Journal of Clinical & Experimental Dermatology Research
Open Access
ISSN: 2155-9554
ISSN: 2155-9554
Case Report - (2020)
Aspergillosis refers to chronic inflammatory changes such as skin, nails, external auditory meatus, sinuses, orbits, bronchial tubes, lungs and meninges caused by some pathogenic Aspergillus. Aspergillosis is an infection caused by a type of mold (fungus). The illnesses resulting from aspergillosis infection usually affect the respiratory system, but their signs and severity vary greatly. It is a common conditioned pathogen fungus, in which Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus terreus, Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus nodulans can cause disease under certain conditions. We reported a case of irritation contact dermatitis which led to fungal infection, confirmed by repeatedly fungal microscopy and fungal culture. We found unreasonable use of topical drugs that not only caused irritation contact dermatitis, but also led to fungal infection through damage skin barrier.
Irritation contact dermatitis; Pruritic erythema; Lower limb; Fungal infection; Aspergillus nodulans
A 44-year-old man patient with half month history of swelling, ulcer, exudate and scab on left lower limb has visited. In 2019- 12-01 to 2019-12-05, this present unreasonable use of traditional Chinese medicine was continued covered for left ankle to treat gout. After the therapy, the patient developed pruritic erythema on his ankle. He later developed swelling, ulcer exudate and scab. Then, the patient arrived to a local hospital to get treated with a topical glucocorticoid and systemic antihistamines for almost one week without significant improvement. Then, he came to our hospital and diagnosed as irritation contact dermatitis cause his medical history and clinical manifestations. He was treated with intravenous drip methylprednisolone (40 mg/6 day), cephalosporium pentahydrate, loratadine citrate and fusidic acid cream (Figure 1). After his admission, we took Ankle X-ray, deep fungus culture, secretion culture and drug sensitive test repeatedly for clinical drug application. Ankle X-ray showed the surrounding soft tissues are slightly swollen. Other report raised the question of fungal infection (Figure 2). To confirm this situation, we did pathological examination. Unfortunately, it left with no evidence of fungal infection (Figure 3). Only the performance of subacute/ chronic cavernous edema dermatitis without special structures such as hyphae and spores had been shown. But the fungal microscopy and secretion culture did not let us down (Figure 2). The report showed the growth of Aspergillus nodulans (Figure 2). According to this report and clinical symptoms, we gave the patient antifungal drugs and Furosemide which reduced lower limb edema. The swelling, ulcer, exudate and scab were significantly relieved before discharge. No recurrence was found on follow-up at 6 months (Table 1).
| Collection date | Return date | Test items | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-12-17 | 2019-12-20 | Deep fungal culture identification | Negative |
| 2019-12-17 | 2019-12-23 | Secretion culture identification | Aspergillus nidulans |
| 2019-12-20 | 2019-12-22 | Secretion culture identification | Negative |
| 2019-12-20 | 2019-12-23 | Deep fungal culture identification | Negative |
| 2019-12-23 | 2019-12-25 | Secretion culture identification | Negative |
| 2019-12-24 | 2019-12-30 | Fungal culture | Aspergillus nidulans |
Table 1: The test of the patient and the result.
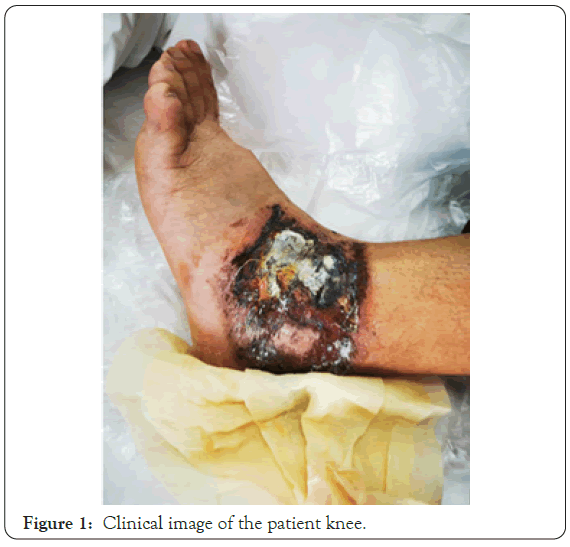
Figure 1: Clinical image of the patient knee.
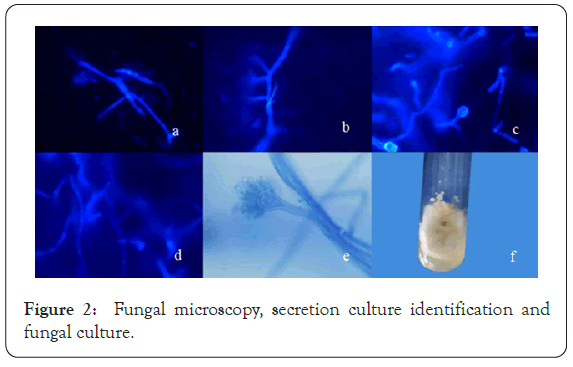
Figure 2: Fungal microscopy, secretion culture identification and fungal culture.
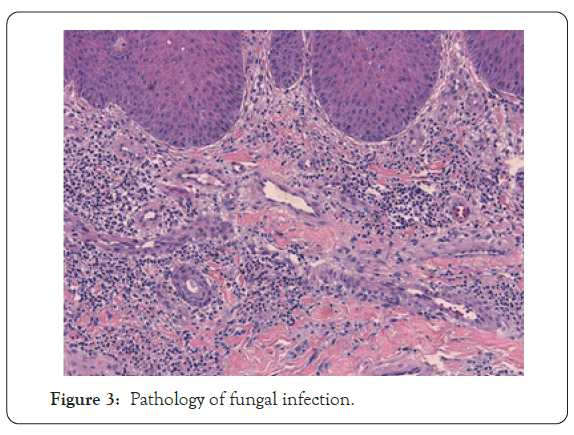
Figure 3: Pathology of fungal infection.
Aspergillosis refers to chronic inflammatory changes such as skin, nails, external auditory meatus, sinuses, orbits, bronchial tubes, lungs and meninges caused by some pathogenic Aspergillus. Aspergillus is a common conditioned pathogen fungus, in which Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus terreus, Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus nodulans can cause disease under certain conditions [1,2].
In this case, the patient did not show the symptoms of the fungal infection initially. So, at the beginning we diagnosed as irritation contact dermatitis only. Along with the disease development, test of fungal microscopy and secretion culture, we realize about the fungal infection. We consider this disease was caused by unreasonable use of traditional Chinese medicine covered and longterm use of hormones aggravate this situation [3,4]. Unreasonable use of medicine could lead to tissue damage and inflammation. Impaired barrier function also participates by promoting bacterial biofilms and creating an environment favoring sensitization [5]. We believe that the patient's medication is similar to TTS (Transdermal Therapeutic System). And Romita P et al. [6] thinks on the basis of reports on sensitization to TTS, there is sufficient evidence to confirm that such therapeutic systems can cause ACD (Allergic Contact Dermatitis), being an ideal environment to elicit contact allergy by long-term use of glucocorticoid or immunosuppressive agent. Long-term use of glucocorticoid could lead to immunosuppressive and can change the form of lesion. Glucocorticoid can aggravate fungal infection. Therefore, during rounds, it is needed to pay attention in the changes in skin damage of patient. Such as contact dermatitis patients during hospitalization and anti-allergy treatment, no significant improvement was seen. Should consider irritant contact dermatitis and fungal infections are mutually reinforcing relationship, further examination and treatment which fungal microscopy, secretion culture antifungal and antifungal agents can help to improve the condition of patients. Currently correlation detection means of skin and skin structure infections fracture and conventional separation methods relative isolation and identification of the type of imperfect relationship be-tween pathogens clinical phenotype is not clear. This case alert us note that shallow fungal disease has a wide range of pathogenic bacteria. We should not only pay attention to contact dermatitis, but also pay attention to pathogenic bacterial infections caused by skin damage. We should be vigilant for patients who are obsessed with Chinese medicine and warn the patient not to blindly believe in the natural and pollution-free claims of herbal treatment. Drug treatments with complex ingredients, unknown ingredients and unknown sources may cause serious consequences. In this case, if the patient continued to use the so-called traditional Chinese medicine treatment on the unhealed wound, the infection may be aggravated; the patient may have distrust of the doctor due to longterm failure to improve. In a complex medical environment, we must not only focus on the treatment of patients' diseases, but also strengthen health education for patients. A moderate increase in patients’ awareness of the disease can increase patient compliance, shorten treatment time, and reduce the chance of recurrence of the disease.
None to declare
Citation: Sun S, Nong X (2020) Irritation Contact Dermatitis Lead to Fungal Infection: Report of One Case. J Clin Exp Dermatol Res. 11:539.
Received: 26-Oct-2020 Accepted: 09-Nov-2020 Published: 16-Nov-2020
Copyright: © 2020 Sun S, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.