Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- ResearchBible
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- Publons
- MIAR
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Research Article - (2019) Volume 8, Issue 3
Acute and Sub-Chronic Toxicity Evaluation of Triplotaxis stellulifera (Benth.) Hutch and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum C.D . Adams Methanol Extract on Mice
Nfozon JN1,4, Tume C1,2*, Kdjo N1, Boyom FF3, Leonard SF1, Dzoyem JP2 and Metinou S42Department of Biochemistry, University of Bamenda, Cameroon
3Department of Biochemistry, University of Yaounde, Cameroon
4Department of Public Health, University of Nairobi, Kenya
Received: 28-May-2019 Published: 17-Jul-2019, DOI: 10.35248/2161-1009.19.8.385
Abstract
Background: Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum are two medicinal plants used in traditional medicine but little information are available on them. The objective of this study was to evaluate oral acute and subchronic toxicity of methanol extract of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum.
Methods: Acute toxicity was evaluated in mice by administrating a single dose of 5000 mg/kg body weight of tested extract. The sub-chronic toxicity was conducted by orally administering methanol extract of Crasssocephalum bougheyanum and Triplotaxis stellulifera at doses of 7.93, 23.8, 71.4, 214.2 mg/kg b.w respectively for 28 days in four groups of mice. Toxicity signs, Body and vital organ weights; serum, hematological and biochemical parameters were monitored during and at the end of the study period and histological cut was done.
Results: In acute toxicity, no death and other signs of toxicity was observed in mice. No significant difference on biochemical parameters, vital organ and body weight of mice were observed as compared to the control animal. Significant difference was observed in Granulocytes%, WBC% and MCV. In sub-chronic toxicity, mice treated with Triplotaxis stellulifera showed a significant decrease in Liver and Spleen weight as compared to control. Hematological parameters also showed significant increase in LYM% on mice treated with both extract. But Triplotaxis stellulifera treated mice also showed significant increase in PLT, GRAN% at the highest concentration and decrease MID%. Significant decreased was also observed on ASAT with both extract.
Conclusion: The data revealed that DL50 of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum is greater than 5000 mg/kg b.w. The oral administration of tested plant extract did not produce any toxic effect on Swiss albino’s mice. However these extracts have been shown to stimulate immune response. We therefore conclude that Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum can be used safely for oral administration.
Keywords
Triplotaxis stellulifera; Crasssocephalum bougheyanum; Methanol extract; Toxicity; Mice
Introduction
Traditional medicine through the use of plants has recently attracted attention because the observation is clear that plants are a natural source of medicine and they have being throughout human history [1]. Elsewhere, a majority of the people in developing countries used traditional herbal medicines to treat a number of diseases and ailments [2,3]. The main Problem in the use of traditional medicine is that the dosage is non-standardized and most of the plants have not been evaluated for toxicity [4]. However, several researchers have pointed out the potential toxicity, as well as the risks associated with the use of certain species of plants and vegetables [5]. The adverse effect observed directly affect organs especially kidney and liver which are more predisposed to toxic effects of xenobiotics during their metabolism and excretion [6]. In example, the work of Peyrin-Biroulet et al., revealed that some plant species have hepatotoxic effects [7]. A major cause of this toxicity includes plant misidentification, use of medicinal plants of unknown toxicity and contamination of medicinal plants with nephrotoxic non-herbal drugs [8]. Thus, it is not saved to consume toxic plant because it can lead to bioaccumulation of toxic herbal compounds or altered detoxification processes [9]. Therefore, before clinical use of the drug, it is very important to study its toxicity [10] in other to identify the safety and to determine the dose level that could subsequently be used. Although many plant have been studied for their toxicity activity such as Alstonia scholaris Stem Bark [11] and Pericampylus glaucus [12] the toxicity of many of them are still unknown.
Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum are two of those multiple traditional plant which are used in traditional medicine and which little information’s are available about their toxicity activity. T. stellulifera is used to treat malaria and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum is used as vegetable and medicine. The aim of this work is to investigate acute and sub-chronic oral dose toxicity of methanol extract of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum in Swiss albino’s mice models, as part of the safety evaluation.
Material and Methodology
Plant identification
Crasssocephalum bougheyanum and Triplotaxis stellulifera plant material were collected from Tombel Subdivision, Kupe Muanenguba Division, South West Region of Cameroon in August 2016. The plants were identified by a botanical expert at the National herbarium in Yaoundé-Cameroon where vouchers are stored and registered as 7635/HNC and 20495/HNC respectively. Leaves and stem were dried at room temperature until crisp dry and grounded using laboratory blender. The plant powder (500 g) where macerated in 2.5 liters of methanol for 48 h at room temperature with frequent striking. The methanol extracts were filtered using No.1 Whatmann filter paper and were evaporated using reduced pressure at 40o C in rotary vacuum evaporator (Büchi R200).
Experimental animals
Swiss albinos mice aged between 8-10 weeks were obtained from Dschang University Animal house, Department of Biochemistry. The animals were randomly selected and kept one per cage and grouped five per dose. They were kept at standard laboratory conditions of temperature (25 ± 2°C), relative humidity (60 ± 5%) and 12/12h light/ dark cycle. Food and water was provided ad libitum. Tree day’s acclimatization was observed before beginning the experiments. Guidelines from Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) on animal studies were followed on handling the animals [13].
Acute toxicity
Up and down method was used to perform a limit test at dose extract of 5000 mg/kg body weight [14] on Swiss albinos’ mice (17-21 g). All the animals were kept for 3-4 hours fasting before experiment with free access to water. Extract dose of 5000 mg/kg body weight was administered to each animal at 48 hours interval by oral gavages. For the first four hours, the animals were denied access to food. Only water was provided ad libitum. Signs of toxicity and fatality were observed up to 14 days and the results recorded. Special attention was given to the first three hours after administration of the extract. Behavioral changes and other parameters such as body weight, urinations, food intake, water intake, respiration, convulsion, tremor, temperature, constipations, changes in eye and skin colors where observed.
Sub-chronic toxicity testing
The animals were divided into five groups each containing five animals. Group 1 was the control and groups 2, 3, 4 and 5 were orally administered with methanol extract of Crasssocephalum bougheyanum and Triplotaxis stellulifera at different doses daily for 28 days. A progression factor of 3 was used to arrive at the four doses (7.93, 23.8, 71.4, 214.2) mg/kg body weight. The animals were fed by food composition described by Telefo [15], and water was provided ad libitum.
Hematological, biochemical and histopathological examination
On the 29th day, animals were anaesthetized in air tight dissection bottle containing cotton soaked in chloroform and blood was collected through cardiac puncture into test tube with and without ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) for hematological and biochemical parameters respectively. Blood without EDTA was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for ten minutes and the serum obtained was kept at -20°C until assayed for biochemical estimation. The tests performed included Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), total proteins, creatinine, total cholesterol and Triglyceride. The anaesthetized animals were later laid on a dissection board and opened up by cutting through vertical mid-line from neck to peritoneum using a pair of scissors. Certain body organs (heart, liver, kidneys, lungs and spleen) were separated and weighed using electronic weighing balance. The liver, kidneys, and spleen were preserved in plastic containers containing 10% formaldehyde solution for histopathological evaluation.
Statistical analysis
All values are expressed as mean ± SD. Comparisons between groups were performed using one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Turkey’s multiple comparison tests using SPSS statistical software v.23. Significant Difference test was used to separate means at a confidence level of 95% (p ≤ 0.05).
Results
Acute toxicity
General sign and behavioral analysis: The acute toxic effect of methanol extract was determined using protocol of the OECD guideline 423 after 14 days of treatment with extract at a dose of 5000 mg/kg. The results are represented on the Table 1. No treatment-related toxic symptoms or mortality were observed after oral administration of a single dose of the tested plant extract. No drug related changes in behavior, breathing, skin effects, water consumption, impairment in food intake were observed on control and extract treated animals on short (4 h) and long (72 h) period observation. Those plant extract have therefore been considered as safe at a dose level of 5000 mg/kg, and the LD50 is >5000 mg/kg.
Table 1: General appearance and behavioral observations of acute toxicity study for control and treated groups.
| Observation | Control group | 7.93 mg/kg | 23.8 mg/kg | 71.4 mg/kg | 214.2 mg/kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digestion | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO |
| Temperature | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Food intake | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Urination | Normal | No effect | No effect | No effect | No effect |
| Rate of respiration | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Change in skin | NO | NO | NO | NO | NO |
| Drowsiness | |||||
| Sedation | No effect | No effect | No effect | No effect | No effect |
| Eye color | No effect | No effect | No effect | No effect | No effect |
| Diarrhea | Not present | Not present | Not present | Not present | Not present |
| General Physique | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Coma | Not present | Not present | Not present | Not present | Not present |
| Death | Alive | Alive | Alive | Alive | Alive |
| Grooming | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Convulsion | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Tremors | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Sleep | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
NO: Not Observed
Effect of treatment on organ and body variation
Tables 2 and 3 show the average body weight as well as weights of vital organs of the animals respectively. There were no significant changes (p ≤ 0.05) in body weight and weights of organs of treated animal compared to control with both extracts.
Table 2: Average body weight (g) of mice on the sacrifice day.
| Extracts | Control (0 mg/kgbw/day) | 5000 (mg/kgbw/day) |
|---|---|---|
| Triplotaxis stellulifera | 18.14 ± 00.01a | 20.19 ± 1.52a |
| Crassocephalum bougueyanum | 18.14 ± 00.02a | 20.26 ± 1.50a |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with different superscript across treatments are significantly different from each other at (p>0.05).
Table 3: Effect of oral administration of methanol extract of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum on organ weight of Swiss albino’s mice.
| Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | Control | 5000 (mg/kgbw/day) | 5000 (mg/kgbw/day) |
| Kidney | 0.25 ± 0.02a | 0.29 ± 0.04a | 0.28 ± 0.33a |
| Heart | 0.09 ± 0.01a | 0.10 ± 0.01a | 0.10 ± 0.05a |
| Spleen | 0.07 ± 0.03a | 0.06 ± 0.02a | 0.06 ± 0.01a |
| Lungs | 0.12 ± 0.0a | 0.10 ± 0.04a | 0.10 ± 0.00a |
| Liver | 0.90 ± 0.03a | 1.07 ± 0.21a | 1.09 ± 0.04a |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with different superscript across treatments are significantly different from each other at (p>0.05).
Effect of treatment of mice with Crasssocephalum bougheyanum and Triplotaxis stellulifera on hematological parameters: The effect of extracts on hematological parameters was examined at the end of treatment. Must of hematological parameters were no significant different except GRAN% which significantly increased and WBC% and MCV which significantly decreased as compared to the control with Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum (Table 4).
Table 4: Effects of methanol extract of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougueyanum on hematological profiles in Swiss albinos mice.
| Plantextract | Dose of Triplotaxis stellulifera (mg/kgbw/day) | Dose of Crassocephalum bougueyanum (mg/kgbw/day) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control (0 mg/kgbw/day) | 5000 | 5000 |
| WBC (103/UL) | 7.10 ± 0.00a | 4.80 ± 0.10b | 3.67 ± 0.23c |
| LYM% | 66.40 ± 0.01a | 65.43 ± 0.51a | 67.05 ± 1.55a |
| MID% | 11.90 ± 0.00a | 12.48 ± 0.75a | 12.10 ± 0.3a |
| GRAN% | 21.70 ± 0.02c | 24.95 ± 0.15a | 23.15 ± 0.45b |
| RBC (106/UL) | 7.38 ± 0.02a | 6.65 ± 1.06a | 7.56 ± 0.65a |
| HGB (g/dl) | 15.40 ± 0.00ab | 12.99 ± 1.38b | 16.23 ± 1.00a |
| HCT (%) | 44.50 ± 0.07a | 41.70 ± 2.50a | 43.15 ± 0.15a |
| MCV (Fl) | 60.30 ± 0.05a | 58.20 ± 0.70b | 52.45 ± 0.45c |
| MCH (pg) | 20.80 ± 0.01a | 20.73 ± 0.59a | 21.47 ± 0.50a |
| MCHC g/dL | 34.60 ± 0.02a | 37.07 ± 2.06a | 37.30 ± 1.52a |
| RDW-CV (%) | 21.60 ± 0.01a | 20.83 ± 1.55a | 18.37 ± 2.07a |
| RDW-SD (Fl) | 42.10 ± 0.00a | 39.48 ± 1.15ab | 33.87 ± 4.05b |
| PLT (103/UL) | 208.00 ± 0.06a | 232.44 ± 21.50a | 219.83 ± 10.25a |
| MPV (Fl) | 8.50 ± 0.01a | 8.77 ± 0.35a | 8.25 ± 0.35a |
| PDW (Fl) | - | - | - |
| PCT (%) | 0.17 ± 0.05a | 0.18 ± 0.03a | 0.17 ± 0.06a |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with different superscript across treatments are significantly different from each other at (p>0.05). PDW: Platelet Distribution Width, LYM: Lymphocytes, WBC: White Blood Cells, RBC: Red Blood Cells, HGB: Haemoglobin, HCT: Hematocrit, MCV: Mean Cell Volume, MCH: Mean Cell Haemoglobin, MCHC: Mean Cell Haemoglobin Concentration, RDW: Red Cell Distribution Width, PLT: Platelets, MPV: Mean Platelet Volume, RDW-CV: Red Cell Distribution Width Cell Volume.
Effect of treatment of mice with Crasssocephalum bougheyanum and Triplotaxis stellulifera on biochemical and histological parameters: The results on biochemical and histological parameters are recorded in Table 5 and Figure 1. No significant difference was observed as compared to control group with both extracts.
Table 5: Effect of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum on mice biochemical parameters
| Parameters | Normal group (0 mg/kgbw/day) | 5000 (mg/kgbw/day) of Triplotaxis stellulifera | 5000 (mg/kgbw/day) of Crassocephalum bougueyanum |
|---|---|---|---|
| TAG (Mmol/l) | 3.08 ± 0.04a | 3.08 ± 0.06a | 2.84 ± 0.91a |
| Cholesterol (Mmol/l) | 1.70 ± 0.10a | 1.64 ± 0.53a | 2.06 ± 0.36a |
| Proteins (g/dl) | 1.16 ± 01a | 1.12 ± 0.05a | 1.07 ± 0.04a |
| Creatinine (µmol/l) | 40.47 ± 0.02a | 41.00 ± 0.7a | 40.99 ± 0.07a |
| Values are expressed as Mean ± D for tree animals per group. Values with different superscript across treatments are significantly different from each other at (p>0.05). TAG=triacylglycerides | |||
Sub-chronic toxicity
Effect of oral administration of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum methanol extract on behavior of mice: Daily oral administration of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum methanol extract for 28 days did not induce any obvious symptom of toxicity. No deaths and clinical signs were recorded in any groups throughout the experimental. Physical observation of the treated mice indicated that none of them showed observable signs of toxicity in their skin, fur, eyes, mucus membrane, or behavioral changes, diarrhea, tremors, salivation, sleep, and coma.
Effect of oral administration of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum methanol extract on mice body and organs weights: Tables 6-8 present the body and organs weights respectively of 28-day treated mice. Normal body weight gains were observed during the study period compared to the control group Table 6. The mean body weights of treated mice did not increased significantly as compared to the control group at p>0.05, on the day of sacrifice.
Table 6: Average body weight of mice on the sacrifice day.
| Body weight (g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extracts | Control | 7.93 (mg/kgbw/day) | 23.8 (mg/kgbw/day) | 71.4 (mg/kgbw/day) | 214.2 (mg/kgbw/day) |
| Triplotaxis stellulifera | 20.91 ± 3.05a | 22.23 ± 5.03a | 22.81 ± 1.48a | 22.81 ± 3.46a | 22.75 ± 4.09a |
| Crassocephalum bougueyanum | 20.91 ± 3.05a | 21.05 ± 2.87a | 21.90 ± 2.91a | 20.52 ± 1.42a | 20.90 ± 2.81a |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with different superscript across treatments are significantly different from each other at (p>0.05).
Table 7: Effect of oral administration of methanol extract of Triplotaxis stellulifera on organ weight of Swiss albino’s mice.
| Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | Control | 7.93 (mg/kgbw/day) | 23.8 (mg/kgbw/day) | 71.4 (mg/kgbw/day) | 214.2 (mg/kgbw/day) |
| Kidney | 0.39 ± 0.0a | 0.39 ± 0.09a | 0.40 ± 0.08a | 0.36 ± 0.07a | 0.37 ± 0.13a |
| Heart | 0.11 ± 0.02b | 0.10 ± 0.01b | 0.10 ± 0.01b | 0.10 ± 0.01b | 0.31 ± 0.04a |
| Spleen | 0.13 ± 0.02a | 0.07 ± 0.02b | 0.08 ± 0.03b | 0.09 ± 0.03b | 0.060.01b |
| Lungs | 0.16 ± 0.02a | 0.16 ± 0.02a | 0.15 ± 0.08a | 0.12 ± 0.02a | 0.13 ± 0.04a |
| Liver | 2.29 ± 0.08a | 1.18 ± 0.05b | 1.24 ± 0.11b | 1.31 ± 0.18b | 1.13 ± 0.23b |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with the different superscript across treatments are significantly different from each other at (p>0.05).
Table 8: Effect of oral administration of methanol extract of Crassocephalum bougueyanum on organ weight of Swiss albino’s mice.
| Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organ | Control | 7.93 (mg/kgbw/day) | 23.8 (mg/kgbw/day) | 71.4 (mg/kgbw/day) | 214.2 (mg/kgbw/day) |
| Kidney | 0.39 ± 0.15a | 0.33 ± 0.05a | 0.42 ± 0.11a | 0.39 ± 0.09a | 0.34 ± 0.11a |
| Heart | 0.11 ± 0.02a | 0.10 ± 0.00a | 0.11 ± 0.02a | 0.11 ± 0.01a | 0.11 ± 0.02a |
| Spleen | 0.13 ± 0.07a | 0.09 ± 0.05a | 0.08 ± 0.03a | 0.09 ± 0.04a | 0.14 ± 0.09a |
| Lungs | 0.16 ± 0.02a | 0.13 ± 0.01a | 0.14 ± 0.02a | 0.14 ± 0.02a | 0.12 ± 0.07a |
| Liver | 1.40 ± 0.11a | 1.14 ± 0.14a | 1.24 ± 0.09a | 1.17 ± 0.20a | 0.92 ± 0.08b |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with the same superscript across treatments are not significantly different from each other at (p>0.05).
Concerning organ weight, they were no significant increase in organs weight of treated mice with Crassocephalum bougheyanum as compared to the control Table 7. Otherwise, treated mice with Triplotaxis stellulifera showed significant decrease in spleen and liver weight firstly, while heart, kidney and lung weight did not showed significant difference as compared to the control group except mice heart weight treated at the highest concentration (Table 8).
Effect of oral administration of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum methanol extract on hematological, biochemical and histological parameters: The effect of sub-chronic administration of T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum on hematological parameters is presented in Tables 9 and 10. Most hematological measures (WBC%, RBC, HGB, MCV, MCHC, RDW-CV, RDW-SD, MPV, MCH, HCT, PDW and PCT), in treated mice with T. stellulifera were not significantly different from the controls. We also observed significant increase in GRAN% at concentration 23.8 mg/kg, increase in PLT and LYMP% whereas decrease in MID% as compared to the control not dose-related (Table 9).
Table 9: Effects of oral administration of methanol extract of Triplotaxis stellulifera on hematological profiles in Swiss albinos mice.
| Dose of Triplotaxis stellulifera (mg/kgbw/day) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | 7.93 (mg/kgbw/day) | 23.8 (mg/kgbw/day) | 71.4 (mg/kgbw/day) | 214.2 (mg/kgbw/day) |
| WBC (103/Ul) | 5.60 ± 0.50ab | 7.45 ± 1.25a | 5.83 ± 1.10ab | 7.95 ± 0.75a | 4.85 ± 0.75b |
| LYM% | 57.95 ± 1.45c | 78.77 ± 6.80a | 67.86 ± 2.80b | 75.20 ± 2.20ab | 77.57 ±.153a |
| MID% | 15.17 ± 2.90a | 7.10 ± 1.50b | 10.57 ± 1.63b | 9.50 ± 0.50b | 8.65 ± 0.05b |
| GRAN% | 25.40 ± .10b | 14.50 ± 2.00c | 29.95 ± 0.55a | 15.15 ± 2.85c | 13.80 ± 0.20c |
| RBC (106/Ul) | 8.96 ± 0.27a | 9.04 ± 0.77a | 9.34 ± 0.47a | 9.92 ± 0.05a | 9.47 ± 0.17a |
| HGB (g/dl) | 17.03 ± 0.91a | 17.20 ± 0.40a | 16.40 ± 1.06a | 17.80 ± 0.10a | 17.83 ± 0.46a |
| HCT (%) | 50.30 ± 0.60a | 52.20 ± 3.30a | 53.90 ± 1.20a | 50.55 ± 0.85a | 53.10 ± 3.61a |
| MCV (fl) | 53.20 ± 1.85a | 55.30 ± 1.40a | 54.60 ± 3.74a | 51.00 ± 0.60a | 56.10 ± 3.75a |
| MCH (pg) | 18.93 ± 0.49a | 17.87 ± 0.31a | 17.53 ± 0.31a | 17.90 ± 0.00a | 18.770 ± .15a |
| MCHC (g/dl) | 35.73 ± 1.10a | 33.17 ± 1.33a | 32.20 ± 1.64a | 35.20 ± 0.40a | 33.63 ± 2.28a |
| RDW-CV (%) | 16.30 ± 1.05a | 16.73 ± 0.61a | 17.40 ± 1.71a | 17.35 ± 1.25a | 16.53 ± 0.45a |
| RDW-SD (%) | 28.00 ± 2.03ab | 27.93 ± 0.81ab | 29.33 ± 2.13ab | 26.40 ± 0.60b | 30.50 ± 0.70a |
| PLT (103/Ul) | 386.00 ± 19.00e | 544.83 ± 10.27b | 424.50 ± 16.50d | 618.00 ± 19.00a | 510.50 ± 10.50c |
| MPV (fl) | 7.633 ± 0.21a | 7.27 ± 0.31a | 7.50 ± 0.85a | 7.45 ± 0.05a | 7.56 ± 0.67a |
| PDW (fl) | 8.12 ± 0.60a | 8.03 ± .23a | 7.73 ± 0.84a | 8.50 ± 0.20a | 7.73 ± 0.15a |
| PCT (%) | 0.35 ± .10a | 0.37 ± 0.03a | 0.39 ± 0.10a | 0.38 ± 0.10a | 0.30 ± 0.09a |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with the same superscript across treatments are not significantly different from each other at (p>0.05). PDW: Platelet Distribution Width, LYM: Lymphocytes, WBC: White Blood Cells, RBC: Red Blood Cells, HGB: Haemoglobin, HCT: Hematocrit, MCV: Mean Cell Volume, MCH: Mean Cell Haemoglobin, MCHC: Mean Cell Haemoglobin Concentration, RDW: Red Cell Distribution Width, PLT: Platelets, MPV: Mean Platelet Volume, RDW-SD: Red Cell Distribution Width Cell Volume.
Hematological parameters measures in mice treated with C. bougheyanum (WBC%, MID, RBC, HGB, MCH, RDW-CV, MPV and PCT) were not significant different except LYMP% which was significantly increased as compared to control (Table 10).
Table 10: Effects of oral administration of methanol extract of Crassocephalum bougueyanum on hematological profiles in Swiss albinos mice
| Dose of Crassocephalum bougueyanum (mg/kgbw/day) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | 7.93 | 23.8 | 71.4 | 214.2 |
| WBC (103/uL) | 5.60 ± 0.50ab | 4.10 ± 1.10b | 6.19 ± 0.90a | 6.85 ± 0.35a | 5.10 ± 0.50ab |
| LYM% | 57.95 ± 1.45c | 77.20 ± 1.10a | 66.95 ± 2.60b | 70.10 ± 2.60ab | 75.95 ± 5.65a |
| MID% | 15.17 ± 2.90a | 12.65 ± 0.35a | 16.40 ± 0.10a | 12.85 ± 0.45a | 14.43 ± 0.67a |
| GRAN% | 25.40 ± 0.10a | 14.15 ± 0.75b | 23.20 ± 2.80a | 15.85 ± 0.95b | 13.65 ± 0.85b |
| RBC (106/uL) | 8.96 ± 0.27a | 9.67 ± 0.29a | 9.31 ± 0.36a | 9.26 ± 0.39a | 8.96 ± 0.21a |
| HGB (g/dl) | 17.03 ± 0.91a | 17.10 ± 0.26a | 17.17 ± 0.46a | 17.30 ± 0.50a | 16.67 ± 0.91a |
| HCT (%) | 46.30 ± 0.40a | 50.23 ± 3.66a | 47.50 ± 1.71a | 47.67 ± 0.55a | 45.70 ± 1.80a |
| MCV (fl) | 53.20 ± 1.85ab | 54.83 ± 2.9a | 52.87 ± 0.47ab | 50.05 ± 0.65b | 51.50 ± 1.20ab |
| MCH (pg) | 18.93 ± 0.49a | 17.63 ± 0.32a | 18.40 ± 0.36a | 18.63 ± 0.81a | 18.53 ± 1.00a |
| MCHC (g/dl) | 35.73 ± 1.10a | 32.27 ± 1.31b | 34.90 ± 0.50a | 35.65 ± 0.15a | 36.10 ± 1.10a |
| RDW-CV (%) | 16.30 ± 1.05a | 16.40 ± 0.7a | 16.83 ± 0.12a | 16.20 ± 0.20a | 16.20 ± 0.66a |
| RDW-SD (fl) | 28.00 ± 2.03ab | 28.40 ± 1.40ab | 29.10 ± 0.70a | 25.80 ± 0.00b | 27.70 ± 0.70ab |
| PLT (103/uL) | 386.00 ± 19.00bc | 373.00 ± 11.00bc | 573.50 ± 11.50a | 441.50 ± 19.50b | 363.00 ± 49.00c |
| MPV (fl) | 7.63 ± 0.21a | 7.57 ± 0.32a | 7.37 ± 0.15a | 7.60 ± 0.44a | 7.47 ± 0.65a |
| PDW (fl) | 10.45±0.15ab | 12.15±.75a | 8.70±0.00b | 9.30±2.10ab | 8.17 ± 0.95a |
| PCT (%) | 0.35 ± 0.09a | 0.29 ± 0.01a | 0.40 ± 0.03a | 0.31 ± 0.04a | 0.28 ± 0.03a |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with the same superscript across treatments are not significantly different from each other at (p>0.05). PDW: Platelet Distribution Width, LYM: Lymphocytes, WBC: white Blood Cells, RBC: Red Blood Cells, HGB: Haemoglobin, HCT: Hematocrit, MCV: Mean Cell Volume, MCH: Mean Cell Haemoglobin, MCHC: Mean Cell Haemoglobin Concentration, RDW: Red Cell Distribution Width, PLT: Platelets, MPV: Mean Platelet Volume, RDW-CV: Red Cell Distribution Width Cell Volume.
Serum biochemical parameters were examined on treated mice with extracts and on control group and the results are presented on the Tables 11 and 12. Serum TAG, ALT, cholesterol, proteins and creatinine were not significantly different as compared to control at P>0.05 in treated mice with Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum Table 10. Moreover, we observed a significant decrease in mice serum ASAT treated with both extract as compared to the control group (Table 11).
Table 11: Effect of Triplotaxis stellulifera methanol extract on serum biochemical parameters.
| Parameters | Normal group | 7.93 mg/kgbw/day | 23.8 mg/kgbw/day | 71.4 mg/kgbw/day | 214.2 mg/kgbw/day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAG (Mmol/l) | 1.50 ± 0.43a | 1. 09 ± 0.16a | 2.52 ± 1.28a | 1.43 ± 0.23a | 1.40 ± 0.16a |
| Cholesterol (Mmol/l) | 2.86 ± 0.75a | 2.51 ± 0.45a | 2.78 ± 0.76a | 2.37 ± 0.23a | 2.47 ± 0.35a |
| Proteins (g/dl) | 4.52 ± 0.18c | 6.71 ± 0.35b | 9.33 ± 1.07a | 6.43 ± 0.16b | 7.18 ± 1.56ab |
| ALAT (U/l) | 8.35 ± 1.46a | 4.50 ± 1.96a | 10.71 ± 4.96a | 11.41 ± 2.34a | 7.24 ± 4.36a |
| ASAT (U/l) | 34.49 ± 2.41a | 15.03 ± 0.17b | 16.74 ± 1.69b | 7.41 ± 1.37c | 8.05 ± 2.72c |
| Creatinine (µmol/l) | 42.47 ± 3.00b | 70.72 ± 8.84a | 57.46 ± 4.42ab | 51.43 ± 9.48ab | 62.78 ± 8.54a |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SD for tree animals per group. Values with the same superscript across treatments are not significantly different from each other at (p>0.05). TAG: Triacylglycerides, ALAT: Alanine Aminotransferase, ASAT: Aspartate Aminotransferase.
Table 12: Effect of Crassocephalum bougheyanum methanol extract on serum biochemical parameters.
| Parameters | Normal group | 7.93 mg/kgbw/day | 23.8 mg/kgbw/day | 71.4 mg/kgbw/day | 214.2 mg/kgbw/day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAG (Mmol/l) | 1.50 ± 0.43a | 1.57 ± 0.66a | 1.58 ± 0.75a | 1.55 ± 0.64a | 1.64 ± 0.80a |
| Cholesterol (Mmol/l) | 2.86 ± 0.75ab | 3.50 ± 0.22a | 3.08 ± 0.33ab | 3.40 ± 0.43ab | 2.20 ± 0.37b |
| Proteins (g/dl) | 4.52 ± 0.18c | 8.42 ± 1.01ab | 10.99 ± 1.11a | 10.19 ± 0.71ab | 7.50 ± 2.10bc |
| ALAT (U/l) | 8.53 ± 1.46b | 17.32 ± 2.24a | 6.59 ± 1.21b | 4.78 ± 0.98b | 6.41 ± 1.75b |
| ASAT (U/l) | 34.49 ± 2.41b | 8.56 ± 1.68d | 18.16 ± 0.75c | 87.80 ± 8.47a | 15.99 ± 0.93c |
| Creatinine (µmol/l) | 42.47 ± 3.00c | 44.20 ± 17.68bc | 89.38 ± 14.53bc | 335.92 ± 44.20a | 181.22 ± 66.30b |
Values are expressed as Mean ± SEM for tree animals per group. Values with the same superscript across treatments are not significantly different from each other at (p>0.05). TAG: Triacylglycerides, ALAT: Alanine Aminotransferase, ASAT: Aspartate Aminotransferase.
Also, no signs of toxicity were observed on mice liver, kidney and spleen histopathological study (Figures 1-4).
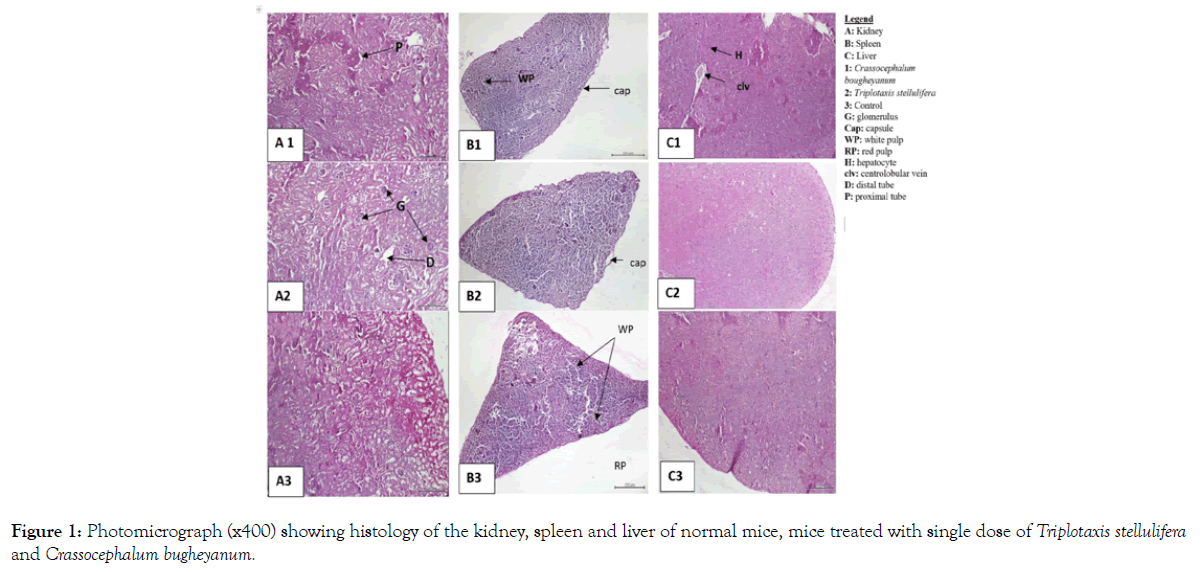
Figure 1: Photomicrograph (x400) showing histology of the kidney, spleen and liver of normal mice, mice treated with single dose of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bugheyanum.
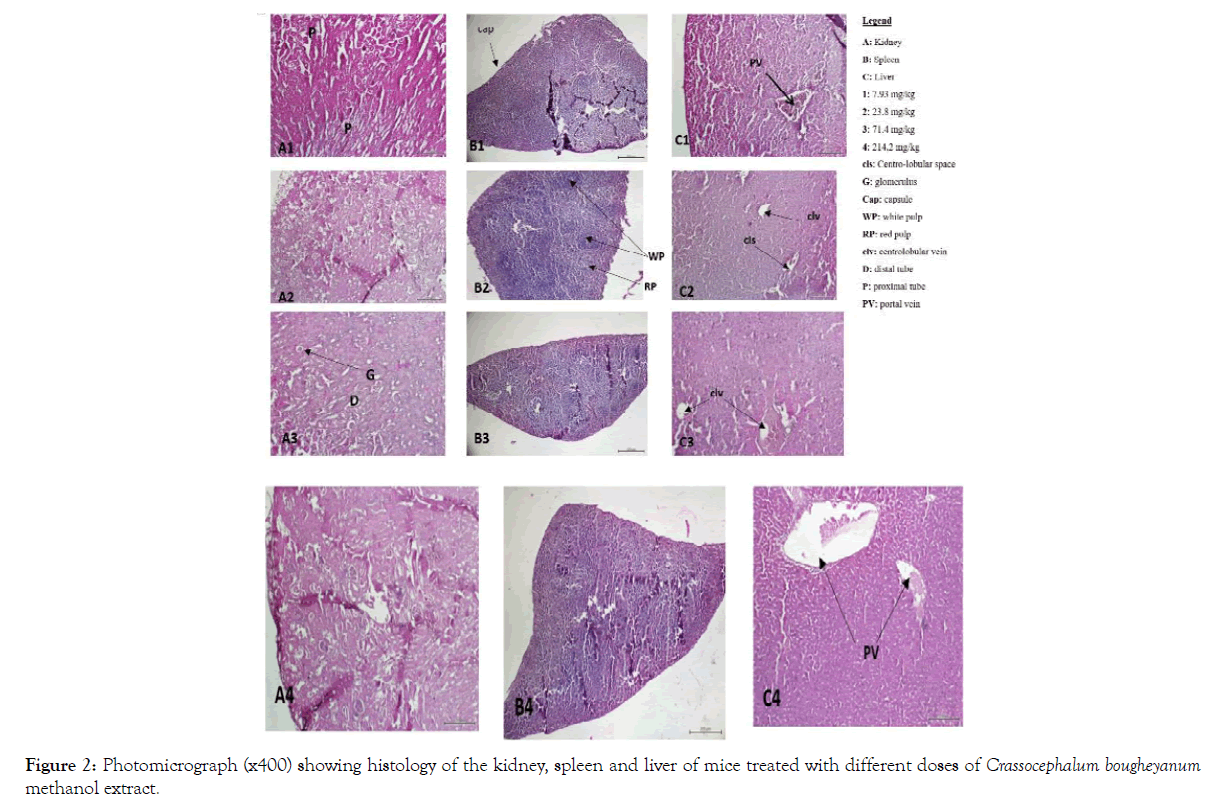
Figure 2: Photomicrograph (x400) showing histology of the kidney, spleen and liver of mice treated with different doses of Crassocephalum bougheyanum methanol extract.
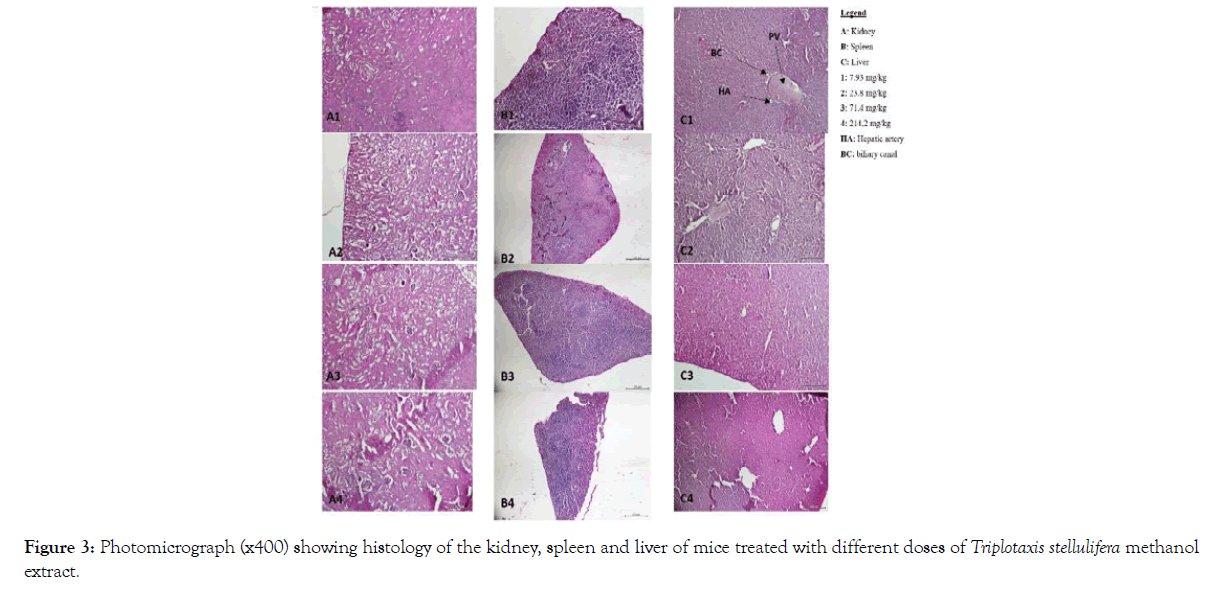
Figure 3: Photomicrograph (x400) showing histology of the kidney, spleen and liver of mice treated with different doses of Triplotaxis stellulifera methanol extract.
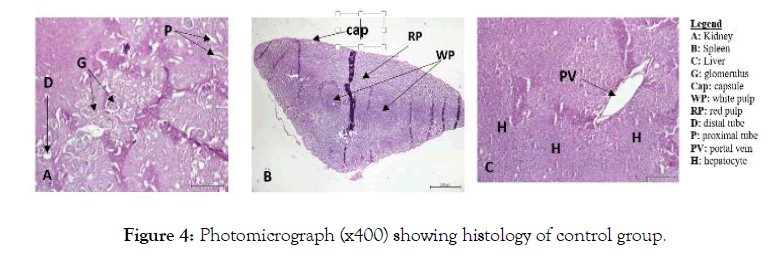
Figure 4: Photomicrograph (x400) showing histology of control group.
Discussion
Since centuries, medicinal plants have been used to treat different diseases [16] however, there is a lack of proven scientific studies on the toxicity and adverse effect of these treatments. Although medicinal plants are recognized to have no side effects, some research has identified the toxic nature of some plants. Hence, the safety profile of the plant has to be established as a guide for the management of its applications and usage in herbal preparations in order to manage the clinical signs and symptoms of the drugs [17]. Thus, the aim of the current study was to evaluate the acute and sub-chronic toxicity of Triplotaxis stellulifera and Crassocephalum bougheyanum in a mice model. Mice model have been used in this study because scientific documentations have revealed that lethal dose data collected from mice might be more appropriate to anticipate the toxic effects in human beings [18]. Toxicity effects of natural remedies in animals and humans are analyzed using some physiological parameters like behavior, body weight; biochemical, hematological parameters and histological analysis [19]. Acute toxicity provides initial information on the mode of toxic action of medicinal plants. The clinical signs and symptoms exerted by drugs on vital body organs are considered as principal observations among toxicity indicators [20].
After acute exposure of T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum on mice, no symptoms of toxicity were observed. Additionally, no mortality was recorded in mice which received methanol extract doses of 5000 mg/kg body weight suggesting that the lethal dose (LD50) is above 5000 mg/kg body weight. Globally harmonized classification system has divided chemicals into five group base on their LD50 [21]. Methanol extract of T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum failed in class 5 and may be considerate as safe and low toxic for oral acute administration [22].
No significant difference was observed on vital organs, body weights and biochemical parameters, suggesting non-toxic effect of a single dose administration of the methanol extract on mice.
The hematological health status of the mice presented significant increase in Granulocytes% means that those plants may involve in immune response. However, non-significant difference in other parameters such as RBC, HGB, MC showed that T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum do not interfere with normal production of those parameters.
Sub-chronic toxicity studies are also an important preliminary data that helps to select natural remedies with potential health benefits for future work [23]. The sub-chronic toxicity study in this work involved oral administration to mice, methanol extracts at doses of 7.93, 23.8, 71.4 and 214.2 mg/kg b.w. No significant changes in animal behavior and body weight have been observed on treated animal in comparison to the control group. It has also been observed no significant difference on organ weights on mice treated with C. bougheyanum. However, significant difference on mice spleen, kidney and liver weights treated with T. stellulifera as compared to the control has been observed and no significant difference on lung and heart weights was observed as compared with the control in mice. Liver, kidney, heart, lungs and spleen are the vital organs of our body which are the major targeted area of any toxic substance metabolically [24]. Liver and kidney play an essential role in the detoxification and the excretion process while Spleen is the secondary lymphoid organ where the immune cells accumulate, waiting for antigen. Body weight and relative weight of vital organs changes are indicators of the effect of an administered substance [25]. However, scientific evidence confirmed that increases or decreases in the body weights are accompanied with accumulation of fats and physiological adaptation responses to the plant extracts rather than to the toxic effects of chemicals or drugs that lead to decrease appetite and, hence, lower caloric intake by the animal [26]. Thus, the change in the kidney, liver and spleen weights might not be an indicator of toxic potential of the extract on those organs.
Blood parameters analysis is very useful for the determination of the anomalies induced by a plant extract [27]. It also helps in providing information about the toxicity mechanism/safe of a therapeutic agent [28]. Lymphocytes are involved in the immune response (specific immune response). The increase in the level of lymphocytes% in mice treated with T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum show that those plant extracts can potentiate immune response by increasing the level of lymphocytes. Thus, we can say that these plant extract should have immunostimulating activity. The condition that reflects abnormally low levels of platelets in circulation is known as Thrombocytopenia, due to a decrease in production of platelets [29]. The administration of some drugs provoke platelet antibodies, resulting in the destruction of platelet leading to thrombocytopenia [30]. The significant increase in Platelets number in mice treated with T. stellulifera show that this plant extract prevent thrombocytopenia and contribute to the innate immune response. Granulocytes are also immune cells involved in innate immune response, especially phagocytosis. The significant increase in the level of granulocytes in mice treated with T. stellulifera at the second concentration once demonstrate the rule of this plant extract in the potentialization of the immune response.
It has been shown that the decrease in some hematological parameters such as RBC (Red Blood Cells, MCV (mean cell volume), MCHC (mean cell hemoglobin concentration), and HGB (hemoglobin) can induce anemia [31]. This study reveal no significant difference in those parameters in treated mice showing that T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum extract do not interfer with the normal production RBC and do not induce anemia. Moreover, some hematological parameter were not significantly different compared to the control such as WBC, RDW-SD, MPV, PCT indicating that those plant extract have no toxic effect against the normal production of those parameters in treated mice.
The analyzing of biochemical parameters is also very important when evaluating the toxic effect of plant extracts. In fact, biochemical parameters may provide useful information regarding the specific tissues such as kidney and Liver which are survival of an organism function [32].
Aspartate Aminotransferase in combination with ALT are considered as good maker of liver disease [33]. High levels of those enzymes are implicated in liver diseases or hepatotoxicity [34-36]. The present study reveals no significant changes in serum ALT level in mice treated with C. bougheyanum and T. stellulifera. We also observed a significant decrease in serum ASAT. This indicates that liver damage caused by these extract cannot be suspected; however the extract may help liver in its function by decreasing it activity.
Proteins are constructive elements in our body, its increase in the body is a signal of tissue or organ damage been repaired. No changed in total serum proteins in treated mice may also imply no presence of liver lesions which may have altered few hepatic functions.
Serum creatinine abnormally high levels indicate kidneys malfunction [37]. No significant change in creatinine level has been observed in mice treated with extracts. This may indicate that methanol extract of T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum may not influence renal function.
Multiple hyperlipidemias are often secondary to many factors e.g. diet, alcohol intake, therapies or to diseases such as nephrosis, diabetes, hypothyroidism or tumors [38]. The decrease in those parameters in animals treated with extract can testify antidiabetic activity of those plants. In this study, the lipid profile showed No significant difference on serum cholesterol level in mice treated with extract compared to the control. Also, the result presented no significant difference in serum TG on mice treated with T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum. Hence, these plants may not be toxic to mice concerning these parameters and may not cause diabetes.
Conclusion
T. stellulifera and C. bougheyanum methanol extract was found to be safe and law toxic despite sub-acute toxicity reveal changes in some biochemical and hematological parameters. Hence detail experimental analysis of chronic toxicity is to be done to further support this study.
REFERENCES
- Prince L, Prabakaran P. Antifungal activity of medicinal plants against plant pathogenic fungus Colletotrichum falcatum. Asian J Plant Sci Res. 2011;1:84-87.
- Liu WJH. Introduction to traditional herbal medicines and their study. Traditional Herbal Medicine Research Methods. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons Inc. 2010;1-26.
- Jain KP, Sonil P, Upmanyu N, Shivhare Y. Evaluation of analgesic activity of Manilkara zapota (Leaves). Eur J Exp Bio. 2011;1:14-17.
- Nabukenya I, Rubaire-Akiiki C, Mugizi D, Kateregga J, Olila D, Höglund J. Sub-acute Toxicity of Aqueous Extracts of Tephrosia vogelii , Vernonia amygdalina and Senna occidentalis in Rats. Nat Prod Chem Res. 2014;2:1-5.
- Agbaire PO, Emudainohwo JOT, Peretiemo-Clarke BO. Phytochemical screening and toxicity studies on the leaves of Manniophyton fulvum. Int J Plant Ani Environ Sci. 2013;3:1-6.
- George P. Concerns regarding the safety and toxicity of medicinal plants-An overview. J Appl Pharmaceut Sci. 2011;1:40-44.
- Peyrin-Biroulet L, Barraud H, Petit-Laurent F, Ancel D, Watelet J, Chone L, et al. Hépatotoxicité de la phytothérapie: données cliniques, biologiques, histologiques et mécanismes en cause pour quelques exemples caractéristiques. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2004;28:540-550.
- Roshni PR, Jyothylekshmi V, Reghu R, Vijayan M. Renal disease with the use of herbal remedies. Int J Pharmaceut Chem Biol Sci. 2014;4:367-371.
- Chen XW, Serag ES, Sneed KB, Zhou SF. Herbal bioactivation, molecular targets and the toxicity relevance. Chem Biol Interact. 2011;192:161-176.
- Anisuzzaman ASM, Sugimoto N, Sadik G, Gafur MA. Sub-acute toxicity study of 5-Hydroxy-2(Hydroxy-Methyl) 4H-pyran-4 One, isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus. Pak J Biol Sci. 2001;4:1012-1015.
- Idris B, Abdulmenem SB, Yasser MT, Bassel Al-Hindi, Majed A, Roziahanim M, et al. Acute and Sub-Acute Toxicity Evaluation of the Methanolic Extract of Alstonia scholaris Stem Bark. Med Sci (Basel). 2016;4:1-14.
- Muhammad K, Mohd SM, Pinaki S, Moklesur RS, Arindam D, Das SK. Evaluation of the acute and sub-acute toxicity of the ethanolic extract of Pericampylus glaucus (Lam.) Merr. in BALB/c mice. J Acute Disease. 2015;4:309-315.
- OECD Acute oral toxicity. Up and down procedure. Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals. 2008.
- Osano KO, Nyamai DW, Ogola PE, Ouko RO, Arika, Bina MW, et al. Evaluation of In vivo Toxicity of Dichloromethane: Methanolic Leaf Extracts of Prosopis juliflora in Female Wistar Albino Rats. J Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016;7:1-11.
- Telefo PB. Contribution à l’étude des plantes médicinales du Cameroun: Influence de l’extrait aqueux du mélange des feuilles d’Aloe buettneri A. Berger (liliacées), Diclipteria Verticillata G.J.H. Amshoff (Acanthacées), Hibiscus macranthus Hochst ex. A Rich (Malvacées), Justicia insularis T. Anders (Acanthacées) sur certains paramètres biochimiques et physiologiques de la reproduction chez les rattes. Thèse de doctorat, 3ème cycle, Université de Yaoundé, Cameroun. 1998.
- Siti SA, Norhaizan ME, Hazilawati H. Histopathologic changes in liver and kidney tisues from male Sprague Dawley rats treated with Rhaphidophora decursiva (Roxb.) Schott extract. J Cytol Histol. 2014;1-6.
- Saleem U, Ahmad B, Ahmad M, Erum A, Hussain K, Irfan Bukhari N. Is folklore use of euphorbia helioscopia devoid of toxic effects? Drug Chem Toxicol. 2016;39:233-237.
- Walum E, Nilsson M, Clemedson C, Ekwall B. The meic program and its implications for the prediction of acute human systemic toxicity. Altern Methods Toxicol. 1995;11:275-282.
- Subramanion LJ, Zakaria Z, Chen Y, Lau YL, Latha LY, Sasidharan S. Acute oral toxicity of methanolic seed extract of cassia fistula in mice. Molecules. 2011;16:5268-5282.
- Secretariat United Nations, Economic Commission for Europe. Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS). United Nations Publications. 2009.
- Yuet Ping K, Darah I, Chen Y, Sreeramanan S, Sasidharan S. Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Study of Euphorbia hirta L. Methanol Extract in Rats. Biomed Res Int. 2013.
- Rosenthal N, Brown S. The mouse ascending: perspectives for human-disease models. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:993-999.
- Auletta CS. Acute, Subchronic and Chronic Toxicology. CRC Press Handbook of toxicology, London. 1995.
- Berenguer-Rivas CA, Castillo AA, Martínez HS, Zapata EP, Hernández JB, Tassé YM. Acute oral toxicity of Azadirachta indica (Neem Tree). Rev Cubana Plant Med. 2013;18:502-507.
- Arsad SS, Mohd Esai N, Hamzah H, Othman F. Evaluation of acute, subacute and subchronic oral toxicity of Rhaphidophora decursiva (Roxb.) Schott extract in male Sprague Dawley rats. J Med Plant Res. 2013;7:3030-3040.
- Khan SA, Epstein JH, Olival KJ, Hassan MM, Hossain MB, Rahman KBMA, et al. Hematology and serum chemistry reference values of stray dogs in Bangladesh. Open Vet J. 2011;1:13-20.
- Yamthe LR, David K, Ngadena YM, Tarkang PA, Agbor GA, Armelle TD. Acute and Chronic Toxicity Studies of the aqueous and ethanol leaf extracts of Carica papaya Linn in Wistar rats. J Nat Prod Plant Resour. 2012;2:617-627.
- Tousson E, El-Moghazy MM, El-Atrsh E. The possible effect of diets containing Nigella sativa and Thymus vulgarison blood parameters and some organs structure in rabbit. Toxicol Ind Health. 2011;27: 107-116.
- Weingand K, Brown G, Hall R, Davies D, Gossett K, Neptun D, et al. Harmonization of animal clinical pathology testing in toxicity and safety studies. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1996;29:198-201.
- Palm M, Lundblad A. Creatinine concentration in plasma from dog, rat, and mouse: A comparison of 3 different methods. Vet Clin Pathol. 2008;34:232-236.
- Olorunnisola OS, Bradley G, Afolayan AJ. Acute and sub-chronic toxicity studies of methanolic extract of Tulbaghia violacea rhizomes in Wistar rats. Afr J Biotechnology. 2012;11:14934-14940.
- Arika WM, Nyamai DW, Osano KO, Ngugi MP, Njagi ENM. Biochemical markers of in vivo hepatotoxicity. J Clin Toxicol. 2016;6:1-8.
- Friedman LS, Martin P, Munoz SJ. Liver function tests and the objective evaluation of the patient with liver disease. Hepatology: A Textbook of Liver Disease. 1996;1:791-833.
- Ramaiah SK. Preclinical safety assessment: current gaps, challenges, and approaches in identifying translatable biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury. Clin Lab Med. 2011;31:161-172.
- Giannini EG, Testa R, Savarino V. Liver enzyme alteration: A guide for clinicians. CMAJ. 2005;172:367-379.
- Davis ME, Bredt ND. “Renal methods for toxicity,” in Principles and Methods of Toxicology, Raven Press, New York, NY, USA. 1994.
- Havel RJ. Pathogenesis, differentiation and management of hypertriglyceridemia. Adv Intern Med. 1969;15:117-154.
- Nabi SA, Kasetti RB, Sirasanagandla S, Tilak TK, Kumar MVJ, Rao CA. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic activity of Piper longum root aqueous extract in STZ induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013;10:13-37.
Citation: Nfozon JN, Tume C, Kdjo N, Boyom FF, Leonard SF, Dzoyem JP, et al. (2019) Acute and Sub-Chronic Toxicity Evaluation of Triplotaxis stellulifera (Beuth) Hutch and Crasssocephalum bougheyanum C.D. Adams Methanol Extract on Mice. Biochem Anal Biochem 8:385. doi: 10.35248/2161-1009.19.8.385.
Copyright: © 2019 Nfozon JN, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.