PMC/PubMed Indexed Articles
Indexed In
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- NSD - Norwegian Centre for Research Data
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- Google Scholar
Useful Links
Share This Page
Journal Flyer

Open Access Journals
- Agri and Aquaculture
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics & Systems Biology
- Business & Management
- Chemistry
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- Food & Nutrition
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Medical Sciences
- Neuroscience & Psychology
- Nursing & Health Care
- Pharmaceutical Sciences
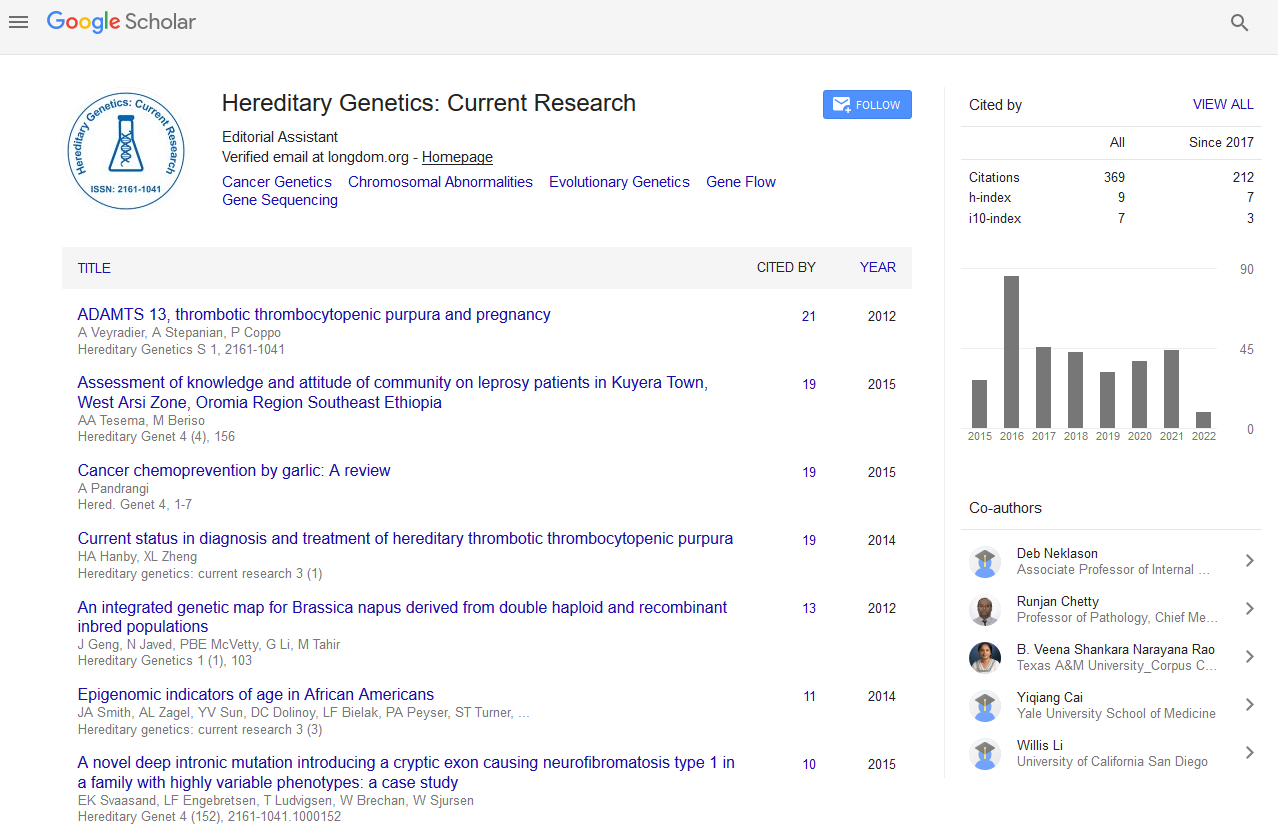
Abstract
An Integrated Genetic Map for Brassica napus Derived from Double Haploid and Recombinant Inbred Populations
Jianfeng Geng, Nasir Javed, Peter B.E. McVetty, Genyi Li and Muhammad Tahir
A hybrid developed from a cross between two diverse Brassica napus cultivars (“Polo” and “Topas”) was used to produce a microspore derived double haploid (DH) population and a single seed descent derived recombinant inbred (RI) population for genetic mapping. Each of the two populations consisting of 190 DH lines and 94 RI lines was characterized for various types (SSR, SRAP, ISSR, SCAR) of polymorphic molecular markers. The DH population was scored for 620 molecular markers while the RI population was scored for 349 molecular markers to construct two independent genetic maps. In both genetic maps, all of the molecular markers were found to cluster in 19 linkage groups (LGs) covered a total genome length of 2244.1 cM and 1649.1 cM for the DH and RI maps, respectively. The data from the two genetic maps was used to construct a consensus integrated genetic map covering a total genome length of 2464.9 cM. Previously published Brassica reference genetic maps were used to assign each of the nineteen LGs to corresponding Brassica napus chromosomes named N01 to N19. To our knowledge, this is the first integrated genetic map based on DH and RI populations developed from the same cross in Brassica napus.