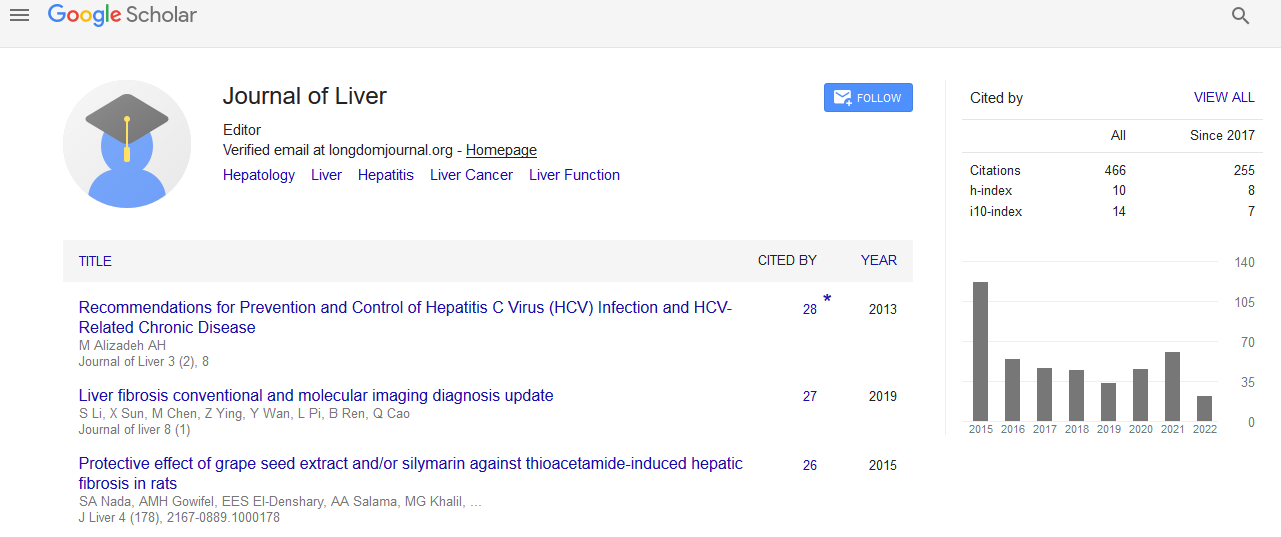
PMC/PubMed Indexed Articles
Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer
Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Examining the effect of aqueous extract of Iranian edible asparagus in prevention of alcoholic liver disease in adult male rats
4th International Conference on Hepatology
April 27-28, 2017 Dubai, UAE
Hossein Kargar Jahromi, Faezeh Sadeghian and Iran Mohammad Mahmoudifard
University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran.
Jahrom Medial University, Iran
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Liver
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) is an important cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Various clinical and laboratory symptoms are detected in ALD. Unfortunately, many patients are initially asymptomatic and can only be diagnosed in case of advanced liver disease that has progressed to complete liver failure. Edible asparagus has antioxidant properties and liver protective effects. Given the increasing prevalence of ALD and the positive effect of several herbal medicines on this disease, the present study aimed to evaluate the effect of aqueous extract of edible asparagus in prevention of ALD. Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: In this experimental study, 40 adult male Wistar rats were divided into 5 groups: sham, control and three experimental groups (received 25% ethanol, 500 mg/kg asparagus extract, 25% ethanol with 500mg/kg respectively - for 70 consecutive days). Serum concentrations of ALT, AST, ALP, TNF-α and GPX were measured. The collected data was analyzed using ANOVA and Duncan's test at p�?�0.05 significance level. Findings: No significant difference was found between control and sham group in terms of all measured parameters. The concentrations of ALT, AST, ALP and TNF-α were significantly higher and the concentration of GPX was significantly lower in the first treatment group compared to control and sham. The concentrations of ALT, AST, ALP and TNF-α were significantly lower in the second treatment group compared to control and sham group. The concentration of GPX was significantly higher in the second treatment group compared to control and sham group. Concentrations of ALT, AST, ALP and TNF-α were significantly higher and the concentration of GPX was significantly lower in the third treatment group compared to control and sham group. Concentrations of ALT, AST, ALP and TNF-α were significantly lower and the concentration of GPX was significantly higher in the third treatment group compared to the first experimental group. Conclusion & Significance: Aqueous extract of edible asparagus with antioxidant properties has a liver protective effect and prevents ALD.
Biography :
Hossein Kargar Jahromi has a PhD in Comparative Histology. He is a member of Research Center for Noncommunicable Diseases, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran and Zoonoses Research Center, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom, Iran.