | Milkhon | Herb | Upper pasture | Flower & leaves | Flowers are dried and powdered which is used in making decoction for cough. It is also as an astringent and purgative agent. | Ornamental plant. |
| 212 | Vitis vinifera L. | Vitaceae | Droch | Climbing tree | Lower Laspur | Whole plant | Ripe fruit is cooling, laxative and diuretic. It can cause gastric problem. | It has both medicinal and nutritional value. Leaves are used in animal feeding. Stem is used for fuel. |
Table 8: Ethnobotanical profile of medicinal and economic plants of Laspur Valley.
Introduction to the study area
Laspur valley is one of the beautiful valleys of Chitral. The boundaries of Laspur are attached with Gilgit in north; Mastuj in south and highly snowy mountains divide it from Swat in west (Nusser and Dickore, 2002). Laspur valley is divided in to six main villages namely Balim, Sor-Laspur, Harchin, Broke, Raman and Gasht. These villages are adjacent to each other and form the valley of Laspur. It is located at a distance of 125 km from Chitral. It has a population approximately 10,000 people distributed in 1500 houses. The literacy rate has risen to a good rate. There are 5 colleges, 18 private and 16 government middle and high schools in Laspur valley. The elevation of Laspur valley is 8000 feet (Faizi, 2013). Temperature hardly exceeds the limit of 26°C and Minimum temperature is -15°C. Shandur, the highest polo ground of the world, is only 6 km away. Shandur is the meadow of Laspur. It is a flat piece of land which is situated at 12230 ft above the sea level. Polo the game of kings and the king of the games is the famous game of Chitral played here since 18th century. The people have a long tradition of sweet and popular music in their native language called khowar. Khowar has been much influenced by persain, its tone and pitch are sweet and gentle and its grammar has no masculine and feminine division. Khowar music has many instruments among them sitar is a stringed instrument while there are drumming instrument called dol, damama and daf. Belu and surnai are also musical instruments. The local people usually like food made up of milk, meat and grains. The bread which is a usual part of a Chitrali (Laspur) meal is unique one called Khesta Shapik. The local food has a number of Desi items some prepared in daily routine and other on special occasions. Laspur is geographically an isolated area with harsh weather conditions; winters are extremly cold. These conditions require warm and appropriate clothes and foot wear. In the past the people of Laspur made their clothes from wool. From wool cloaks, caps, socks, waist coats, blankets, gloves, scarfs and carpets etc, are made. However the fashion of these handicrafts has changed e.g., now these wears are fashionable and lighter while the modern cloak is made shorter, designed beautifully and lighter as compared to previous one (Informal interview from elders, 2014).
Data collection and preservation
Sampling process was selected for this study so those people were chosen who have deep understanding of effect and influence of medicinal and economic plants. Different methodologies were followed with respect to collection of plant material, identification, shade drying and preservation of plant specimens. Plants were organized alphabetically by family name, local name and ethnobotanical uses. During the survey interviews were carried out using questionnaire from seniors, elders, shepherds, practitioners, formers, teachers including both males as well as females to collect ethnobotanical knowledge. Among 160 informants, 50 were female and 110 were male. For this study different strategies of data collection were selected. For onlion data collection, ISI web of science, Pubmet and google scholar etc, are used. During field survey, questionnaire method of data collection was adopted in order to get more elaborate and descriptive data. Semi structure interviews were conducted with key informants. These interviews were about the local names, local uses, distribution, flowering time, wild/cultivated, habit, climate, temperature, medicinal usefulness, plant parts used, locality, economical value and other uses. The specimens were collected at different localities and different habitats. Interviews were conducted with the prepared set of questions. During survey fields, gardens and hills were visited and plants were observed and collected. Pictures of plants were taken through a digital camera, during vegetative, flowering and fruiting seasons. After plant collection, the plant specimen were cleaned, hard-pressed, dried, preserved, mounted on herbarium sheets. The determined specimens were submitted to the Department of Botany SBBU Sub-Campus Chitral after the completion of research work.The data collected was analysed, classified and tabulated to be presented in a scientific, regular and in a way easy to understand.
A total of 212 plants belonging to 55 families were explored from Laspur valley, which are used as ethnobotanically and ethnomedicinally by local inhabitants. There are 4 gymnosperms, 208 angiosperms (24 monocots and 184 dicots) plant species. Habit wise 157 plant species are herbs, 32 species are shrubs while 23 species are trees. Among Gymnosperms 2 species are shrubs and 2 species are trees while no herbs found in gymnosperms. In monocot of angiosperm all the 24 species are herbs. Among dicots of angiosperm 134 plant species are herbs, 29 are shrubs and 21 are trees. Asteraceae is reported to be largest family having maximum number of species (30) followed by Fabaceae (20 species), Poaceae (15 species), Brassicaceae (14 species), Rosaceae (12 species), Apiaceae (9 species), Solanaceae, Ranunculaceae and Salicaceae (each with 7 species), Lamiaceae (6 species), Polygonaceae (5 species), Amaranthaceae and Malvaceae (each with 4 species) and Cupressaceae, Boraginaceae, Caryophyllaceae, Chenopodiaceae, Cucarbitaceae, Grossulariaceae, Cyperaceae and Alliaceae (each with 3 species). All the other families are represented by less than 3 species. These plants are used for many purposes as Medicine, fodder, vegetable, firewood, fruit, condiment, fencing, timber, ornamental, thatching purpose, facial mask and agricultural tools etc. Based on utility 155 plants were used as fodder including gymnosperms with one species and angiosperms with 154 species (135 dicots and 19 monocots), medicinal 100 species including 2 species of gymnosperms and 98 species of angiosperms (89 dicots and 9 monocots), fire wood 47 species including 4 gymnosperms and 43 angiosperms species, vegetables 36 species of angiosperms, ornamental 31 species including 1 species of gymnosperm and 30 species of angiosperms (27 dicots and 3 monocots), timber 17 species including 1 species of gymnosperm and 16 species of angiosperms, fruit 10 species of angiosperm, facial mask/facial cream 10 species (9 angiosperms and 1 gymnosperm). Some other uses include condiments, thatching purposes, agricultural tools, shampoos, baskets and washing materials etc. Among these collected plants, 85 species are cultivable (1 gymnosperm, 11 monocots and 73 dicots) and 127 are wild (3 gymnosperms, 13 monocots and 111 dicots). All plant species collected are alphabetically arraranged on the basis of taxonomic groups i.e., Gymnosperms, Angiosperms (Monocots and Dicots) are arranged with their botanical names, local names, part used, occurrence and local practices. During investigation it is noticed that many species such as Juniperus excelsa, Ferula narthex, Heracleum maximum, Betula utilis, Vicia faba, Ribes grossularia, Fraxinus excelsior and Bergenia stracheyi etc, are extensively exploided by the local people for various ethnobotanical uses. The current study specified that all plants have medicinal and economic importance but there is a necessary to explore their important properties and develop awareness among the local community.
Ethnobotanical study of Laspur valley, Chitral, KPK, Pakistan showed that there is diversity of plant species, in spite of its harsh environmental condition, short life cycle and higher elevation. During field visit 212 plant species have been documented belonging to 55 families, consisting of 48 dicot families (184 species), 5 monocot families (24 species) and 2 gymnosperm families (4 species). The 2 families of gymnosperm are Ephedraceae and Cupressaceae. Monocot families are Poaceae, Alliaceae, Iridaceae, Cyperaceae and Xanthorrhoeaceae. Among monocots the largest species containing family is Poaceae (15 species), after that Cyperaceae as well as Alliaceae (each having 3 species), Iridaceae (2 species) and Xanthorrhoeaceae (1 species). Among dicot the largest species containing family is Asteraceae (30 species), followed by Fabaceae (20 with species), Brassicaceae (with 14 species), Rosaceae (12 species), Apiaceae (9 species), Solanaceae, Ranunculaceae and Salicaceae (each with 7 species), Lamiaceae (6 species) and other families have less than 5 species. Totally 100 species are used as medicine, 155 species as fodder, 10 species as fruits, 47 species as firewood, 36 species as vegetable, 10 species as facial mask, 31 species as ornamental, and 17 as timber wood. Some species are used as broom, condiment, hair shempo, soap and agricultural tools etc. Habit wise 157 plant species are herbs (24 monocots and 133 dicots), 32 species are shrubs (2 gymnosperms and 30 dicots) while 23 species are trees (2 gymnosperms and 21 dicots). Majority of these plants are wild. The current survey was conducted to assess and explore the traditionally vital plants of Laspur valley of Chitral with general information and their folk uses. The indigenous knowledge of plants is in danger of disappearing forever due to lack of interest among new generations. Replanting is impressive to conserve habitat [30]. Indigenous practices and information about plants are going to be vanishing just because of deficiency of printed papers and low-income cultures [31,32]. To conserve these medicinal and economically important plants, there is a great demand of conservation, management, supervision, protection plant resources and conduction of field research is impressive. Deforestation and overgrazing has declined the habitat [33]. Consumption and harvesting of plant species can often result in their genetic depletion [34]. The residants of Chitral still rely on therapeutic floras for majority of their illnesses; therefore there is a risk of plant extinction [15]. Most of the people are unaware about appropriate procedures and period of collection of live plants; due to which loss of plants occur [18]. There is miss management in grazing land. Therefore, it is very important to document and preserve this wealth of knowledge for future generations. Secondly the people have no awareness about importance of medicinal plants. Therefore, it is necessary to let the residents know the wise use of medicinal and economically important plants.
Citation: Bibi N (2019) Profile of the Medicinal and Economic Plants of Laspur Valley Chitral, Pakistan. Med Aromat Plants (Los Angeles) 8: 330. doi: 10.35248/2167-0412.19.8.330
Received: 22-Feb-2019 Accepted: 12-Mar-2019 Published: 18-Mar-2019 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-0412.19.8.330
Copyright: © 2019 Bibi N. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.