Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- JournalTOCs
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
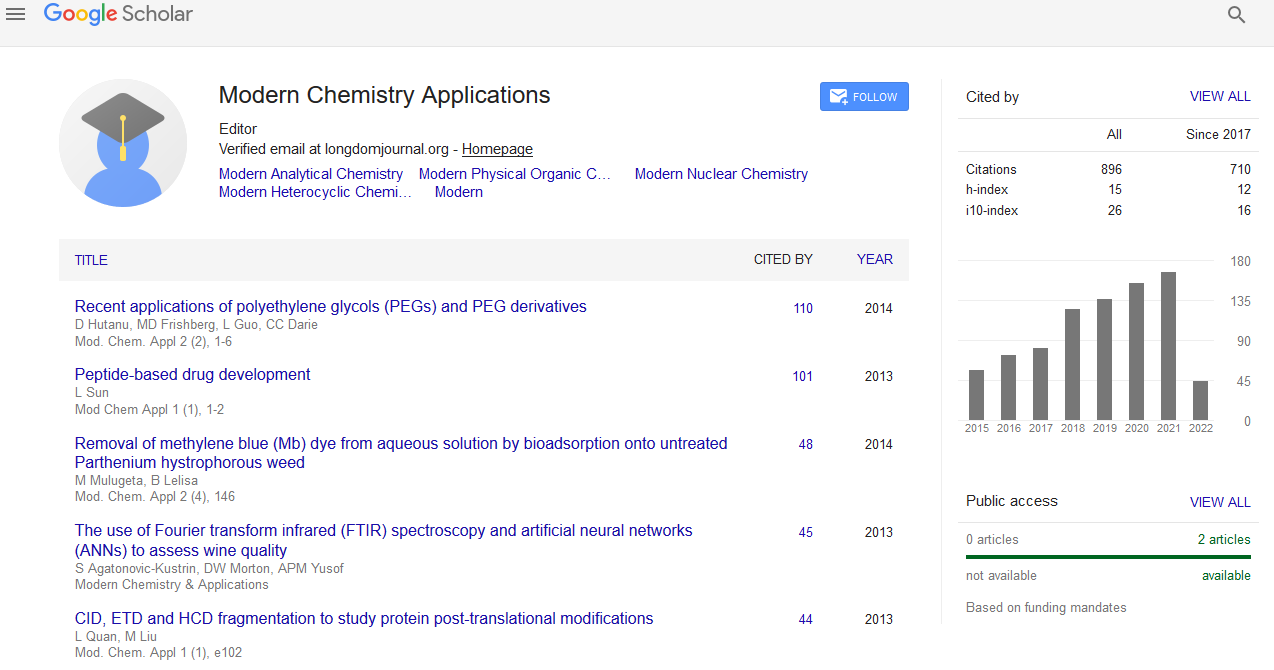
Abstract
Antioxidant Edible Mushrooms: A Green and Rapid Electrochemical Study with the Aqueous Extracts
Priyankar Maji, Shibani Basu, Bimal K Banik and Jhuma Ganguly
A greener and rapid electrochemical technique was performed by indium doped tin oxide (ITO) glasses as working electrode in cyclic and differential pulse voltammetry to screen the antioxidant activities of the aqueous extracts of different species of edible mushrooms Plureotus florida, Calocybe indica and Tricholoma gigantum found in West Bengal. The ITO glasses as electrode was very sensitive for the detection of electrical potentiality with 10 μl of 20 μg/ml (volume and concentration) concentration in phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) for the isolated aqueous extracts of mushrooms along with ascorbic acid and gallic acid as standards. In addition to the electrochemical study, the spectrophotometric assays were used to evaluate the antioxidant constituents, their reducing power and free radical scavenging ability of the extracts. The results obtained from both electrochemical and spectrophotometrical assays were in good agreement to each other for the detectable and significant range of antioxidant potentiality of these extracts. The present electrochemical ITO electrode method is a greener, efficient, cost effective, recyclable, and less cumbersome for detection of antioxidant properties of mushrooms compared to the other available electrochemical techniques.