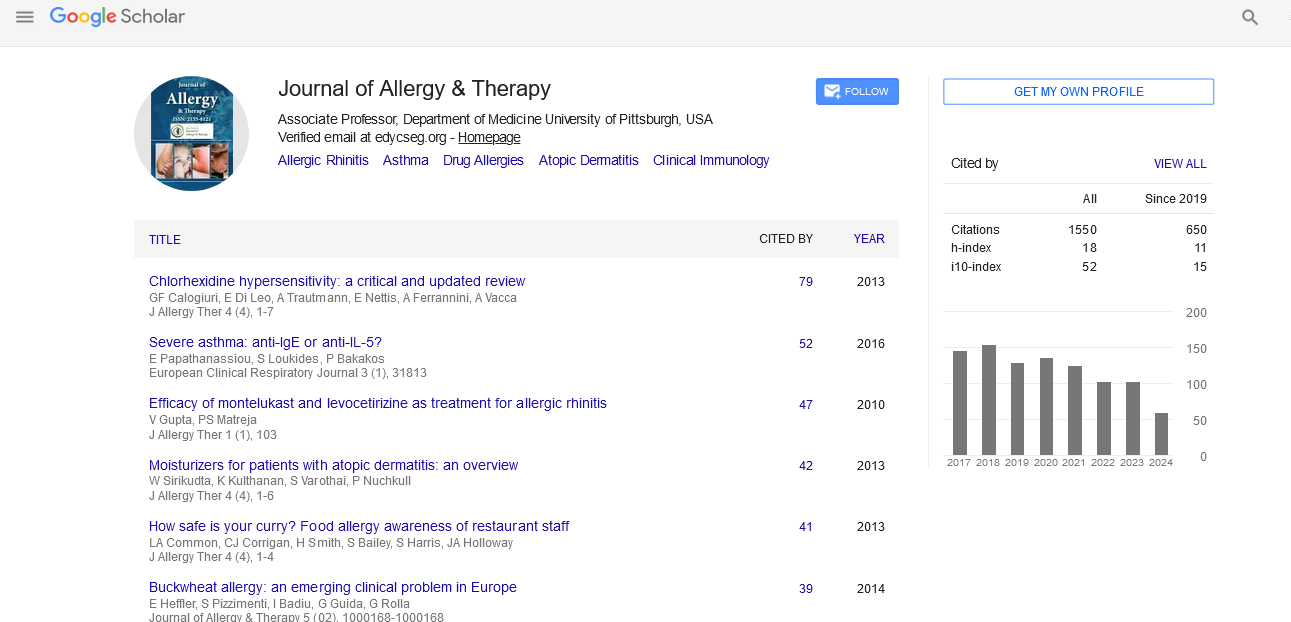
PMC/PubMed Indexed Articles
Indexed In
- Academic Journals Database
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- JournalTOCs
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Allergic onset against hyaluronidase used to treat overcorrection of hyaluronic acid filler injection
11th International Conference on ALLERGY, ASTHMA & CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
September 07-08, 2017 | Edinburgh, Scotland
Tatiana Chioro and Adilson da Costa
Hospital do Servidor P�?ºblico Estadual â�?�? IAMSPE, Brazil
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Allergy Ther
Abstract:
Hyaluronic acid (HA) is biocompatible, easy-to-use, and reversible filler which is broadly-based filler in cosmetic medicine. More and more, non-expert physicians and non-physicians practitioners have been performing fillers in a large number of patients, which notices a high risk of unwanted outcomes, either in efficacy and safety fields. Unwanted results can mean overcorrection and asymmetries, as well as adverse events against these injectable fillers. Although HA-based fillers are defined as temporary materials, they can last up to 12 months or longer. Hyaluronidase is an endogenous enzyme that has a potent activity, which lets it to hydrolyze tissue HA, which is the key element of connective tissue. Given that, commercial hyaluronidase, when injected in areas wherein HA-based filler was placed, destroys HA and gives the possibility to adjust overcorrection and asymmetries. Although hyaluronidase has been used worldwide, only a few allergic reactions have been reported. Most of the described patients showed allergic reactions after peribulbar anesthesia for eye surgery despite the large use of HA fillers in aesthetic medicine. A 29-year-old Brazilian female patient was subjected to a 0.01 mL hyaluronidase injection (Pineda Laboratories, Sao Paulo, Brazil) in order to treat a malar hypercorrection as result of filling with HA. After about 10 minutes, she evolved with discrete erythema and edema at the injection site. A vial of 1 mL intramuscular injection of 5 mg/mL betamethasone dipropionate+2 mg/mL betamethasone disodium phosphate 2 mg/mL (BetaTrinta, Eurofarma, Sao Paulo/SP, Brazil) was immediately administered. After 1 hour, however, the patient presented an intense edema in her left hemiface, which suggested angioedema onset; this adverse event was immediately treated by injecting 4 mL of 500 mg hydrocortisone sodium succinate which helped her to clinically overcome such condition. Though, the patient was discharged to home with 40 mg/day/3 days of micronized prednisolone. A complete clinical improvement was observed in five days. In summary, side effects against hyaluronidase injections are rare in accordance with already published scientific literature; however, it is extremely important for professionals of cosmetic medicine to be an emergency conduct at their office.
Biography :
Tatiana Chioro is a Brazilian Physician with experience in Cosmetic Dermatology. She is Member of Brazilian Society of Dermatology, American Academy of Dermatology and European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. She is also an MSc candidate at Hospital do Servidor Público Estadual – IAMSPE, Brazil.