Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Proquest Summons
- Scholarsteer
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
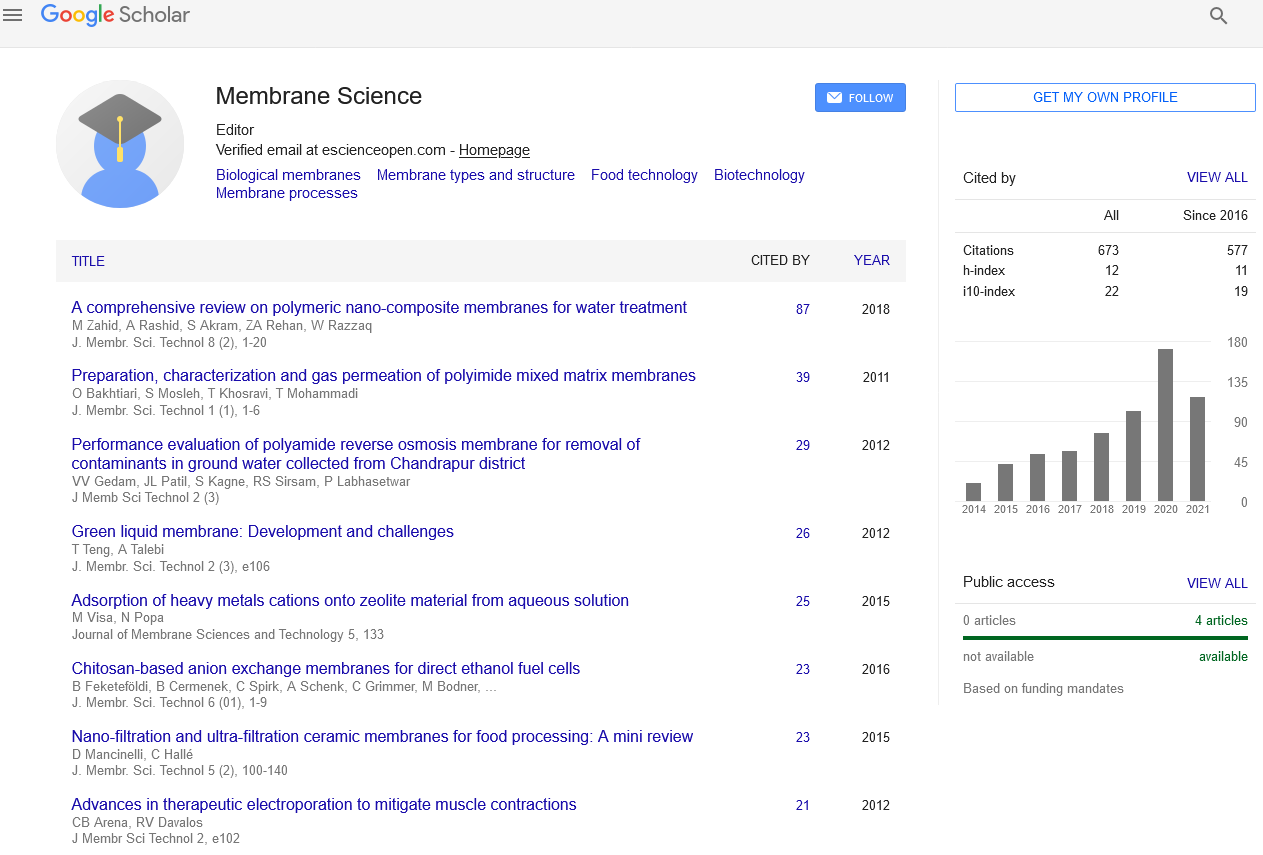
Abstract
Influence of Functionalized Multiwall Carbon Nano-Tube on the Structure and Performance of Cellulose Di-Acetate Based Forward Osmotic Membrane for Desalination Process
Xiulan Zhao, Jianfang Sheng, Lijing Zhu, Anjiang Zhang and Lixin Xue
To improve the performance of Cellulose di-acetate (CDA) based forward osmotic (FO) membrane in sea water desalination process, functionalized multi-walled carbon nano-tubes (MWCNTs) were blended as additives at varied compositions, from 0 to 5 wt%, into the solutions to prepare FO membranes using a classical phase-inversion method. The structure and property of the formed membranes were characterized by Fourier transfer infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transitional Electron Microscopy (TEM), Water Flux and Reverse Solute Flux Tests. It was found that the content of functionalized MWCNTs was an important factor influencing the morphology, porous structures and properties of the blend membranes. SEM, AFM and TEM images of the blend membranes showed that the surface morphology and the cross-sectional morphology changed with the content of functionalized MWCNTs. It is interesting to see that at the presence of functionalized MWCNTs, the surface contact angle and the reverse solute flux of the FO membranes could be greatly improved without significantly affecting the pure water flux. With the addition of only about 1 wt% MWCNTs, the water flux of CDA based FO membrane was increased from 10.5 to 12.5 L/m2h while its reverse solute flux was reduced from 1.8 to below 0.3 mol/m2h. Desalination tests with 3.5 wt% simulated seawater feed solution had shown that the blend membrane with 1 wt% MWCNTs, was 366% higher in water flux and 53% lower in reverse solute flux than those of pure CDA FO membrane. These results suggest that CDA bases FO membranes modified with functionalized MWCNTs could possess good potential to be further developed for practical applications in the sea water desalination processes.