Journal of Antivirals & Antiretrovirals
Open Access
ISSN: 1948-5964
ISSN: 1948-5964
Research Article - (2021)
Since the inception of the COVID-19 pandemic, a large number of clinical trials on Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) for SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19 disease) have been registered. The information is scattered at different resources making it difficult for researchers, scientists, health care professionals, and the general public to remain up-to-date on the latest CAM clinical trials being registered for COVID-19. The Complementary and Alternative Medicine Clinical Trials Database CoVAM is developed to provide the scientific community easy access to the latest information on the CAM clinical trials registered globally for COVID-19 disease. To develop the CoVAM, MySQL was used. API management was done through NodeJs (with express), and Angular 11 was used as front end. The CoVAM is a single platform organized by ten CAM subtypes such as Acupuncture, Auricular point pressing, Ayurveda, Chiropractic, Homeopathy, Psychotherapy, Siddha, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), Vitamins and dietary supplements, and Yoga/Exercise. Each subtype has information on CAM medicines/ therapy being registered, the full title of the clinical trial, sponsor name, sponsor protocol number/ID, age of the population, study type, actual number of participant enrolment for the trial, followed by the start date, phase, and status of the clinical trial. Each fact is linked to the clinical trial databases from where the information was procured. Additionally, CoVAM is hyperlinked with PubMed for providing recent updates on COVID-19 and CAM research. To the best of our knowledge, CoVAM is a first-of-its-kind database that provides comprehensive information on globally registered CAMs related clinical trials conducted on COVID-19 disease.
Alternative medicine; Clinical trial; COVID- 19; Database; SARS-CoV-2
COVID-19 is a severe acute respiratory disease caused by SARS- CoV-2 with clinical manifestations such as dry cough, sore throat, fever, body ache, difficulty in breathing, etc., [1]. The virus transmits mainly through discharge from the nose or droplets of saliva when person having SARS-CoV-2 infection coughs or sneeze. Old age people and those with co-morbid medical conditions are at high risk of developing serious illness. Globally, there have been 156,496,592 confirmed cases and 3,264,143 COVID-19 related deaths as per WHO until 8th May 2021 [2].
The first generation of vaccines has been approved for emergency use by drug regulatory authorities of different nations. However, they are not advised to people with allergies, autoimmune disorders, suppressed immune systems which covers a large segment of the global population [3,4]. Moreover, the continuous genetic variation in the SARS-CoV-2 genome is creating new variants such as Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, etc. which are influencing the efficacy of vaccines. The virus is finding new ways to escape our immune system, and if in-case that happens, we will have to find alternative ways to protect ourselves. Even after taking the prescribed doses of vaccines, a group of people are getting COVID-19 disease with mild to moderate symptoms. Scientists around the globe are interested in finding the solution to reduce the impact of adverse symptoms observed in patients suffering from COVID-19 disease. Since the inception of the COVID-19 disease, public health practitioners are promoting and trying to find the solution for the management of COVID-19 disease through complementary and alternative medicine (CAM; diagnostic and therapeutic disciplines used along with conventional medicine) [5,6]. In China itself, the total number of confirmed cases treated by Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has reached 60,107 [7]. An Ayurvedic (Traditional Indian System of Medicine) drug ‘Coronil’ has got certification from AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga, and Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, and Homeopathy) Ministry in India as a drug that can be used as a supporting measure in COVID-19 disease [8-10]. Another drug AAYUDH Advance is also announced as a clinically tested medicine for COVID- 19 management and treatment [11]. Since the beginning of the SARS-CoV-2 outspread to the world, researchers and clinicians have started clinical trials on CAMs, and registered their studies at various clinical trial databases of the world. To the best of our knowledge, there is only one database available on TCM clinical trials on COVID-19; however, an all- inclusive database on different CAM subtypes is still unavailable [12]. Sieving out information pertaining to CAM from multiple clinical trial-related databases can prove to be a cumbersome and time taking process. In order to make the process of extracting information related to CAM straightforward, a comprehensive and user-friendly database “CoVAM” (COVID-19 Alternative Medicine Clinical Trials Database) was developed. It provides the scientific community with the information of CAM clinical trials on SARS- CoV-2 at a single platform, thereby making the process of searching user-friendly and time-saving, preventing the knowledge obtained from these clinical trials from getting lost in the vast ocean of COVID-19 clinical trials. “CoVAM” helps in knowing the CAM drugs/therapies on which clinical trials are going and if that drug/therapy has been registered for one or more times.
Records on COVID-19 and CAM comprising acupuncture, auricular point pressing, ayurveda, chiropractic, homeopathy, psychotherapy, siddha, TCM, yoga and exercise, and vitamins and dietary supplements were systematically collected, filtered, and compiled using a query set of keywords/synonyms till 26th March 2021 (S1). Briefly, the screening of records was performed on 15 different clinical trial databases from where the records on COVID-19 clinical trials and CAM were included. In addition, freewheeling searches of the health ministry and government websites of different countries were also performed to retrieve all the relevant records on registered CAM-related COVID-19 clinical trials (Table 1). If the same medicines/therapy were registered at two or more databases then they were clubbed as one entry represented by all databases links. However, if the title, sponsor protocol number/ID, studies type, number of enrolments, the start date of the clinical trial, phase, or status of clinical trial varies then they were considered as separate entries; which could be of interest to certain readers. Two authors Zoya Mann and Avani Srivastava screened all the clinical trials. Another author Vishwas Sharma merged the records and performed a quality check of a random selection of 10% of all the records. Discrepancies were resolved when a consensus was not reached, a fourth author Avani Srivastava was consulted. Proofreading of all the included records was performed by Zoya Mann and Avani Srivastava.
| S No. | Database | Database link |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Clinical Trials | https://clinicaltrials.gov/ |
| 2 | EU Clinical Trials Register | https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/search |
| 3 | Global Clinical Trials Data (GCT) | https://www.globalclinicaltrialsdata.com/ |
| 4 | Chinese Clinical Trial Register (ChiCTR) | http://www.chictr.org.cn/searchprojen.aspx |
| 5 | Clinical Trials Registry- India (CTRI) | http://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials |
| 6 | Pan African Clinical Trials Registry | https://pactr.samrc.ac.za/ |
| 7 | Clinical Research Information Service (CRIS) | https://cris.nih.go.kr/cris/en/search |
| 8 | EBSCO Information Services | https://www.ebsco.com/ |
| 9 | Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT) | https://www.irct.ir/search/ |
| 10 | Peruvian Registry of Clinical Trials | https://ensayosclinicos-repec.ins.gob.pe |
| 11 | Brazilian Clinical Trials Registry (RUBEC) | https://ensaiosclinicos.gov.br/ |
| 12 | Australian New Zealand Clinical Trials Registry (ANZCTR) | http://www.anzctr.org.au/ |
| 13 | Thai Clinical Trials Registry (TCTR) | http://www.thaiclinicaltrials.org/# |
| 14 | NIPH Clinical Trials | https://rctportal.niph.go.jp/en/result |
| 15 | European Network of Centres for Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacovigilance (ENCePP) | http://www.encepp.eu/encepp/studySearch.html |
Table 1: Databases screened and their respective links.
A total of 292 clinical trials on CAM were obtained after the screening of records using a set of keywords/synonyms (S1). For easy access and option for periodic update of information, the database CoVAM was developed using MySQL. API management was done through NodeJs (with express), and Angular 11 was used as front end.
CoVAM database features
It provides end-user the facility to view and navigate through different CAM topics. While going through a specific CAM subtype such as Ayurveda, Auricular point pressing, etc. The end-user can search all entries/data or can rapidly perform a selective search by selecting a particular heading from the drop-down menu above the search bar and typing the relevant search term in the ‘search box’. The CoVAM also gives the featured information of COVID-19 clinical trial statistics, and ongoing research on COVID-19 and CAM via hyperlinking to PubMed [13,14]. The primary functions are summarized in Figure 1.
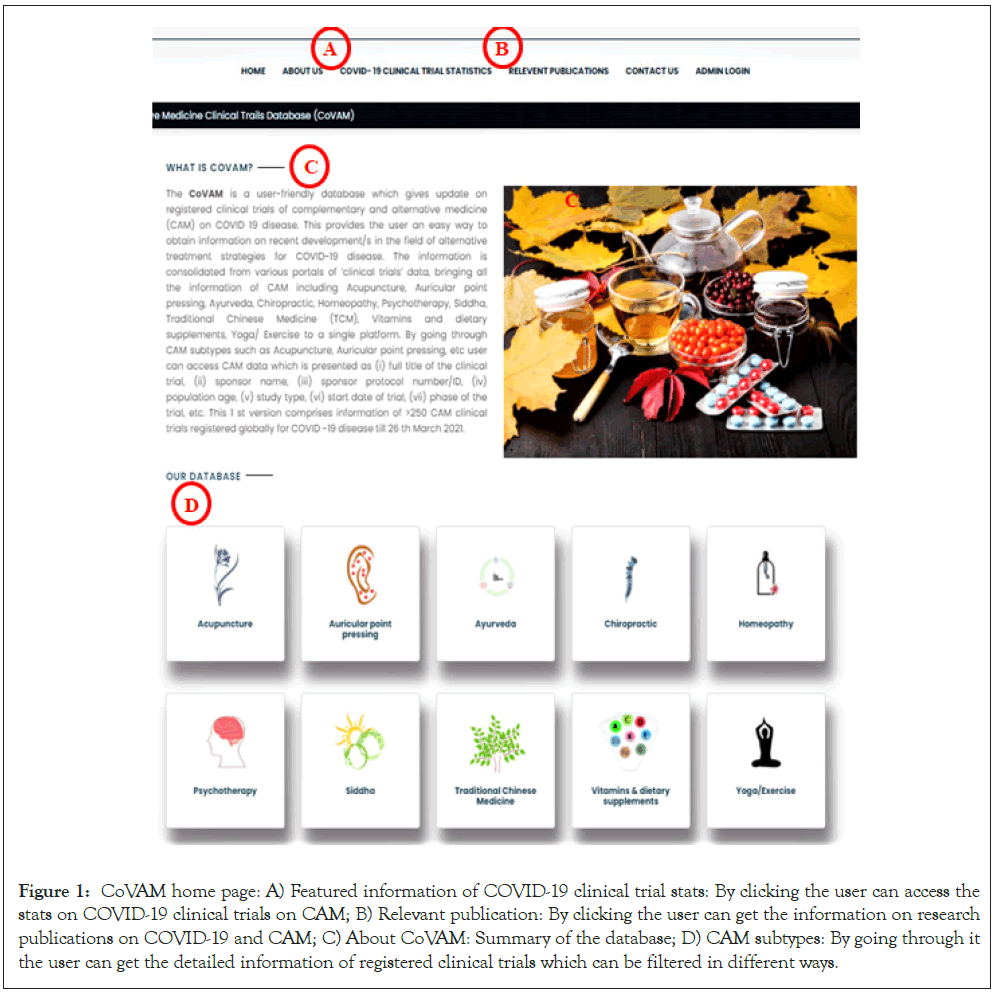
Figure 1: CoVAM home page: A) Featured information of COVID-19 clinical trial stats: By clicking the user can access the stats on COVID-19 clinical trials on CAM; B) Relevant publication: By clicking the user can get the information on research publications on COVID-19 and CAM; C) About CoVAM: Summary of the database; D) CAM subtypes: By going through it the user can get the detailed information of registered clinical trials which can be filtered in different ways.
The CoVAM database gives comprehensive and all-encompassing information about the CAM-related clinical trials on COVID-19 disease. For updated research publications on CAM and SARS- CoV-2, the database is hyperlinked to PubMed. Our database would be useful for scientists, healthcare personnel, and the common man involved with finding the solutions for the management of COVID-19 disease. The 1st version of CoVAM includes >250 COVID-19 related clinical trials on our CAM database, however, we are still working and will periodically update the entries of trials which will be reflected on the CoVAM ‘Latest News’ section.
We included ten CAM subtypes i.e, acupuncture, auricular point pressing, ayurveda, chiropractic, homeopathy, psychotherapy, siddha, TCM, yoga and exercise, and vitamins and dietary supplements, for this release but will expand our horizon to ensure that the users get the latest and updated information on COVID-19 related clinical trials on CAM. There is a duplication of 14 clinical trial records which we have uploaded as separate entries, as they have different registration dates at different databases (particularly the Chinese Clinical Trial Register (ChiCTR) and ClinicalTrials (NCT) trials registered at Global Clinical Trials Data (GCT) database); therefore, records should be interpreted with caution. Although, along with freewheeling search, 15 databases were referred there is a great possibility that few clinical trials or databases might have not been covered. Hence, we appreciate and look forward to end-user feedback to guide us for further enhancements.
Scientists and health care personnel are seeking alternative options to manage vulnerable groups for whom the COVID-19 vaccines are not advised. CoVAM will help in providing factual information regarding ongoing clinical trials on CAM under one roof without having to perform the cumbersome task of sieving out information through various public search web engines. Hence, it will help health care professionals by letting them keep tabs on ongoing trials in different fields of CAM thereby, aiding them in the treatment that they can provide to improve a patient’s method of care. The database has been made keeping in mind the needs of the society and the fact that with each other’s support we may exterminate COVID-19.
CoVAM is free and open to all users and there is no login requirement. CoVAM can be accessed online.
We thank all the members of the Society for Life Sciences and Human Health for their help and support. The grammar was checked by Grammarly software and the plagiarism was checked by Duplichecker software.
The work is done for humanity by the members of the non- profitable charitable trust (Society for Life Sciences and Human Health, 84/8, K, Allahpur, Prayagraj, U.P, India) and is not supported by any funding organization.
None declared.
VS and AS conceived and designed the project. ZM, AS, and VS performed the screening. AN, and AV worked on the designs. AS developed the database. VS, AS, ZM, and AN wrote the first draft of the manuscript. AN, VS, and PR reviewed and wrote the final version of the manuscript.
Citation: Sharma V, Mann Z, Sharma A, Srivastava A, Raghav PK, Singh R, et al. (2021) CoVAM: Complementary and Alternative Medicine Clinical Trials Database for COVID-19 Disease. J Antivir Antiretrovir. 13:228.
Received: 02-Jul-2021 Accepted: 16-Jul-2021 Published: 23-Jul-2021 , DOI: 10.35248/1948-5964.21.13.228
Copyright: © 2021 Sharma V, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.