PMC/PubMed Indexed Articles
Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- The Global Impact Factor (GIF)
- Open Archive Initiative
- VieSearch
- International Society of Universal Research in Sciences
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)
- CiteFactor
- Scimago
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
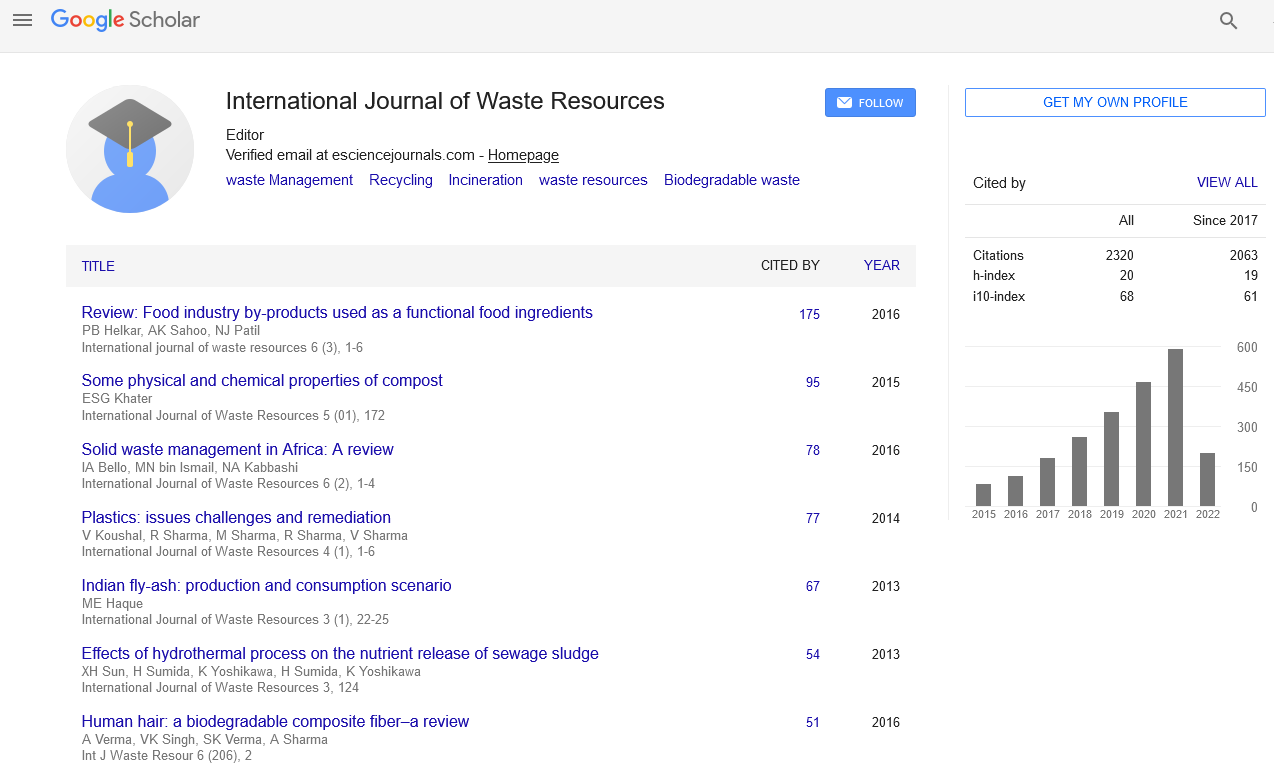
Abstract
Waste Amount Survey and Physio-Chemical Analysis of Municipal Solid Waste Generated in Gujranwala-Pakistan
Kashif Nadeem, Kiran Farhan and Hassan Ilyas
Due to rapid population growth, increased industrial development and enhanced living standard, the per capita waste generation rates has been increased in the urban areas. The composition of the solid waste varies from region to region depending upon the income level, climatic conditions, social behavior and industrial production; influencing the per capita waste generation. The current study attempts to document the waste generation rates, composition and physio-chemical characteristics of the municipal solid waste produced in the Gujranwala City. The study was carried out for 8 days from 9-16 February 2015. For all physio-chemical analysis and testing standard ASTM methods have been used. The results of the study reveals that, all waste types contains 67 % to 99.1 % organic waste except street sweeping which have the lowest organic content (30%).Whereas, non-biodegradable fraction varies between 0.5 % to 4.5 % for all types of wastes. The accumulative apparent specific gravity was found 234 kg/m3. The chemical parameters (moisture, ash and combustible fraction) were found within optimum range.