Chemotherapy: Open Access
Open Access
ISSN: 2167-7700
ISSN: 2167-7700
Perspective - (2023)Volume 11, Issue 3
Breast cancer is a group of diseases in which cells in breast tissue change and divide uncontrolled, typically resulting in a lump or mass. Most breast cancers begin in the lobules (milk glands) or in the ducts that connect the lobules to the nipple.
Breast cancer is usually detected during screening, before symptoms appear, or after a woman notices a lump. The majority of mammogram masses and breast lumps are benign (not cancerous). When cancer is suspected, tissue for microscopic examination is typically obtained through a needle biopsy and, less frequently, through a surgical biopsy. The type of biopsy is determined by a number of factors, including the size and location of the mass, as well as patient factors, preferences, and resources.
Types of breast cancer
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): Earliest from of cancer is often DCIS than it progresses to IDC. DCIS define as a neoplastic proliferation of epithelial cells confined to the ductal system and it characterized by the subtle to marked cytological atypia as well as an inherent tends to progress DCIS. In figure 1 there is an over view differences between Ductal Carcinoma in situ and Wall of duct. Invasive ductal carcinoma may not cause any symptoms at first. A screening mammogram (X-ray of the breast) frequently reveals an abnormal area, prompting additional testing (Figure 1).
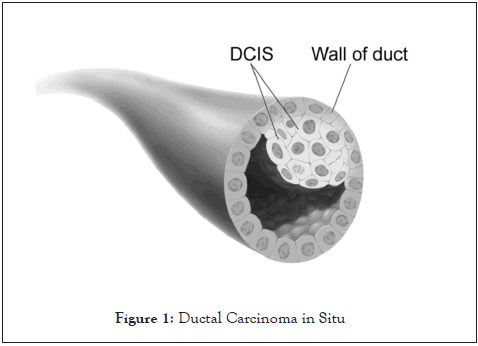
Figure 1: Ductal Carcinoma in Situ.
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): Once the cells have invaded through the basement membrane and outside the duct it is called Invasive Ductal Carcinoma. It is one of the most common types of breast cancer, also known as infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Invasive ductal carcinomas account for approximately 80% of all breast cancers. It spread to the breast tissues around it and although it can affect women of any age, it is more common as women get older. Approximately two-thirds of women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer are 55 or older. Men are also affected by invasive ductal carcinoma.
The following are the first signs of breast cancer, including invasive ductal carcinoma:
• Swelling of the entire or a portion of the breast, skin irritation, or dimpling breast pain.
• Nipple pain or inward nipple redness, scariness, or thickening of the nipple or breast skin.
• A nipple discharge other than breast milk an underarm lump.
• In figure 2 there is an over view differences between Invasive Ductal Carcinoma in situ and Wall of duct (Figure 2).
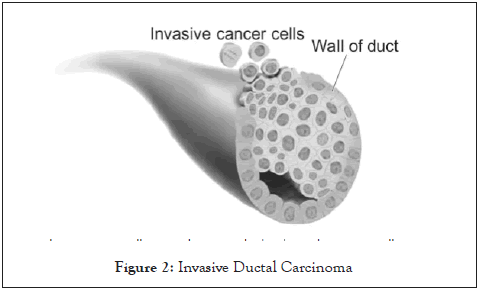
Figure 2: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma.
Treatments of breast cancer
Surgery: Breast-conserving surgery is also known as lumpectomy, quadrantectomy, partial mastectomy, or segmental mastectomy. It is a procedure in which only the cancer portion of the breast is removed. Including pain, temporary swelling, tenderness, and hard scar tissue that form in the surgical site are the side effects to this surgery. Mastectomy is also a surgery to remove the entire breast tissue is removed, sometimes along with the other nearby tissue. The entire breast is removed during breast cancer surgery. A mastectomy is performed when a woman cannot be treated with breast-conserving surgery, which saves the majority of the breast. There are 3 types of mastectomy Simple mastectomy, Skin-sparing mastectomy, and Modified radical mastectomy. Reconstructive surgery Breast reconstruction surgery is one of the breast cancer treatments that can be used to restore the form and appearance of the breast. Breast reconstruction comes in a variety of forms.
Radiotherapy: It is also known as radiation therapy use to kill cancer cell with high energy rays. It affects only the cells of the body part that is treated with the radiation. It can be delivered by either external beam radiotherapy or brachytherapy. Radiation therapy to the head or neck can have the following negative effects mouth is parched, Sores in the mouth and gums, Swallowing problem, Jaw stiffness is a common ailment, Nausea, Hair loss is a common problem, Lymphedema is a form of swelling, Tooth rotting is a common problem.
The significance of whole course nutrition for breast cancer patients cannot be overstated. We managed the nutrition of patients with breast cancer over the course of their treatment using a multidisciplinary medical care cooperation model that included the primary nurse (during hospitalization)/case manager (familybased follow-up), nutrition liaison, nutrition nurse, and physician. This model deserves to be implemented and popularised in patient nutrition management.
Citation: Yan ZL (2023) Insights into Breast Cancer. Chemo Open Access. 11: 192.
Received: 13-Oct-2021, Manuscript No. CMT-21-12857; Editor assigned: 15-Oct-2021, Pre QC No. CMT-21-12857 (PQ); Reviewed: 16-May-2022, QC No. CMT-21-12857; Revised: 22-Sep-2023, Manuscript No. CMT-21-12857 (R); Published: 29-Sep-2023 , DOI: 10.35248/2167-7700.23.11.192
Copyright: © 2023 Yan ZL. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.