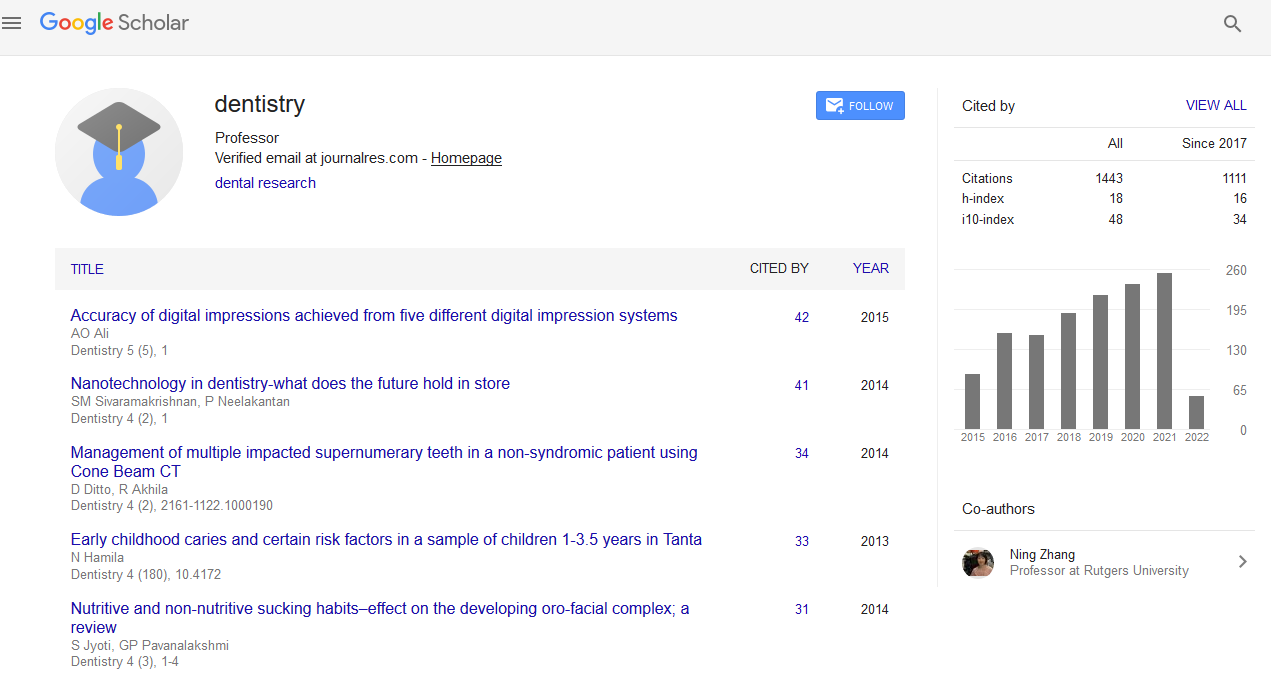
Citations : 1817
Dentistry received 1817 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Genamics JournalSeek
- JournalTOCs
- CiteFactor
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Directory of Abstract Indexing for Journals
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
Abstract
Quantitative Analysis of the Relationship Between Maxillary Incisors and the Incisive Canal by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in an Adult Population of Mangaluru
D. Vaishnavi * , V Harshitha , Kumar Kishore
Objective: Maxillary anterior teeth play a role in the aesthetics, phonetics, and mastication. For successful orthodontic treatment evaluating the morphology of the alveolar bone and incisive canal would help in avoiding root resorption, dehiscence, and fenestration. This study is aimed to research the configurational relationships among maxillary incisors, alveolar bone, and incisive canal through Cone Beam Computerated Tomography(CBCT). Materials and Methods: CBCT images of 35 orthodontic patients were for length of the canal(L); angles palatal plane and the maxillary alveolar border(θ1),the incisive canal(θ2), and maxillary incisor(θ3); distance from the right maxillary incisor to the incisive canal(D). All the measurements were performed on sagittal plane with the exception of (D) which was made on axial plane. Statistical analysis was performed on the above parameters using two sample test and Pearson’s correlation analysis. Results: There was no statistically significant difference between males and females for all the variables although there large interindividual variation.There was a positive moderate correlation between θ1 and θ2(0.480), θ1 and θ3 (0.487), θ2 and θ3(0.345). The mean value for L and D were 10.38 mm and 4.14 mm respectively. Conclusion: There exists large interindividual variability for canal, proximity of incisors with that incisive canal which could not be precisely predicted by the conventional cephalograms. The results of the study could be helpful clinically in planning orthodontic treatment for significant intrusion and retraction of maxillary incisors. Keywords : Maxillary incisors; Incisive canal; Tomographyaxillary anterior teeth play a role in the aesthetics, phonetics, and mastication. For successful orthodontic treatment evaluating the morphology of the alveolar bone and incisive canal would help in avoiding root resorption, dehiscence, and fenestration. This study is aimed to research the configurational relationships among maxillary incisors, alveolar bone, and incisive canal through Cone Beam Computerated Tomography(CBCT). METHODS: CBCT images of 35 orthodontic patients were for length of the canal(L); angles palatal plane and the maxillary alveolar border(θ1),the incisive canal(θ2), and maxillary incisor(θ3); distance from the right maxillary incisor to the incisive canal(D). All the measurements were performed on sagittal plane with the exception of (D) which was made on axial plane. Statistical analysis was performed on the above parameters using two sample test and Pearson’s correlation analysis. RESULTS: There was no statistically significant difference between males and females for all the variables although there large interindividual variation.There was a positive moderate correlation between θ1 and θ2(0.480), θ1 and θ3 (0.487), θ2 and θ3(0.345). The mean value for L and D were 10.38 mm and 4.14 mm respectively. CONCLUSION: There exists large interindividual variability for canal, proximity of incisors with that incisive canal which could not be precisely predicted by the conventional cephalograms. The results of the study could be helpful clinically in planning orthodontic treatment for significant intrusion and retraction of maxillary incisors. Keywords : Maxillary incisors; Incisive canal; TomographyMaxillary anterior teeth play a role in the aesthetics, phonetics, and mastication. For successful orthodontic treatment evaluating the morphology of the alveolar bone and incisive canal would help in avoiding root resorption, dehiscence, and fenestration. This study is aimed to research the configurational relationships among maxillary incisors, alveolar bone, and incisive canal through Cone Beam Computerated Tomography(CBCT). METHODS: CBCT images of 35 orthodontic patients were for length of the canal(L); angles palatal plane and the maxillary alveolar border(θ1),the incisive canal(θ2), and maxillary incisor(θ3); distance from the right maxillary incisor to the incisive canal(D). All the measurements were performed on sagittal plane with the exception of (D) which was made on axial plane. Statistical analysis was performed on the above parameters using two sample test and Pearson’s correlation analysis. RESULTS: There was no statistically significant difference between males and females for all the variables although there large interindividual variation.There was a positive moderate correlation between θ1 and θ2(0.480), θ1 and θ3 (0.487), θ2 and θ3(0.345). The mean value for L and D were 10.38 mm and 4.14 mm respectively. CONCLUSION: There exists large interindividual variability for canal, proximity of incisors with that incisive canal which could not be precisely predicted by the conventional cephalograms. The results of the study could be helpful clinically in planning orthodontic treatment for significant intrusion and retraction of maxillary incisors. Keywords : Maxillary incisors; Incisive canal; Tomography
Published Date: 2021-06-22; Received Date: 2021-06-01