Indexed In
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
- Quality Open Access Market
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
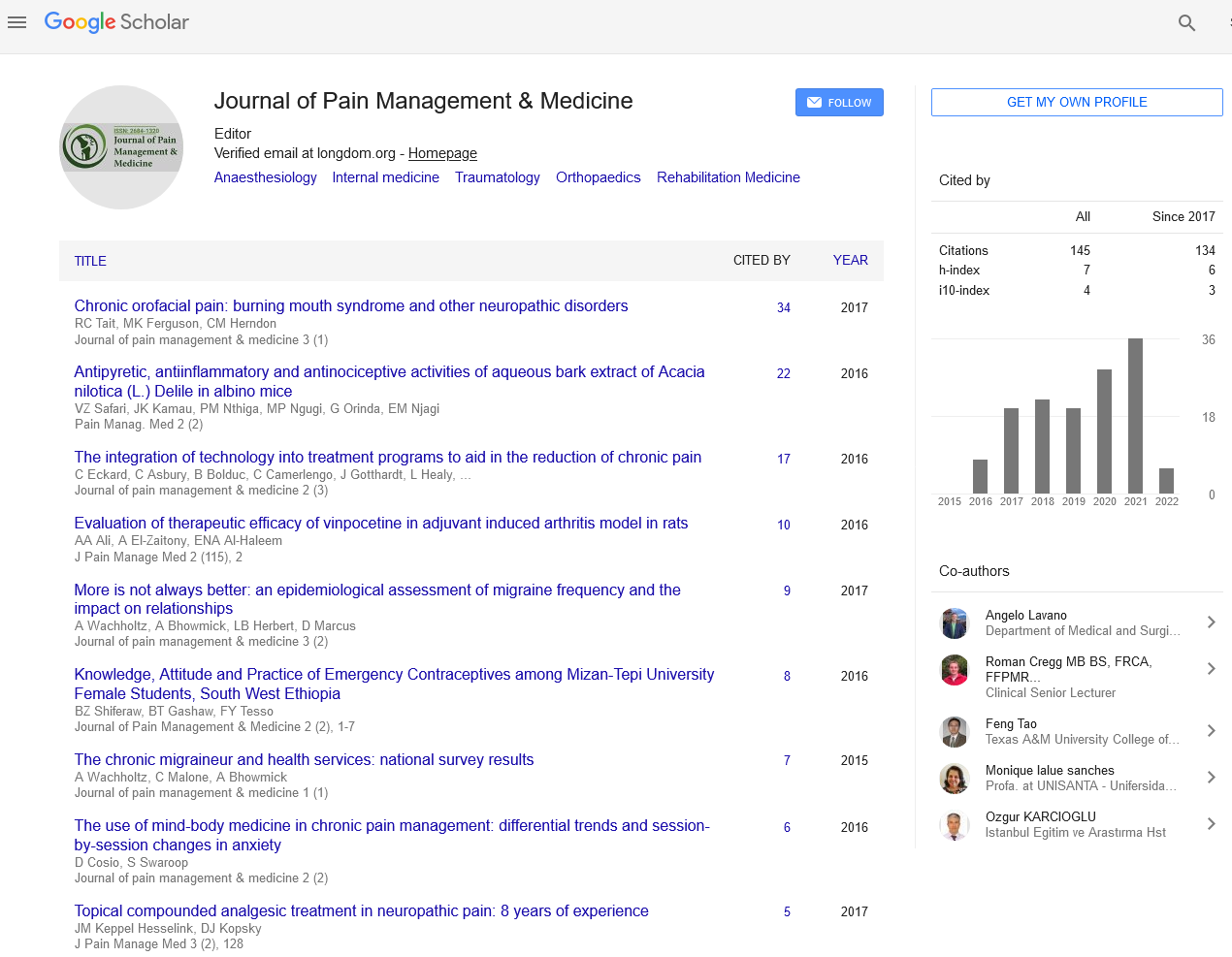
Abstract
Evaluation of Therapeutic Efficacy of Vinpocetine in Adjuvant Induced Arthritis Model in Rats
Azza A Ali, Asmaa S El-Zaitony and Ekram N Abd Al-Haleem
Introduction: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an incurable chronic inflammatory disorder. Indomethacin is used for symptomatic management of RA; its long term use is associated with potentially life-threatening deleterious side effects. Vinpocetine is an alkaloid extracted from the periwinkle plant used for treating cerebrovascular disorders with no significant side effects. Recent evidences demonstrate its anti-inflammatory properties. Objective: To evaluate the anti-inflammatory, analgesic and neuroprotective activities of vinpocetine against RA as well as the associated neurological disorders and to investigate its influence on the anti-inflammatory activity of indomethacin in rats. Methods: Complete Freund’s adjuvant induced arthritic rats were treated for 3 weeks with indomethacin (1, 2 mg/ kg P.O.) and/or vinpocetine (20 mg/kg P.O.). Body weight, ankle diameter, arthritic score, serum tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin one beta (IL-1β), tissue expression of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) were determined and gait score were assessed. Brain monoamines levels and behavior in the swimming test were also measured. In addition, histopathological examinations of hind paw and brain tissues as well as X-ray examinations of the paw were performed. Results: Combination therapy of vinpocetine with indomethacin significantly improved analgesic and inflammatory parameters as compared to indomethacin alone. Vinpocetine alone decreased the inflammatory markers in the same extent as indomethacin. In some parameters, vinpocetine has equal effect as the combination therapy. It also decreased swimming time while increased direction score together with increased brain norepinepherine and serotonin as well as serum total anti-oxidant capacity (TAC) level. Histopathological and X-ray examinations supported these results. Conclusion: Vinpocetine has potent anti-arthritic, anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects. It also potentiates the anti-inflammatory action of indomethacin. It also improves RA associated depression. Thus, it can be used either alone or in combination with indomethacin to avoid or to decrease the serious side effects of indomethacin and to improve RA associated depression.