Journal of Psychology & Psychotherapy
Open Access
ISSN: 2161-0487
ISSN: 2161-0487
Research Article - (2021)Volume 11, Issue 5
When adolescents are taught the skill of social problem solving as a mediating variable in relation to the variables of parenting and family styles, adolescents’ attitudes toward drug use in adolescents will be reduced. They were selected from the Cochran’s formula and examined. Then, questionnaires including Bamrind parenting styles, attitudes toward addiction, social problem-solving skills in both adaptive and maladaptive dimensions, and a socioeconomic level questionnaire were administered. To evaluate the research results, statistical method of path analysis was used and to evaluate the adequacy of the model, appropriate statistical indicators were used. Based on the results of this study, the components of parenting styles, the component of maladaptive social problem-solving skills and the component of attitudes toward addiction have no significant effect on attitudes and drug use, but the component of adaptive social problem-solving skills has no significant effect on attitudes and drug use. This article will provide statistical reasons for the impact of parenting styles and family variables on social problem-solving mediation on adolescent addiction attitudes.
Background and purpose: Drug use is one of the most important and serious issues at the international level, which has been studied from various aspects. Drug use is a multifaceted phenomenon that affects all fundamental pillars of society. Numerous studies have highlighted risk factors and protectors such as family and individual factors against drug use. However, few studies have emphasized the role of mediators such as social problem-solving skills. Therefore, this study was designed to predict the attitude of drug use in adolescents based on risk factors of family education with the mediation of social problem solving skills in attitude to addiction in order to design a model to explain the tendency to drug use.
Methods: In this study, which was a descriptive and correlational study, the study population was students from all educational levels in Ghaemshahr. A total of 378 people were selected using the Cochran’s formula. Then the questionnaires that are included the parenting styles, Bam rind parenting styles (33 questions), addiction attitudes (53 questions), social problem-solving skills (55 questions), a socio-economic level questionnaire was administered to them. In this study, statistical method of path analysis was used. To evaluate the adequacy of the model, Kay Do index, normalized fitness index, adaptive fitness index, fitness index, square root of estimation error, adjusted fitness index, incremental fitness index and abnormal fitness index were used.
Findings: In estimating the coefficients of the effect of family socioeconomic status (with 2.35=2.35 trajectory coefficient) in predicting the attitude towards drug use in adolescents, there is a direct, positive, and significant relationship. Also, in estimating the impact coefficients of adaptive problem-solving skills (1.63, path coefficient 1.33) in predicting attitudes towards drug use in adolescents, direct and positive but meaningless relationship and incompatible problem solving (, t=3.39 0.27 path coefficient) in Predicting attitudes toward drug use in adolescents is a direct, significant, and negative relationship, and in estimating the effects of parenting styles (t=-2.48 trajectory coefficients). -19) There is a direct, negative, and significant relationship in predicting attitudes towards drug use in adolescents.
Conclusion: Based on the results of this study, the components of parenting styles the component of incompatible social problemsolving skill and the component of attitude towards addiction on attitude and drug use have a significant relationship. Drug use is not a significant relationship.
Attitude; Educational risk factors; Family risk factors; Model design
Drug use, which is a multifaceted phenomenon, is one of the most serious human problems in recent years, which weakens the foundations of human society, and its prevention requires the application of various theories in various scientific disciplines and methods and techniques. The results of a study have shown that drug use can have many negative messages due to various factors such as family social group’s friends’ personality and individual factors [1].
1. The biological-psychological-social phenomenon of drug use in adolescents is one of the most critical issues facing today’s societies. Drug use-alcohol and tobacco in adolescents 12 to 18 years old, especially in high school is still a major problem in many countries.
2. In fact, middle school is a vulnerable time to start taking drugs.
3. According to a recent study, 31 percent of eighth graders had a history of alcohol use and 19.6 percent had a history of drug use.
4. Various studies of poor family functioning drug use in the family inefficient parental supervision-lack of family cohesion incorrect parenting practices-lack of emotional connection with parents-lack of family support-drug availability-conflict between parents-lack of skills to solve the problem Social Issue-Inadequate Social Environment-Inadequate Cultural Environment-High-risk group of friends Variables related to individual injuries such as outbreak-violence-aggression-stress anxiety and lack of academic progress have been introduced as risk factors.
5. According to a 2018 study, nearly 30 percent of teens have experienced drug use. The most common experience of drug use was during school. The study found that 23.9 percent of teens who experienced drugs were between the ages of 12 and 17.
6. It is difficult to treat addiction and break its vicious cycle, and the community’s treatment system requires different approaches to medication, psychotherapy, rehabilitation, and rehabilitation. In such cases, prevention is logically a substitute for treatment. The purpose of prevention is to delay the onset of drug use in society. Thus, preventing people from using drugs in the community means preventing heavy costs from being imposed on the community by people living with AIDS and other diseases-reducing productivity in the workplace-the occurrence of crime and not endangering the next generation. According to Lowe, drug use is a quite common phenomenon among adolescents today. About 70 percent of teens between the ages of 12 and 18 have experienced drug use, such as alcohol and psychedelics, in the pre-high school years. The researchers found that taking drugs once or more at this age could put them at risk for addiction and educating teens on how to deal effectively with drugs could have a significant impact on attitudes and negative attitudes. Therefore, one of the precautionary measures against drug use is to inform people about drugs and their dangers and harms correcting and changing people’s attitudes from a positive attitude towards a negative attitude towards addiction and finally the correct treatment methods and the skill of solving a social problem and dealing with it.
7. Recent research based on the role of parenting methods and social problem-solving skills in both adaptive and maladaptive dimensions in the tendency to drug use found that social interaction such as family bonding is the strongest predictor of adolescent drug use that directly and indirectly from It predicts drug use through individual and social capabilities.
8. M-JS Kafman (2013) found in their research that drug use in maladaptive families in which adolescents have emotional and behavioral problems is higher than in maladaptive families where the family is more mentally healthy.
9. Claund Mark T. Finberg found that harmful family factors such as risk factors and social factors in school can be an especially important factor in adolescents’ drug addiction. Correcting and solving the social problem is a more effective determinant of adolescents ‘tendency to use drugs, and unlike social factors, it can be the most important risk factor and protector in adolescents’ negative tendency to use drugs. These results show a causal interaction between the preservative and suggest that to investigate substance abuse in adolescents, attention should be paid to the interaction and interaction of adolescents with family factors.
10. According to the official statistics of addiction and the fight against narcotics in Iran, a total of 2 million and 880 thousand people are consuming drugs. According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime, in 2019, about 35 million people worldwide suffer from drug-related disorders and need medical care.
11. Numerous studies have emphasized the role of family and individual variables as risk factors and drugs. However, the direct and indirect relationship between these factors and how it affects drug use is not truly clear. The attitude towards drug use among adolescents should pay attention to this issue based on risk and educational factors and according to the skill of solving the social problem, and finally provide a model in explaining the tendency to use drugs. Barbara L; Victoria H; Susana M; Rabert C; Schalach R; Christian M; Jou S; Michael J; Mark T [2].
The present study was conducted on high school students in Ghaemshahr in the academic year 1397 and 1398. In terms of purpose other than applied research and in terms of research method, a descriptive correlational study of the statistical population of the present study includes 26593 adolescent girls and boys in the city. In line with the purpose of the research, 378 people (193 boys and 185 girls) were selected by stratified random sampling according to the volume based on the regional Indian category of education and using the Cochran’s formula. The age range of the subjects in this study was 16-19 years. The frequency of parents in this study was examined in terms of income level and occupation. The research instrument consisted of 4 questionnaires in which the questionnaires a) Attitude Scale.
Include 50 questions whose components are 1) Attitude towards the physiological effects of drugs 2) Attitude towards the psychological effects of drugs 3) Attitude towards the effects Social Drugs 4) Attitude towards the dangers of drug use 5) Attitude towards drug use or interest in drug use. The validity of the test was greater than or equal to 0.38 and the validity of this test in the subscales of drug attitudes was minimum alpha 0.79 (for the scale of physiological effects of drugs) and maximum 0.87 (for the scale of interest in drug use). The total validity of the scale was 0.94. B) Social problem-solving skills scale includes 25 questions in two dimensions of adaptive attitude towards problem solving, logical style and maladaptive negative attitude towards problem solving, impulsive-careless style, avoidance Style.
Using Cronbach’s alpha method to evaluate the validity of the factors of the social problem-solving questionnaire, alpha coefficients for each of the factors of positive orientation towards the problem, negative orientations towards the problem, logical problem solving, avoidance style and carelessness/aggression style 0.68,0.75,0.62,0.68,0.68 and the alpha factor of the whole instrument were 0.69 69. C) Parenting scales include 30 questions and three components that include authoritarian parenting style, authoritarian parenting style and negligent parenting style. In this questionnaire, the narrative coefficients of Beria for easy, authoritarian, and authoritative styles were equal to 0.81, 0.86 and 0.78. Also, the internal consistency coefficients and validity of the questionnaire for negligent, authoritarian, and authoritarian methods were 0.69, 0.70 and 0.79, respectively. D) Socioeconomic status questionnaire included questions related to personal, educational, occupational characteristics, monthly and annual income, housing characteristics, vehicle, and number of annual trips among students. To study and compile the model, the statistical method of solving structural equations and LISREL software were used. To evaluate the adequacy of the model, chisquare, normative fit index, adaptive fit index, goodness fit index, squared root of estimation error, adjusted goodness index, incremental fit index and non-normalized fit index were used [3].
Findings
The present study investigates the relationship between attitudes and drug use and four components that include family socioeconomic status, adaptive social problem solving skills, maladaptive problem-solving skills, and parenting styles. Table 1 shows the results of path analysis and determination of path coefficient, value of t and coefficient of determination of components. The socio-economic status of the family (t=-2.35, coefficient of 0.15) has a relationship (direct, positive, and significant) in predicting attitudes toward drug use in adolescents. Problem-solving skills not consistent with (t=1.62, path coefficient 0.13) influence predicting attitudes toward substance use in adolescents (direct positive but not significant relationship). Incompatible problemsolving skills with.(t=-3.39, path coefficient-0.27-) in predicting attitudes toward substance use in adolescents (in a direct negative and significant relationship) parenting styles with (t=- 2.48, path coefficient-0.19) in predicting Attitude and substance use influence adolescents (direct negative and significant relationship). As can be seen in Figure 1, there is a significant relationship between the components of family socio-economic status, adaptive problem-solving skills, and parenting styles other than the component of adaptive problem-solving skills.
| Result | Statistical t | Coefficient of the path | Dimensions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Significant | 2/35 | 0/15 | Socio-economic status of the family |
| Not significant. | 1/62 | 0/13 | Adaptive problem-solving skills |
| Significant | -3/39 | -0/27 | Incompatible problem-solving skills |
| Significant | -2/48 | -0/19 | Parenting styles |
Table 1: Results of path analysis of the attitude model to drug use in the situation of standard coefficients.Result statistical t coefficient of the path dimensions.
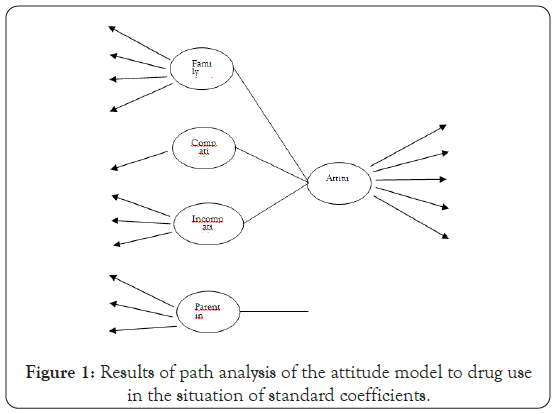
Figure 1: Results of path analysis of the attitude model to drug use in the situation of standard coefficients.
As can be seen, the introduction of maladaptive problem-solving skills and parenting styles is negative, and the components of family socioeconomic status and the introduction of adaptive problem-solving skills are positive. It does not make sense, (Figure 2) the main model of research in the meaningful state of coefficients in community problem solving skills, parenting styles, family level and attitudes toward drug use (Table 2) examines the contribution of each component of attitudes toward drug use in adolescents. (0.95) has the greatest effect and physiological effects with standard factor load (0.64) have the least effect in explaining the attitude towards drug use (Table 3) examines the contribution of each component of adaptive problem-solving skills in adolescents.
| Component priority in explaining the variable | Result | The coefficient of determination R2 |
Standard Factor Load | Sub-component |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fifth | Significant | 0/40 | 0/63 | Attitude towards physiological effects |
| Fourth | Significant | 0/50 | 0/71 | Attitude towards psychological effects |
| First | Significant | 0/90 | 0/95 | Attitude towards social effects |
| Third | Significant | 0/42 | 0/65 | Attitude towards risks |
| Second | Significant | 0/68 | 0/83 | Attitude towards consumption |
Table 2: Status of variables explaining attitudes toward consumption.
| Priority | Result | The coefficient of determination R2 |
Standard Factor Load | Sub-component |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Significant | 0/80 | 0/89 | Positive attitude |
| Second | Significant | 0/33 | 0/58 | Problem solving |
Table 3: Status of variables explaining adaptive problem solving skills.
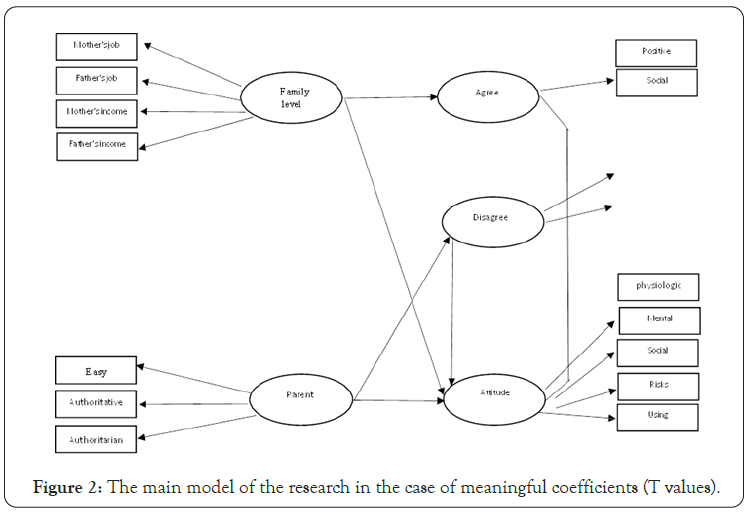
Figure 2: The main model of the research in the case of meaningful coefficients (T values).
According to Table 3, also the results of confirmatory factor analysis. Has a compatible issue (Table 4) examines the contribution of each component of maladaptive problemsolving skills in adolescents. According to Table 4, the results of confirmatory factor analysis also show the factor load of each of the components of maladaptive problem-solving. The effect of social style with standard factor load (0.76) has the least effect on explaining maladaptive problem solving skills (Table 5) examines the share of each of the components of the socio-economic level of the family in adolescents) And the most impact and the mother’s job with a standard factor load (0.72) has the least impact on explaining the family situation (Table 6) examines the share of each of the components of parenting styles in adolescents. Careful parenting with a standard factor load (0.73) has the least effect on explaining parenting [4].
| Priority | Result | The coefficient of determination R2 |
Standard Factor Load |
Sub-component |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Significant | 0/64 | 0/80 | Negative attitude |
| Third | Significant | 0/58 | 0/76 | Avoid solution |
| Second | Significant | 0/62 | 0/79 | Impulsive |
Table 4: Status of variables explaining maladaptive problem solving skills.
| Priority | Result | The coefficient of determination R2 |
Standard factor load | Sub- component |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fourth | Significant | 0/52 | 0/72 | Mother's job |
| Third | Significant | 0/53 | 0/73 | Father's job |
| Second | Significant | 0/59 | 0/77 | Mother's income |
| First | Significant | 0/68 | 0/83 | Father's income |
Table 5: Status of variables explaining family status.
| Priority | Result | The coefficient of determination R2 |
Standard Factor Load | Sub-component |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Second | Significant | 0/54 | 0/74 | Easy parenting |
| First | Significant | 0/64 | 0/80 | Authoritarian parenting |
| First | Significant | 0/61 | 0/78 | Authoritative parenting |
Table 6: Status of the variables explaining parenting.
The aim of this study was to predict the attitude toward drug use among adolescents based on educational-family risk factors and to design a model to explain the tendency to use drugs in adolescents. According to Table 1, it can be concluded that the socio-economic status of the family is a direct and significant predictor of adolescents’ attitudes toward drug use. (Standard coefficient 0.15 and t=2.33) This relationship shows that with increasing socioeconomic level of families, negative attitudes toward drugs will improve and these results with the findings of Ghobadipour et al. [12] Hosseini et al. [13] Seidan et al. [14]. It was also observed that the relationship between adaptive problem solving skills in predicting drug use in adolescents (standard coefficient 0.13 F=1.62), although positive, is not significant. This relationship shows that by increasing social adaptive problem solving skills, attitudes toward drugs can be improved in adolescents, and this finding is supported by the findings of Levy et al. [7] Barbara et al. [8] Michelle J. et al. [10]. Corresponds to Ghobadipour et al. [12]. In addition, the results of Table 1 shows that maladaptive problem-solving skills in predicting drug use in adolescents have a direct, negative and significant relationship (standard coefficient -0.15, t=2.33). This relationship shows that problem-solving skills decrease with learning. Social maladaptation can improve attitudes toward drugs in adolescents. This finding is consistent with the results of other researchers. Finally, the results of the study show that parenting styles are also directly, negatively and significantly related to attitudes toward substance use in adolescents (standard coefficient-0.19, t=-2.48), but authoritative parenting style is a positive predictor of negative attitudes. Adolescents are addicted to drugs. This relationship shows that learning the correct parenting practices can improve attitudes toward drugs in adolescents. Findings with the results of Robert . et al. [9] Ghobadipour et al. [12] Johnston et al. [4] it is consistent. According to Table 2, the results show that in the variables that explain the attitude towards drug use, the component of attitude towards social effects is the strongest explanatory of the attitude towards drug use (standard coefficient 0.95, R2=0.90). These results are consistent with the findings of Sharon Levy et al. [7] Michelle. et al. [10] Louise et al. [1]. The reason may be that the subjects are more mature and the peer group and friends are the most influential. On this group of people [5-14].
Studies show that drug use is one of the worst human problems in recent years, which undermines the foundations of human society and is not limited to Iran. That is why the concern of its expansion is the concern of all governments and nations. The prevalence and rate of consumption varies from time to time and from community to community. But what is clear is that its consumption and prevalence are increasing day by day, and as we get closer to the present, the age decreases and teenagers and young people access it easily and at a low cost. Over the years, research has shown that a set of factors can play a role in the tendency to use drugs, among which individual, environmental, social and family factors are the most important. Positive and negative attitudes toward drug use were introduced as one of the indicators of risk and protective factors. Therefore, modifying people’s attitudes about addiction from a positive to a negative attitude and training the necessary skills to solve the problem in the face of this social problem can prevent them from becoming addicted to drugs.
It is suggested that the model of social problem solving skills training be designed both at the family level and at the school level. Because paying attention to this, in addition to teaching the correct way of educating parents with adolescents, increases their skills in solving individual and social problems. It is recommended that educational environments with a combination of prevention approaches based on family and social context in the form of planning and training social problem solving skills in a strategic and operational way to raise their level of awareness in effective performance in the face of this social tension. Due to the impact of parenting styles on the tendency and attitude towards drug use, it is necessary for all schools and government agencies to develop appropriate educational programs in recognizing parenting styles and informing them of risk factors. In general, research on social sciences and humanities is particularly complex and imposes many restrictions on researchers in conducting research. Therefore, the questionnaires used in the present study were in the field of measuring the variables that people when using such questionnaires in most cases chose answers that are socially friendly or these questionnaires out of ease. They responded with care and reluctance. In addition, the use of the questionnaire itself is considered as a limitation in human research, which means that it examines the attitudes of individuals and not the reality under study.
Citation: Parsian M, Eagli SK (2021) Explain the Causal Relationships between Family Risk Factors and Attitudes toward Substance use and the Mediating Role of Social Problem Solving. J Psychol Psychother. 11:407.
Received: 14-May-2021 Accepted: 28-May-2021 Published: 04-Jun-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/2161-0487.21.11.407
Copyright: © 2021 Parsian M, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.